Biology 9 Integumentary System and Anatomical Terms Lab
... Microscopic Examination of the Skin For this portion of the lab, you will examine images from "The JayDoc Histoweb" made available by the University of Kansas Medical Center at the following web address: http://www.kumc.edu/instruction/medicine/anatomy/histoweb/index.htm. The links are also availabl ...
... Microscopic Examination of the Skin For this portion of the lab, you will examine images from "The JayDoc Histoweb" made available by the University of Kansas Medical Center at the following web address: http://www.kumc.edu/instruction/medicine/anatomy/histoweb/index.htm. The links are also availabl ...
Muscles of the Knee
... - Do NOT cross the hip joint. - Because of that, they are only responsible for knee extension. - VMO (Vastus Medialis Oblique) is an important muscle to focus on rehabbing following major knee surgery. - Responsible for the last 15 degrees of Knee Extension, also known as “Terminal Knee Extension” - ...
... - Do NOT cross the hip joint. - Because of that, they are only responsible for knee extension. - VMO (Vastus Medialis Oblique) is an important muscle to focus on rehabbing following major knee surgery. - Responsible for the last 15 degrees of Knee Extension, also known as “Terminal Knee Extension” - ...
Chapter 5 Lecture Notes
... When and Where Not to Use Medical Terms: Avoid using any type of obscure medical terminology, jargon, abbreviations, or acronyms when talking to patients or families. Resist the urge to use complex medical terminology when a simple, term will do. Anatomy and Physiology: Anatomy, the study of body st ...
... When and Where Not to Use Medical Terms: Avoid using any type of obscure medical terminology, jargon, abbreviations, or acronyms when talking to patients or families. Resist the urge to use complex medical terminology when a simple, term will do. Anatomy and Physiology: Anatomy, the study of body st ...
2401_Ch8.pdf
... Characterized by having a fluid filled joint capsule. These are complex joints. Articular cartilage - covers surface of both bones Fibrous capsule - makes up outer layer of joint capsule (may also form ligaments inside the capsule) Synovial membrane - makes up inner surface of capsule, not present o ...
... Characterized by having a fluid filled joint capsule. These are complex joints. Articular cartilage - covers surface of both bones Fibrous capsule - makes up outer layer of joint capsule (may also form ligaments inside the capsule) Synovial membrane - makes up inner surface of capsule, not present o ...
The HUMAN BODY - davis.k12.ut.us
... • All chemical substances essential for maintaining life – atoms-compounds-molecules. ...
... • All chemical substances essential for maintaining life – atoms-compounds-molecules. ...
pdf
... Asymptomatic patients do not requiere treatment after confirming the soft tissue mass to be an accesory muscle. In symptomatic patients treatment varies from fasciotomy, when exercise-induced compartimental syndorme occurs, to muscle excision or neurolysis if nerve compression or claudication are th ...
... Asymptomatic patients do not requiere treatment after confirming the soft tissue mass to be an accesory muscle. In symptomatic patients treatment varies from fasciotomy, when exercise-induced compartimental syndorme occurs, to muscle excision or neurolysis if nerve compression or claudication are th ...
Whiplash Syndrome
... suboccipital muscle group. Anteriorly, the extension – the three composite movements of the sternocleidomastoid, longus colli and longus capitis upper cervical unit (type II). Bilateral contraction of are of primary concern, although other anterior muscles all suboccipital muscles produces extension ...
... suboccipital muscle group. Anteriorly, the extension – the three composite movements of the sternocleidomastoid, longus colli and longus capitis upper cervical unit (type II). Bilateral contraction of are of primary concern, although other anterior muscles all suboccipital muscles produces extension ...
FOR THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS ANSWER: A. if choices 1, 2
... 13. Characteristics of a femoral hernia include which of the following? 1. Weakness in the abdominal wall at the femoral ring 2. Protrusion of the intestine through the femoral ring into the femoral triangle 3. Possible strangulation resulting in impairment of blood supply to the herniated bowel 4. ...
... 13. Characteristics of a femoral hernia include which of the following? 1. Weakness in the abdominal wall at the femoral ring 2. Protrusion of the intestine through the femoral ring into the femoral triangle 3. Possible strangulation resulting in impairment of blood supply to the herniated bowel 4. ...
The Arthropods:
... specific functions (tagmatization). Chitinous exoskeleton used for support and protection Paired, jointed appendages Growth accompanied by molting (ecdysis) ...
... specific functions (tagmatization). Chitinous exoskeleton used for support and protection Paired, jointed appendages Growth accompanied by molting (ecdysis) ...
Annelida (segmented worms)
... Their body shapes also vary and usually reflect their lifestyles. Active species, such as those that hunt for their food and some burrowers, have bodies with segments that are all very similar in appearance to one another. They have well-developed flap like appendages, eyes, and other sensory or ...
... Their body shapes also vary and usually reflect their lifestyles. Active species, such as those that hunt for their food and some burrowers, have bodies with segments that are all very similar in appearance to one another. They have well-developed flap like appendages, eyes, and other sensory or ...
The Human Body workforce planning
... Muscles band together to form muscle groups which work together When the muscles contract, they pull on the tendons which pull on the bones and cause our limbs to move ...
... Muscles band together to form muscle groups which work together When the muscles contract, they pull on the tendons which pull on the bones and cause our limbs to move ...
No Slide Title
... • 30 bones per limb • Brachium or arm contains the humerus • Antebrachium or forearm contains the radius & ulna (radius on thumb side) • Carpus or wrist contains 8 small bones arranged in two rows • Manus or hand contains 19 bones in 2 groups – 5 metacarpals in the palm – 14 phalanges in the fingers ...
... • 30 bones per limb • Brachium or arm contains the humerus • Antebrachium or forearm contains the radius & ulna (radius on thumb side) • Carpus or wrist contains 8 small bones arranged in two rows • Manus or hand contains 19 bones in 2 groups – 5 metacarpals in the palm – 14 phalanges in the fingers ...
Anatomy Semester Pretest MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one
... C) making a section through the heart to observe its interior D) examining the surface of a bone E) viewing muscle tissue through a microscope 8) Which of the following is an anterior body landmark: ...
... C) making a section through the heart to observe its interior D) examining the surface of a bone E) viewing muscle tissue through a microscope 8) Which of the following is an anterior body landmark: ...
Body Organization
... – Your body systems work together to ensure that your body maintains a stable internal environment ...
... – Your body systems work together to ensure that your body maintains a stable internal environment ...
BIOL241StudyGuide LabPracticalsBIOL241
... * parts of the tibia - lateral condyle, medial condyle, tibial tuberosity, intercondylar eminence,medial malleolus * parts of the fibula - head, neck, lateral malleolus * types of tarsals - calcaneus, talus, cuboid, navicular, first, second, and third (lateral, intermediate and medial) cuneiform * ...
... * parts of the tibia - lateral condyle, medial condyle, tibial tuberosity, intercondylar eminence,medial malleolus * parts of the fibula - head, neck, lateral malleolus * types of tarsals - calcaneus, talus, cuboid, navicular, first, second, and third (lateral, intermediate and medial) cuneiform * ...
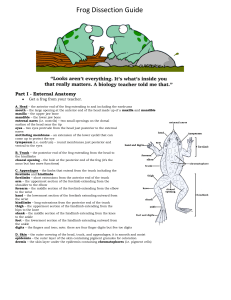
Frog Dissection Guide
... use scissors to cut along the center of the body from the cloaca to the lip. Turn back the skin, cut toward the side at each leg, and pin the skin flat. The diagram above shows how to make these cuts Lift and cut through the muscles and breast bone to open up the body cavity. If your frog is a femal ...
... use scissors to cut along the center of the body from the cloaca to the lip. Turn back the skin, cut toward the side at each leg, and pin the skin flat. The diagram above shows how to make these cuts Lift and cut through the muscles and breast bone to open up the body cavity. If your frog is a femal ...
Pages 20-35
... Cutaneous Maximus - This muscle covers most of the sides of the body in the thoracic and abdominal areas. It serves to twitch the skin to avoid irritants. It originates from muscles in the axilla, the thorax, and abdomen, and inserts on the skin. It is not found in man. Platysma - This is another cu ...
... Cutaneous Maximus - This muscle covers most of the sides of the body in the thoracic and abdominal areas. It serves to twitch the skin to avoid irritants. It originates from muscles in the axilla, the thorax, and abdomen, and inserts on the skin. It is not found in man. Platysma - This is another cu ...
OMT for Extremity Complaints Handouts
... Treatment – Contact radial head with fingers, encouraging anterior motion while hyperextending the elbow joint. ...
... Treatment – Contact radial head with fingers, encouraging anterior motion while hyperextending the elbow joint. ...
Lower extremity-I
... Under deep fascia the muscles are located within the gluteÂal region. These are three layers of muscles. First layer of muscles consists of gluteus maximus muscle and upper part of gluteus medius muscle. The gluteus maximus is a large muscle that arises from the outer surface of the ilium, from the ...
... Under deep fascia the muscles are located within the gluteÂal region. These are three layers of muscles. First layer of muscles consists of gluteus maximus muscle and upper part of gluteus medius muscle. The gluteus maximus is a large muscle that arises from the outer surface of the ilium, from the ...
SELECT THE ONE BEST ANSWER OR COMPLETION 1. The
... A. if choices 1, 2 and 3 are correct B. if choices 1 and 3 are correct C. if choices 2 and 4 are correct D. if only choice 4 is correct E. if all are correct 32. Which of the following statements apply to the opthalmic artery? 1. It is a branch of the internal carotid artery 2. it passes through the ...
... A. if choices 1, 2 and 3 are correct B. if choices 1 and 3 are correct C. if choices 2 and 4 are correct D. if only choice 4 is correct E. if all are correct 32. Which of the following statements apply to the opthalmic artery? 1. It is a branch of the internal carotid artery 2. it passes through the ...
Study Guide for Lab Quiz #2 Below is the material that could be
... Lab Manual, Exercise 11: Articulations and Body Movements Movements: flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, rotation vs. circumduction, pronation/supination, dorsiflexion/plantar flexion, inversion/eversion. Joint names to recognize (which bones form them?): Temporomandibular, Intercarpal, Atlantoo ...
... Lab Manual, Exercise 11: Articulations and Body Movements Movements: flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, rotation vs. circumduction, pronation/supination, dorsiflexion/plantar flexion, inversion/eversion. Joint names to recognize (which bones form them?): Temporomandibular, Intercarpal, Atlantoo ...
Lecture Outline ()
... • 30 bones per limb • Brachium or arm contains the humerus • Antebrachium or forearm contains the radius & ulna (radius on thumb side) • Carpus or wrist contains 8 small bones arranged in two rows • Manus or hand contains 19 bones in 2 groups – 5 metacarpals in the palm – 14 phalanges in the fingers ...
... • 30 bones per limb • Brachium or arm contains the humerus • Antebrachium or forearm contains the radius & ulna (radius on thumb side) • Carpus or wrist contains 8 small bones arranged in two rows • Manus or hand contains 19 bones in 2 groups – 5 metacarpals in the palm – 14 phalanges in the fingers ...
Evaluation of the Lumbar Spine
... • The articulations between two consecutive lumbar vertebrae form three joints – One joint is formed between the two vertebral bodies and the intervertebral disc (IVD) – The other two joints are formed by the articulation of the superior articular process of one vertebra and the inferior articular p ...
... • The articulations between two consecutive lumbar vertebrae form three joints – One joint is formed between the two vertebral bodies and the intervertebral disc (IVD) – The other two joints are formed by the articulation of the superior articular process of one vertebra and the inferior articular p ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.