ANATOMY OF THE LOWER LIMB
... The foramen is the only conduit between the pelvic cavity and the buttock. Number of structures emerge from the pelvis in to the gluteal region above or below the piriformis muscle in the greater sciatic ...
... The foramen is the only conduit between the pelvic cavity and the buttock. Number of structures emerge from the pelvis in to the gluteal region above or below the piriformis muscle in the greater sciatic ...
presence of triple gantzer`s muscle - a rare
... Anomalous muscles usually do not result in adverse symptoms but are of academic interest. However, these muscles can create neurovascular compression at times. Muscle anomalies of the upper extremity are recognized causes of peripheral nerve disorder. KolohNevin Syndrome (Anterior Interosseous Nerve ...
... Anomalous muscles usually do not result in adverse symptoms but are of academic interest. However, these muscles can create neurovascular compression at times. Muscle anomalies of the upper extremity are recognized causes of peripheral nerve disorder. KolohNevin Syndrome (Anterior Interosseous Nerve ...
Human Body Systems - walker2015
... Red blood cells – take up oxygen in the lungs and deliver it to cells White blood cells – the body’s disease fighters (part of immune system) Platelets – cell fragments used in forming blood clots (that make scabs) ...
... Red blood cells – take up oxygen in the lungs and deliver it to cells White blood cells – the body’s disease fighters (part of immune system) Platelets – cell fragments used in forming blood clots (that make scabs) ...
The Skeletal System
... 12 pairs Articulate with the vertebral column posteriorly First 7 ribs attach to the sternum – true Next 5 pairs attach indirectly to the sternum or not at all – false • Last 2 ribs lack sternal attachment – floating • Space between the ribs – intercostal spaces ...
... 12 pairs Articulate with the vertebral column posteriorly First 7 ribs attach to the sternum – true Next 5 pairs attach indirectly to the sternum or not at all – false • Last 2 ribs lack sternal attachment – floating • Space between the ribs – intercostal spaces ...
Rat dissection - WordPress.com
... 1. Locate the liver, which is a dark colored organ suspended just under the diaphragm. The liver functions to produce bile, which aids in digesting fat. 2. The esophagus pierces the diaphragm and moves food from the mouth to the stomach. It is distinguished from the trachea by its lack of cartilage ...
... 1. Locate the liver, which is a dark colored organ suspended just under the diaphragm. The liver functions to produce bile, which aids in digesting fat. 2. The esophagus pierces the diaphragm and moves food from the mouth to the stomach. It is distinguished from the trachea by its lack of cartilage ...
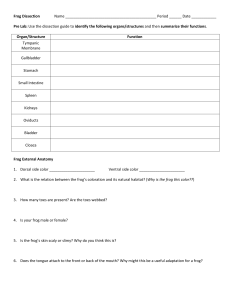
Pre Lab: Use the dissection g
... 1. The membrane holds the coils of the small intestine together: ___________________________________________ 2. This organ is found under the liver, it stores bile: ______________________________________________________ 3. There are _________________ lobes in the liver. 4. The organ that is the firs ...
... 1. The membrane holds the coils of the small intestine together: ___________________________________________ 2. This organ is found under the liver, it stores bile: ______________________________________________________ 3. There are _________________ lobes in the liver. 4. The organ that is the firs ...
SKELETAL DIVISIONS
... • Forms the longitudinal axis of the body • Divided into three parts – Skull – Vertebral column – Bony thorax ...
... • Forms the longitudinal axis of the body • Divided into three parts – Skull – Vertebral column – Bony thorax ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
... pararectal spaces to provide excellent access to the lateral pelvic sidewall and pelvic lymph nodes. F. Pelvic lymphadenectomy (external and internal iliac vessels). G. Pelvic lymphadenectomy (obturator fossa). H. Development of the uterine and superior vesical arteries. I. The uterine artery has be ...
... pararectal spaces to provide excellent access to the lateral pelvic sidewall and pelvic lymph nodes. F. Pelvic lymphadenectomy (external and internal iliac vessels). G. Pelvic lymphadenectomy (obturator fossa). H. Development of the uterine and superior vesical arteries. I. The uterine artery has be ...
To increase the capacity of the underlying structures to withstand the
... The underlying basal bone (beneath the retromolar pad) is resistant to resorption. Coverage of this area will also provide some border seal. An overload of the mucosa will occur if the bases covering the area are too small in outline. Remember: Mandibular dentures do not rely on suction from a perip ...
... The underlying basal bone (beneath the retromolar pad) is resistant to resorption. Coverage of this area will also provide some border seal. An overload of the mucosa will occur if the bases covering the area are too small in outline. Remember: Mandibular dentures do not rely on suction from a perip ...
Slide ()
... A long axis section through the heart profiles the cardiac septum to show the thin valve of the oval foramen (open arrow) on the left atrial side and the muscular rim on the right atrial side. The cut reveals the infolding of the right atrial wall at the superior rim that is filled with epicardial f ...
... A long axis section through the heart profiles the cardiac septum to show the thin valve of the oval foramen (open arrow) on the left atrial side and the muscular rim on the right atrial side. The cut reveals the infolding of the right atrial wall at the superior rim that is filled with epicardial f ...
C H A P T E R
... 3. The parietal, temporal, and sphenoid bones, and the first cervical vertebra (the atlas) articulate with the occipital bone. 4. The seven bones that form the orbit are the frontal and sphenoid bones that form the roof of the orbit; the maxilla and palatine bones that form the floor of the orbit; t ...
... 3. The parietal, temporal, and sphenoid bones, and the first cervical vertebra (the atlas) articulate with the occipital bone. 4. The seven bones that form the orbit are the frontal and sphenoid bones that form the roof of the orbit; the maxilla and palatine bones that form the floor of the orbit; t ...
C H A P T E R
... 3. The parietal, temporal, and sphenoid bones, and the first cervical vertebra (the atlas) articulate with the occipital bone. 4. The seven bones that form the orbit are the frontal and sphenoid bones that form the roof of the orbit; the maxilla and palatine bones that form the floor of the orbit; t ...
... 3. The parietal, temporal, and sphenoid bones, and the first cervical vertebra (the atlas) articulate with the occipital bone. 4. The seven bones that form the orbit are the frontal and sphenoid bones that form the roof of the orbit; the maxilla and palatine bones that form the floor of the orbit; t ...
Oh, Pigs - TeacherWeb
... deep to the pectoral and brachial muscles. It is the primary flexor of the antebrachium (lower foreleg). It lies upon the anterior-medial surface of the humerus. In man the muscle has two heads (biceps) while in the pig it arises by means of a single tendon that passes over the humerus to insert upo ...
... deep to the pectoral and brachial muscles. It is the primary flexor of the antebrachium (lower foreleg). It lies upon the anterior-medial surface of the humerus. In man the muscle has two heads (biceps) while in the pig it arises by means of a single tendon that passes over the humerus to insert upo ...
ECOLOGY SPRING 2009 - Florida International University
... -Parazoa (Sponges - the simplest animals) lack defined tissues and organs -Have the ability to disaggregate and aggregate their cells -Eumetazoa (all other animals) have distinct and well-defined tissues -Have irreversible differentiation for most cell types ...
... -Parazoa (Sponges - the simplest animals) lack defined tissues and organs -Have the ability to disaggregate and aggregate their cells -Eumetazoa (all other animals) have distinct and well-defined tissues -Have irreversible differentiation for most cell types ...
Masticatory Anat CR
... History of Centric Relation “The most retruded relation of the mandible to the maxillae when the condyles are in the most unstrained position in the glenoid fossae from which lateral movement can be made, at any given degree of jaw separation.” The Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms, 1st Edition: The ...
... History of Centric Relation “The most retruded relation of the mandible to the maxillae when the condyles are in the most unstrained position in the glenoid fossae from which lateral movement can be made, at any given degree of jaw separation.” The Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms, 1st Edition: The ...
7-3.3 Notes
... internal organs, and to provide attachment sites for the muscles. Even though each system in the human body performs its own function, the different systems work together and depend on one another for the body to function successfully. Examples of relationships between the major body systems may be: ...
... internal organs, and to provide attachment sites for the muscles. Even though each system in the human body performs its own function, the different systems work together and depend on one another for the body to function successfully. Examples of relationships between the major body systems may be: ...
AMA 179 powerpoint
... Internal respiration: exchange of gases in all body cells, oxygen is released into cells from the capillaries and carbon dioxide is sent from the cells into the ...
... Internal respiration: exchange of gases in all body cells, oxygen is released into cells from the capillaries and carbon dioxide is sent from the cells into the ...
Foundational Information for Kinesiology
... FOLLOWING THIS SUMMER. I have laid this out in an order of learning that I think you should study. I. Anatomical Terminology a. Know what each term means and several examples of how you would use these terms to describe anatomical locations Anterior vs Posterior Superior vs Inferior Distal vs ...
... FOLLOWING THIS SUMMER. I have laid this out in an order of learning that I think you should study. I. Anatomical Terminology a. Know what each term means and several examples of how you would use these terms to describe anatomical locations Anterior vs Posterior Superior vs Inferior Distal vs ...
Renal04-PostAbdominalWall
... b. fibers run downward and laterally to enter the thigh behind the inguinal ligament and insert into lesser trochanter of femur c. enclosed in a fibrous sheath derived from the lumbar fascia which is thickened above to form the medial arcuate ligament of the diaphragm d. flexes the thigh at the hip ...
... b. fibers run downward and laterally to enter the thigh behind the inguinal ligament and insert into lesser trochanter of femur c. enclosed in a fibrous sheath derived from the lumbar fascia which is thickened above to form the medial arcuate ligament of the diaphragm d. flexes the thigh at the hip ...
1. Maxillary bone 2. Maxillary teeth 3. Mandibular arch 4. Vomerine
... Pulmocutaneous artery (24) The artery that sends blood to the skin and lungs for oxygenation. Renal portal vein (72) The vein which brings blood from the kidney region to the liver. Right auricle (20) The top right chamber of the heart which receives deoxygenated blood from all over the body and pum ...
... Pulmocutaneous artery (24) The artery that sends blood to the skin and lungs for oxygenation. Renal portal vein (72) The vein which brings blood from the kidney region to the liver. Right auricle (20) The top right chamber of the heart which receives deoxygenated blood from all over the body and pum ...
File
... hyper flexion, arm external and internal rotation with medial and lateral rotation. The last but the most known movement of the shoulder joint is cicumduction. Cicumduction is a circular movement, which combines flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction so that the movement of the body-part descr ...
... hyper flexion, arm external and internal rotation with medial and lateral rotation. The last but the most known movement of the shoulder joint is cicumduction. Cicumduction is a circular movement, which combines flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction so that the movement of the body-part descr ...
BO notes - buechner
... Organ – made up of different types of tissues Organ system – consists of different organs that work closely together Organism – made up of the organ systems ...
... Organ – made up of different types of tissues Organ system – consists of different organs that work closely together Organism – made up of the organ systems ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.