Appendicular notes - Littlemiamischools.org
... • Sliding joints between them • Posterior view (thumb)The (pinky) ...
... • Sliding joints between them • Posterior view (thumb)The (pinky) ...
Sports Injuries
... to the biceps brachii muscle when it has been worked or overloaded • Pain on the proximal end of biceps • Flexion of shoulder and elbow painful ...
... to the biceps brachii muscle when it has been worked or overloaded • Pain on the proximal end of biceps • Flexion of shoulder and elbow painful ...
Clinical Examination Shoulder
... Abducted arm slowly lowered – May be able to lower arm slowly to 90° (deltoid function) – Arm will then drop to side if rotator cuff tear ...
... Abducted arm slowly lowered – May be able to lower arm slowly to 90° (deltoid function) – Arm will then drop to side if rotator cuff tear ...
Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
... The utricle and saccule respond to changes in head position relative to gravity and movement in one direction. Hair cells are arranged in clusters and project into a gelatinous material containing otoliths. When the head’s orientation changes, the hair cells are tugged on, sending nerve impuls ...
... The utricle and saccule respond to changes in head position relative to gravity and movement in one direction. Hair cells are arranged in clusters and project into a gelatinous material containing otoliths. When the head’s orientation changes, the hair cells are tugged on, sending nerve impuls ...
Frontal bone - PA
... superior and lateral part of the skull. They join together at a suture on the midline and also join with the frontal bones. The word "parietal" means wall and these bones form much of the lateral "walls" of the skull. • 3. Temporal bones - These bones make up the "temple" region of the skull superio ...
... superior and lateral part of the skull. They join together at a suture on the midline and also join with the frontal bones. The word "parietal" means wall and these bones form much of the lateral "walls" of the skull. • 3. Temporal bones - These bones make up the "temple" region of the skull superio ...
Exercise is very important. It is one of our everyday life activities. It
... ureter, a tube that lets urine trickle to the bladder. When we exercise our circulatory system increases in speed, and our heart beats faster and deeper bcause the heart needs to transport blood quicker. The sympatetic nerve tells the heart to beat faster. The body cells need more oxygen and nutrien ...
... ureter, a tube that lets urine trickle to the bladder. When we exercise our circulatory system increases in speed, and our heart beats faster and deeper bcause the heart needs to transport blood quicker. The sympatetic nerve tells the heart to beat faster. The body cells need more oxygen and nutrien ...
Earthworm lab analysis
... 8. How can you tell the ventral from the dorsal side of the earthworm? ...
... 8. How can you tell the ventral from the dorsal side of the earthworm? ...
Appendicular Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs∗
... the adductor longus, adductor brevis, and adductor magnus adduct the thigh and medially rotate it. The pectineus muscle adducts and exes the femur at the hip. The thigh muscles that move the femur, tibia, and bula are divided into medial, anterior, and posterior compartments. The medial compartmen ...
... the adductor longus, adductor brevis, and adductor magnus adduct the thigh and medially rotate it. The pectineus muscle adducts and exes the femur at the hip. The thigh muscles that move the femur, tibia, and bula are divided into medial, anterior, and posterior compartments. The medial compartmen ...
Exam 2 Review Key - Iowa State University
... E) a four chambered heart Follow up: What are the four characteristics shared by all chordates? Notochord, pharyngeal slits, postanal tail 10.) Why is the amniotic egg considered such an important evolutionary breakthrough? A) Without amniotic eggs there would be no Denny's B) The shell allows repro ...
... E) a four chambered heart Follow up: What are the four characteristics shared by all chordates? Notochord, pharyngeal slits, postanal tail 10.) Why is the amniotic egg considered such an important evolutionary breakthrough? A) Without amniotic eggs there would be no Denny's B) The shell allows repro ...
PAC01 Abdomen
... NEW MATERIAL--The Abdomen - the region of the body between the thorax and the pelvis. It is surrounded by the abdominal wall. It is separated from the thorax by the diaphragm. It is continuous inferiorly with the pelvic cavity. The abdominal cavity contains the peritoneum, most of the digestive orga ...
... NEW MATERIAL--The Abdomen - the region of the body between the thorax and the pelvis. It is surrounded by the abdominal wall. It is separated from the thorax by the diaphragm. It is continuous inferiorly with the pelvic cavity. The abdominal cavity contains the peritoneum, most of the digestive orga ...
Biology 11 - Human Anatomy
... ____________ (soft spots) are soft, membranous spots between the incompletely formed cranial bones of a fetus or embryo; allow skull compression and expansion, and include the ______: a. __________ – in temple area where frontal, parietal, and sphenoid bones join b. _________ – at medial junction of ...
... ____________ (soft spots) are soft, membranous spots between the incompletely formed cranial bones of a fetus or embryo; allow skull compression and expansion, and include the ______: a. __________ – in temple area where frontal, parietal, and sphenoid bones join b. _________ – at medial junction of ...
Appendicular Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs∗
... the adductor longus, adductor brevis, and adductor magnus adduct the thigh and medially rotate it. The pectineus muscle adducts and exes the femur at the hip. The thigh muscles that move the femur, tibia, and bula are divided into medial, anterior, and posterior compartments. The medial compartmen ...
... the adductor longus, adductor brevis, and adductor magnus adduct the thigh and medially rotate it. The pectineus muscle adducts and exes the femur at the hip. The thigh muscles that move the femur, tibia, and bula are divided into medial, anterior, and posterior compartments. The medial compartmen ...
Virtual Beetle Dissection Activity
... torquata beetles. While exploring, answer the following questions. If an answer is not available in the dissection tool, check the beetle story or the terms list for the information you need. ...
... torquata beetles. While exploring, answer the following questions. If an answer is not available in the dissection tool, check the beetle story or the terms list for the information you need. ...
practice exam
... field exercises. Physical ex revealed wrist drop and weakness of grasp but normal elbow extension. There is no loss of sensation in affected limb. Which nerve is affected? Ulnar a. If affected, abduction and adduction of fingers can be affected (due to interosseous muscles) b. ONLY muscle innervat ...
... field exercises. Physical ex revealed wrist drop and weakness of grasp but normal elbow extension. There is no loss of sensation in affected limb. Which nerve is affected? Ulnar a. If affected, abduction and adduction of fingers can be affected (due to interosseous muscles) b. ONLY muscle innervat ...
Anatomical details in brainstem and cisterns revealed by
... however single-shot EPI suffers severe distortion near bone and air. The purpose of the present study is to compare the visibility of small structures in brainstem and cisterns between the images with RESOLVE and those with single-shot EPI both using unidirectional MPG.. Methods Four patients with v ...
... however single-shot EPI suffers severe distortion near bone and air. The purpose of the present study is to compare the visibility of small structures in brainstem and cisterns between the images with RESOLVE and those with single-shot EPI both using unidirectional MPG.. Methods Four patients with v ...
Vertebral Column
... lumbar areas and kyphosis in the thoracic. Articulation is through the articular facets referred to as superior and inferior articular facets. Facet joints are synovial gliding joints so there is a little bit of motion at each segment called translatory movement (they all move). Called apophyseal or ...
... lumbar areas and kyphosis in the thoracic. Articulation is through the articular facets referred to as superior and inferior articular facets. Facet joints are synovial gliding joints so there is a little bit of motion at each segment called translatory movement (they all move). Called apophyseal or ...
Acc_Bio_Resp_Quiz_Quiz_Trade
... 8. What is the name of the windpipe? Why is it covered in cartilaginous rings? ~ Trachea. So that the airway remains open 9. What are the two branches of the trachea called that lead into the lungs? ~ Bronchi 10. How thick are capillary and aveoli walls? Why is this important? ~ 1 cell thick. Diffus ...
... 8. What is the name of the windpipe? Why is it covered in cartilaginous rings? ~ Trachea. So that the airway remains open 9. What are the two branches of the trachea called that lead into the lungs? ~ Bronchi 10. How thick are capillary and aveoli walls? Why is this important? ~ 1 cell thick. Diffus ...
172_eposter - Stanley Radiology
... Spike and wave activity within the thalamocortical network can cause absence seizures and other forms of epileptic behaviour. Thalamocortical dysrhythmia is associated with impulse control disorders such as OCD, Parkinsons disease, ADHD and other form of chronic psychosis. Damage to these fibe ...
... Spike and wave activity within the thalamocortical network can cause absence seizures and other forms of epileptic behaviour. Thalamocortical dysrhythmia is associated with impulse control disorders such as OCD, Parkinsons disease, ADHD and other form of chronic psychosis. Damage to these fibe ...
Incisions made in the direction of Langer`s lines are less likely to
... the patient stand upright the outline of the coin will be oval with the long axis indicating Langer’s line. It is useful to know the surface marking of the entrance of the superior vena cava into the right atrium when positioning a central venous catheter. It is represented by a transverse line 2.5 ...
... the patient stand upright the outline of the coin will be oval with the long axis indicating Langer’s line. It is useful to know the surface marking of the entrance of the superior vena cava into the right atrium when positioning a central venous catheter. It is represented by a transverse line 2.5 ...
8.1_Respiratory_Anatomy_
... 5. Terminal bronchioles - the last part of the conducting zone. * No gaseous exchange occurs in the structures listed above. 6. Respiratory bronchioles - branch from the terminal bronchioles. Their walls are 2-3 cells thick, but as their name suggests, CO2 and O2 can diffuse across the walls of thes ...
... 5. Terminal bronchioles - the last part of the conducting zone. * No gaseous exchange occurs in the structures listed above. 6. Respiratory bronchioles - branch from the terminal bronchioles. Their walls are 2-3 cells thick, but as their name suggests, CO2 and O2 can diffuse across the walls of thes ...
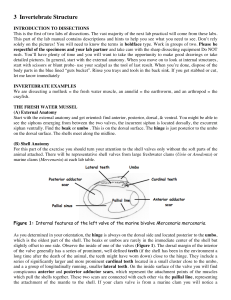
3 Invertebrate Structure
... pleiopods are also referred to as gonopods. openings on the base of the fifth pair of thoracic walking legs. If your specimen is male, or on the base of the third pair of walking legs, if it is female. Notice structural modifications on the first and second pairs of abdominal pleiopods (gonopods) of ...
... pleiopods are also referred to as gonopods. openings on the base of the fifth pair of thoracic walking legs. If your specimen is male, or on the base of the third pair of walking legs, if it is female. Notice structural modifications on the first and second pairs of abdominal pleiopods (gonopods) of ...
Anatomy and Physiology of the Velopharyngeal
... ○ The posterior wall of the pharynx moves anteriorly towards the velum ○ The lateral walls of the pharynx move medially to the velum At rest, the velum is in its lowest position During the production of oral sounds, the velum moves posteriorly and superiorly The phonetic context influences the eleva ...
... ○ The posterior wall of the pharynx moves anteriorly towards the velum ○ The lateral walls of the pharynx move medially to the velum At rest, the velum is in its lowest position During the production of oral sounds, the velum moves posteriorly and superiorly The phonetic context influences the eleva ...
Motor systems
... Motor Unit Motoneuron + muscle fibers it innervates Range in size from a few muscle fibers (e.g. extraocular muscles) To hundreds of fibers (e.g. digits) To thousands of fibers (e.g. trunk and major limb segments) Smaller motor units yield more refined control a motor “fovea” ...
... Motor Unit Motoneuron + muscle fibers it innervates Range in size from a few muscle fibers (e.g. extraocular muscles) To hundreds of fibers (e.g. digits) To thousands of fibers (e.g. trunk and major limb segments) Smaller motor units yield more refined control a motor “fovea” ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.