Slide 1
... The condyles are elliptical in shape and diverge as they pass backwards The lower surface of each condyle is everted and convex from before backwards and from side-to-side ...
... The condyles are elliptical in shape and diverge as they pass backwards The lower surface of each condyle is everted and convex from before backwards and from side-to-side ...
Ultrasound-Guided Right Internal Jugular Vein Access
... This following cartoon demonstrates the various relationships between the carotid and IJ that exist. The normal appearance is indicated on the left-hand side of the cartoon. One can see a reversal in which the IJ is actually medial to the carotid. One can see a situation in which the IJ is either pa ...
... This following cartoon demonstrates the various relationships between the carotid and IJ that exist. The normal appearance is indicated on the left-hand side of the cartoon. One can see a reversal in which the IJ is actually medial to the carotid. One can see a situation in which the IJ is either pa ...
Summary
... the dorsal surface of the cricoid lamina, while the lateral cricoarytenoid muscle arises from the proximal third of the rostral border of the cricoid arch and inserts on the base of the arytenoid cartilage. The transverse arytenoid muscle is a small muscle consists of two lateral portions united in ...
... the dorsal surface of the cricoid lamina, while the lateral cricoarytenoid muscle arises from the proximal third of the rostral border of the cricoid arch and inserts on the base of the arytenoid cartilage. The transverse arytenoid muscle is a small muscle consists of two lateral portions united in ...
Axilla - eCurriculum
... Connective tissue septa of the breast A. The glandular tissue and more superficial fat in each lobe are separated from adjacent lobes by the retinacula cutis (Grants 12 th ed 1.4). These connective tissue septa extend from the dermis to the fascia that over lies the pectoralis major muscle. ...
... Connective tissue septa of the breast A. The glandular tissue and more superficial fat in each lobe are separated from adjacent lobes by the retinacula cutis (Grants 12 th ed 1.4). These connective tissue septa extend from the dermis to the fascia that over lies the pectoralis major muscle. ...
Bones and Skeletal Tissues
... Stages in Endochondral Ossification Anatomy of Epiphyseal Growth Areas • In epiphyseal plates of growing bones: • Cartilage is organized for quick, efficient growth • Cartilage cells form tall stacks • Chondroblasts at the top of stacks divide quickly • Pushes the epiphysis away from the diaphysis • ...
... Stages in Endochondral Ossification Anatomy of Epiphyseal Growth Areas • In epiphyseal plates of growing bones: • Cartilage is organized for quick, efficient growth • Cartilage cells form tall stacks • Chondroblasts at the top of stacks divide quickly • Pushes the epiphysis away from the diaphysis • ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Quiz on Shoulder and Spine
... 13. The muscle that is pictured to the lower portion of the illustration and is responsible for adducting and medially rotating the arm is The posterior deltoid The trapesius The latissimus ...
... 13. The muscle that is pictured to the lower portion of the illustration and is responsible for adducting and medially rotating the arm is The posterior deltoid The trapesius The latissimus ...
PowerPoint Lecture - Dr. Stuart Sumida
... Inferior gluteal Internal pudendal Obturator Middle rectal Inferior vesicle Superior vesicle ...
... Inferior gluteal Internal pudendal Obturator Middle rectal Inferior vesicle Superior vesicle ...
Introduction
... cilia action at the gill edge Most parts of the digestive system, including the esophagus, stomach, digestive gland, and intestine, are located within the foot and visceral mass. To study the various structures enclosed within the visceral mass, you will need to cut along the ventral surface of the ...
... cilia action at the gill edge Most parts of the digestive system, including the esophagus, stomach, digestive gland, and intestine, are located within the foot and visceral mass. To study the various structures enclosed within the visceral mass, you will need to cut along the ventral surface of the ...
Ankle and Lower Leg - ProvidencePanthersSportsMedicine
... – Major nerves of the lower leg are the tibial and common peroneal – Major arteries include the posterior and anterior tibial arteries – Primary veins consist of popliteal, peroneal and anterior and posterior tibial veins. ...
... – Major nerves of the lower leg are the tibial and common peroneal – Major arteries include the posterior and anterior tibial arteries – Primary veins consist of popliteal, peroneal and anterior and posterior tibial veins. ...
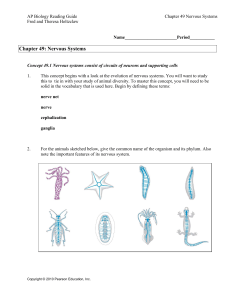
AP Bio Ch 49 Reading Guide
... 20. How does a hydrostatic skeleton work? What evolutionary advantages might such a skeleton provide? ...
... 20. How does a hydrostatic skeleton work? What evolutionary advantages might such a skeleton provide? ...
You have 24 vertebrae in your spinal column. Two are special
... you to turn your head and neck. The atlanto-axial joint connects the atlas to the axis. They are part of the vertebral column, which supports the peripheral nervous system. ...
... you to turn your head and neck. The atlanto-axial joint connects the atlas to the axis. They are part of the vertebral column, which supports the peripheral nervous system. ...
Superior mesenteric artery
... - Can be recognized by a constriction on its surface 13- Rugae = Mucosal folds of stomach:- Mainly longitudinal 14- Muscle fibers of stomach are longitudinal, transverse & oblique 15- Left gastric A. supplies a- Lower 1/3 of esophagus b- Upper right part of stomach 16- Left gastro-epiploic A. & shor ...
... - Can be recognized by a constriction on its surface 13- Rugae = Mucosal folds of stomach:- Mainly longitudinal 14- Muscle fibers of stomach are longitudinal, transverse & oblique 15- Left gastric A. supplies a- Lower 1/3 of esophagus b- Upper right part of stomach 16- Left gastro-epiploic A. & shor ...
Stiffness
... • Five metacarpals - numbered I-V, lateral to medial • 14 phalanges - two in the thumb (pollex) and three in ...
... • Five metacarpals - numbered I-V, lateral to medial • 14 phalanges - two in the thumb (pollex) and three in ...
Body diagrams during pregnancy
... See larger images at the TEENbirth Connection here (pre-pregnancy) and here ( full-term), as well as diagrams showing what your body looks like during the . Sep 27, 2010 . diagram of a fetus during the First trimester (week 1-week 12) See how. For some women, body image is a huge concern during preg ...
... See larger images at the TEENbirth Connection here (pre-pregnancy) and here ( full-term), as well as diagrams showing what your body looks like during the . Sep 27, 2010 . diagram of a fetus during the First trimester (week 1-week 12) See how. For some women, body image is a huge concern during preg ...
Superficial Portion of Abductor Pollicis Brevis Muscle
... This muscle is related in the background with the opponens pollicis muscle (OP), which lies below and laterally, and the FPBsup, which lies inferiorly and medially. The gap formed by these two muscles and the APB muscle enters the thenar branch of the median nerve (recurrent branch of median nerve C ...
... This muscle is related in the background with the opponens pollicis muscle (OP), which lies below and laterally, and the FPBsup, which lies inferiorly and medially. The gap formed by these two muscles and the APB muscle enters the thenar branch of the median nerve (recurrent branch of median nerve C ...
Practice Written Exam 2 (2012)
... is brought to the ED, your patient is unconscious. Her blood pressure drops, heart rate increases, and demonstrates poor capillary perfusion. A previous diagnosis of a duodenal ulcer indicates that it has eroded directly into one of her arteries causing this sudden hemorrhaging. Which of the followi ...
... is brought to the ED, your patient is unconscious. Her blood pressure drops, heart rate increases, and demonstrates poor capillary perfusion. A previous diagnosis of a duodenal ulcer indicates that it has eroded directly into one of her arteries causing this sudden hemorrhaging. Which of the followi ...
10 Respiratory System SB Powerpoint
... Air enters the body through the nasal passages and mouth, and passes via the pharynx and larynx to the trachea. ...
... Air enters the body through the nasal passages and mouth, and passes via the pharynx and larynx to the trachea. ...
Spinographic Interpretation
... iv. Level of hard palate v. “S” Line construction 1. Mark the center of anterior tubercle and center of posterior arch 2. Connect these two lines vi. Stress Vertebra Line 1. Extend a line along the posterior body of C2 2. Extend a line along the posterior body of C7 or lowest visible cervical 3. The ...
... iv. Level of hard palate v. “S” Line construction 1. Mark the center of anterior tubercle and center of posterior arch 2. Connect these two lines vi. Stress Vertebra Line 1. Extend a line along the posterior body of C2 2. Extend a line along the posterior body of C7 or lowest visible cervical 3. The ...
Annelida By: Omar Abdulkader, Marcus Bray
... • Contraction of these muscle against each other and the coelomic fluid cause the organism to move. • Most annelids have chaetae which are bristles that provide traction for burrowing. Marcus Bray ...
... • Contraction of these muscle against each other and the coelomic fluid cause the organism to move. • Most annelids have chaetae which are bristles that provide traction for burrowing. Marcus Bray ...
Structural vs Functional Approach in Musculoskeletal Pathologies
... What is the difference between structural and functional pathologies? How do you diagnose and treat them? Why is it important that we (and you) understand both? Finally we will cover some specific cases of these two kinds of pathologies. ...
... What is the difference between structural and functional pathologies? How do you diagnose and treat them? Why is it important that we (and you) understand both? Finally we will cover some specific cases of these two kinds of pathologies. ...
anatomy team
... The foot is a complex structure. There are 26 bones in each foot alone. The foot is also well muscled and is supported by ligaments and tissue known as fascia. Support is of prime importance in the foot, as it bears the weight of the body and must adopt different configurations to permit ...
... The foot is a complex structure. There are 26 bones in each foot alone. The foot is also well muscled and is supported by ligaments and tissue known as fascia. Support is of prime importance in the foot, as it bears the weight of the body and must adopt different configurations to permit ...
Slide 1 - FA Davis PT Collection
... A. The lateral view of a typical lumbar vertebra shows the large body and zygapophyseal facets. B. The superior view of a typical lumbar vertebra shows transverse and spinous processes and superior zygapophyseal facets. C. The posterior view of a lumbar vertebra shows the location of the mamillary a ...
... A. The lateral view of a typical lumbar vertebra shows the large body and zygapophyseal facets. B. The superior view of a typical lumbar vertebra shows transverse and spinous processes and superior zygapophyseal facets. C. The posterior view of a lumbar vertebra shows the location of the mamillary a ...
Slide 1 - FA Davis PT Collection
... A. The lateral view of a typical lumbar vertebra shows the large body and zygapophyseal facets. B. The superior view of a typical lumbar vertebra shows transverse and spinous processes and superior zygapophyseal facets. C. The posterior view of a lumbar vertebra shows the location of the mamillary a ...
... A. The lateral view of a typical lumbar vertebra shows the large body and zygapophyseal facets. B. The superior view of a typical lumbar vertebra shows transverse and spinous processes and superior zygapophyseal facets. C. The posterior view of a lumbar vertebra shows the location of the mamillary a ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.