illust-loc-12-acup-pts-save-life-2
... Ht/Heart 7 Shen Men • Spirit Gate. Calms the Spirit/Shen On the transverse wrist crease, in the small depression between the outer wrist bone (pisiform) and the outer arm bone (ulna). Ht/Heart 6 On the palm-side (palmar) surface of the forearm, 0.5 cun (up the arm) proximal to the transverse wrist ...
... Ht/Heart 7 Shen Men • Spirit Gate. Calms the Spirit/Shen On the transverse wrist crease, in the small depression between the outer wrist bone (pisiform) and the outer arm bone (ulna). Ht/Heart 6 On the palm-side (palmar) surface of the forearm, 0.5 cun (up the arm) proximal to the transverse wrist ...
Dissection Guide - Home Science Tools
... skin up so that you only cut the skin and none of the organs underneath. After cutting through the skin, carefully pull it back and pin it down on either side, cutting the membrane layer underneath as necessary. 3. A thin membrane covers the organs to keep them securely in place while the snake move ...
... skin up so that you only cut the skin and none of the organs underneath. After cutting through the skin, carefully pull it back and pin it down on either side, cutting the membrane layer underneath as necessary. 3. A thin membrane covers the organs to keep them securely in place while the snake move ...
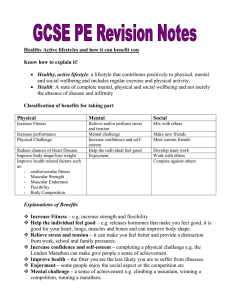
GCSE Revision bookle..
... Weights and reps depend on what you are trying to improve e.g. strength=more weight less reps; muscular endurance= lower weight more reps. Number of sets usually 2/3 e.g. 2 sets of 10 reps. Recovery should be about 1-2 min between sets. And frequency of training must allow for rest days or easier tr ...
... Weights and reps depend on what you are trying to improve e.g. strength=more weight less reps; muscular endurance= lower weight more reps. Number of sets usually 2/3 e.g. 2 sets of 10 reps. Recovery should be about 1-2 min between sets. And frequency of training must allow for rest days or easier tr ...
Abdomen (plate 249) - located between the thorax and the pelvis
... - in the inferior part of the AL Wall, down near the inguinal regions, the fascia is divided into two layers: 1- Superficial Layer – “camper’s fascia” - primarily fat tissue 2- Membranous Layer (deep to camper’s fascia) – “scarpas’ fascia” - only in inferior part Tranversalis Fascia - firm membranou ...
... - in the inferior part of the AL Wall, down near the inguinal regions, the fascia is divided into two layers: 1- Superficial Layer – “camper’s fascia” - primarily fat tissue 2- Membranous Layer (deep to camper’s fascia) – “scarpas’ fascia” - only in inferior part Tranversalis Fascia - firm membranou ...
Anatomy of: larynx, trachea, and bronchi
... Summary Larynx (the voice box) is organ responsible for phonation is the respiratory system, and it also helps in deglutition and respireation (obviously) It’s composed of four major structures: 1-Cartilaginous skeleton 3- Muscles ...
... Summary Larynx (the voice box) is organ responsible for phonation is the respiratory system, and it also helps in deglutition and respireation (obviously) It’s composed of four major structures: 1-Cartilaginous skeleton 3- Muscles ...
Over View of Thorax
... Is a broad central partition that separates the two laterally placed pleural cavities”. ...
... Is a broad central partition that separates the two laterally placed pleural cavities”. ...
Nose, Nasal cavity & Paranasal sinuses & Pharynx
... Shows three horizontal bony projections, the superior, middle & inferior conchae ...
... Shows three horizontal bony projections, the superior, middle & inferior conchae ...
APPENDICULAR SKELETON
... ____ 17. Bones of the ankle ____ 18. Bones forming the instep of the foot ____ 19. Opening in a coxal bone formed by the pubic and ischial rami ____ 20. Sites of muscle attachment on the proximal end of the femur ____ 21. Tarsal bone that articulates with the tibia 26. For each of the following stat ...
... ____ 17. Bones of the ankle ____ 18. Bones forming the instep of the foot ____ 19. Opening in a coxal bone formed by the pubic and ischial rami ____ 20. Sites of muscle attachment on the proximal end of the femur ____ 21. Tarsal bone that articulates with the tibia 26. For each of the following stat ...
The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton
... There are 14 phalanges on each foot Each phalanx consists of a base, shaft, and head There are 2 phalanges in the big toe, or hallux, and 3 phalanges in each of the other four digits ...
... There are 14 phalanges on each foot Each phalanx consists of a base, shaft, and head There are 2 phalanges in the big toe, or hallux, and 3 phalanges in each of the other four digits ...
Notes about Arthropods The arthropods are the largest group
... Arthropods have one pair of jaws called mandibles. Mandibles can look like pincers or the jaws of plyers (think of ants or horseflies), but mandibles can also be shaped like a needle for jabbing (mosquitoes), a rolled up tube (butterflies) or a flexible, extendable tube (house flies). Holding, chewi ...
... Arthropods have one pair of jaws called mandibles. Mandibles can look like pincers or the jaws of plyers (think of ants or horseflies), but mandibles can also be shaped like a needle for jabbing (mosquitoes), a rolled up tube (butterflies) or a flexible, extendable tube (house flies). Holding, chewi ...
Bone
... Ask the patient to stick out his/her tongue. The tongue will deviate to the side of the nerve with the lesion (b/c of unilateral paralysis of the genioglossus muscle, which protracts the tongue). 11. All of the “glossus” muscles are innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) except ________, which ...
... Ask the patient to stick out his/her tongue. The tongue will deviate to the side of the nerve with the lesion (b/c of unilateral paralysis of the genioglossus muscle, which protracts the tongue). 11. All of the “glossus” muscles are innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) except ________, which ...
The peritoneum
... 2. At rectal venous plexus Hepatic portal vein → splenic vein → inferior mesenteric vein → superior rectal vein → rectal venous plexus → inferior rectal and anal veins → internal iliac vein → ...
... 2. At rectal venous plexus Hepatic portal vein → splenic vein → inferior mesenteric vein → superior rectal vein → rectal venous plexus → inferior rectal and anal veins → internal iliac vein → ...
ADDITIONAL HEAD OF STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID MUSCLE
... muscle across the side of neck. It divides the side of the neck into anterior and posterior triangles. It is an important surgical landmark as it is related to many neurovascular structures in the neck. It originates from two heads. The sternal head is rounded and tendinous. It originates from the u ...
... muscle across the side of neck. It divides the side of the neck into anterior and posterior triangles. It is an important surgical landmark as it is related to many neurovascular structures in the neck. It originates from two heads. The sternal head is rounded and tendinous. It originates from the u ...
Face Time! - Mayfield City Schools
... • Cheek bones • Articulate with the zygomatic processes of the temporal bones posteriorly and the zygomatic process of the frontal bone superiorly and with the zygomatic processes of the maxillae ...
... • Cheek bones • Articulate with the zygomatic processes of the temporal bones posteriorly and the zygomatic process of the frontal bone superiorly and with the zygomatic processes of the maxillae ...
boundaries of thoracic cage
... Is a broad central partition that separates the two laterally placed pleural cavities”. It extends: • From the sternum to the bodies of the vertebrae; and • From the superior thoracic aperture to the diaphragm. • Imaginary plane passes through T 4 divides it into superior ...
... Is a broad central partition that separates the two laterally placed pleural cavities”. It extends: • From the sternum to the bodies of the vertebrae; and • From the superior thoracic aperture to the diaphragm. • Imaginary plane passes through T 4 divides it into superior ...
APSpring14_142E1Aans..
... When constricted, the iris increases the amount of light that is focused on the macula The inferior oblique muscle of the eye elevates the eye Chorid lies between the retina and the sclera The retina is thinner near the ciliary muscle than near the macula ...
... When constricted, the iris increases the amount of light that is focused on the macula The inferior oblique muscle of the eye elevates the eye Chorid lies between the retina and the sclera The retina is thinner near the ciliary muscle than near the macula ...
OVER VIEW OF THORAX
... Is a broad central partition that separates the two laterally placed pleural cavities”. It extends: • From the sternum to the bodies of the vertebrae; and • From the superior thoracic aperture to the diaphragm. • Imaginary plane passes through T 4 divides it into superior ...
... Is a broad central partition that separates the two laterally placed pleural cavities”. It extends: • From the sternum to the bodies of the vertebrae; and • From the superior thoracic aperture to the diaphragm. • Imaginary plane passes through T 4 divides it into superior ...
Bicipital origin of plantaris muscle – a case report
... Thus, it can be called the third head of gastrocnemius but the muscle fibers of this slip of plantaris muscle lower down merged with common belly of plantaris muscle. It is in consonance with the idea advocated by McMurrich that the plantaris is a derivative of the deeper portion of the lateral head ...
... Thus, it can be called the third head of gastrocnemius but the muscle fibers of this slip of plantaris muscle lower down merged with common belly of plantaris muscle. It is in consonance with the idea advocated by McMurrich that the plantaris is a derivative of the deeper portion of the lateral head ...
SA04su5a
... 7) Postganglionic neurons carried in CN X innervate which one of the following structures? a) smooth muscles of the eye causing miosis b) sublingual salivary gland c) lacrimal gland d) the heart decreasing rate and force of contraction e) the heart increasing rate and force of contraction 8) Neurot ...
... 7) Postganglionic neurons carried in CN X innervate which one of the following structures? a) smooth muscles of the eye causing miosis b) sublingual salivary gland c) lacrimal gland d) the heart decreasing rate and force of contraction e) the heart increasing rate and force of contraction 8) Neurot ...
Postural Assessment
... The strength and length of muscles involved in joint motion must be balanced. The balance is based on force couple (two or more translatory forces that in combination produce rotation) principle among muscles involved in the three cardinal planes of motion. When a force couple is out of balance, the ...
... The strength and length of muscles involved in joint motion must be balanced. The balance is based on force couple (two or more translatory forces that in combination produce rotation) principle among muscles involved in the three cardinal planes of motion. When a force couple is out of balance, the ...
Digestive system
... A number of terms will be used quite frequently in the dissection exercises. These terms are used to describe the location of parts on the organism. Some of these terms (anterior, distal, dorsal, lateral, medial, posterior, proximal, and ventral) are often used relatively. For example, if we say tha ...
... A number of terms will be used quite frequently in the dissection exercises. These terms are used to describe the location of parts on the organism. Some of these terms (anterior, distal, dorsal, lateral, medial, posterior, proximal, and ventral) are often used relatively. For example, if we say tha ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.