full text
... The testes and the colleteric glands are found in the posterior part of the body, in the vicinity of the stalk. In figures 3 to 6 the central parts of sections from one animal are drawn, each following section from a slightly farther anterior plane than its predecessor. The visceral mass forms the c ...
... The testes and the colleteric glands are found in the posterior part of the body, in the vicinity of the stalk. In figures 3 to 6 the central parts of sections from one animal are drawn, each following section from a slightly farther anterior plane than its predecessor. The visceral mass forms the c ...
Ch7_lecture notes Martini 9e
... • Lacrimal sulcus • Location of the lacrimal sac • Leads to the nasolacrimal canal (between orbit and nasal cavity) • The Mandible • Functions of the mandible • Forms the lower jaw • Articulations of the mandible • Mandibular fossae of the temporal bones • Marks of the mandible ...
... • Lacrimal sulcus • Location of the lacrimal sac • Leads to the nasolacrimal canal (between orbit and nasal cavity) • The Mandible • Functions of the mandible • Forms the lower jaw • Articulations of the mandible • Mandibular fossae of the temporal bones • Marks of the mandible ...
Volume 142, 1999 57 A REPORT ON ANOMALIES OF DIGASTRIC
... a) The medial part of the anterior belly originates bilaterally at the digastric fossa of the mandible, continues dorsally as the aponeurotic attachment fixed to the body of the hyoid bone. b) The lateral part of the anterior belly originates bilaterally on the lower margin of the body of the mandib ...
... a) The medial part of the anterior belly originates bilaterally at the digastric fossa of the mandible, continues dorsally as the aponeurotic attachment fixed to the body of the hyoid bone. b) The lateral part of the anterior belly originates bilaterally on the lower margin of the body of the mandib ...
The lesser wing
... the lateral aspect articulates with the labyrinth of the ethmoid bone above and with the orbital process of the palatine bone below. The inferior aspect articulates with the nasal septum in the midline the ethmoid anteriorly and the vomer inferiorly and also with the sphenoidal process of the palati ...
... the lateral aspect articulates with the labyrinth of the ethmoid bone above and with the orbital process of the palatine bone below. The inferior aspect articulates with the nasal septum in the midline the ethmoid anteriorly and the vomer inferiorly and also with the sphenoidal process of the palati ...
Glossary of Key Terms and Concepts
... Glossary of Key Terms and Concepts - Chapter 7 Anterior cardinal veins - These bilaterally symmetrical, paired veins drain blood from the head and neck into their respective common cardinal veins during the early 4th week. The distal ends of the anterior cardinals give rise to the internal jugular v ...
... Glossary of Key Terms and Concepts - Chapter 7 Anterior cardinal veins - These bilaterally symmetrical, paired veins drain blood from the head and neck into their respective common cardinal veins during the early 4th week. The distal ends of the anterior cardinals give rise to the internal jugular v ...
Surgical technique illustrated in the anatomy laboratory
... hyoid bone to the thyroid isthmus are removed. This dissection includes superficial lymphatics in this region as well as Delphian lymph nodes. The thyroid isthmus is then divided and the thyroid lobes are elevated laterally to expose the anterior tracheal wall. Inferior to the thyroid, the pretrache ...
... hyoid bone to the thyroid isthmus are removed. This dissection includes superficial lymphatics in this region as well as Delphian lymph nodes. The thyroid isthmus is then divided and the thyroid lobes are elevated laterally to expose the anterior tracheal wall. Inferior to the thyroid, the pretrache ...
answers
... 4. __D___ Which of the following nerves arise (at least in part) from vertebral level C2? A. Lesser occipital nerve B. Great Auricular nerve C. Supraclavicular nerves D. A and B E. All of the above 5. __E___ Which of the following arteries arise from the first part of the Subclavian artery (as it c ...
... 4. __D___ Which of the following nerves arise (at least in part) from vertebral level C2? A. Lesser occipital nerve B. Great Auricular nerve C. Supraclavicular nerves D. A and B E. All of the above 5. __E___ Which of the following arteries arise from the first part of the Subclavian artery (as it c ...
questions
... 4. ______ Which of the following nerves arise (at least in part) from vertebral level C2? A. Lesser occipital nerve B. Great Auricular nerve C. Supraclavicular nerves D. A and B E. All of the above 5. ______ Which of the following arteries arise from the first part of the Subclavian artery (as it c ...
... 4. ______ Which of the following nerves arise (at least in part) from vertebral level C2? A. Lesser occipital nerve B. Great Auricular nerve C. Supraclavicular nerves D. A and B E. All of the above 5. ______ Which of the following arteries arise from the first part of the Subclavian artery (as it c ...
potential - Club Therappy
... Power wheelchair joystick or rear wheel manual wheelchair location not optimal for reach Back support too wide ...
... Power wheelchair joystick or rear wheel manual wheelchair location not optimal for reach Back support too wide ...
Branches of Vagus Nerve
... It leaves the skull through the hypoglossal canal, then it has a short course in the carotid sheath (with internal carotid artery, internal jugular vein, glossopharyngeal, vagus and accessory nerves). It passes between the internal carotid artery and internal jugular vein (covered by the posterior b ...
... It leaves the skull through the hypoglossal canal, then it has a short course in the carotid sheath (with internal carotid artery, internal jugular vein, glossopharyngeal, vagus and accessory nerves). It passes between the internal carotid artery and internal jugular vein (covered by the posterior b ...
CLAVICLE (collar bone)
... Hold the humerus on the anterior surface of your arm with the olecranon fossa touching your skin (facing posteriorly). What direction is the head facing? It should be should face medially towards the body. ...
... Hold the humerus on the anterior surface of your arm with the olecranon fossa touching your skin (facing posteriorly). What direction is the head facing? It should be should face medially towards the body. ...
Maxillary Reconstruction
... The space between the restored anterior, superior, and inferior walls of the maxilla can usually be filled with soft tissue (muscle/fat) nasal lining may or may not be necessarily restored. The temporalis flap covers bone effectively in these types of reconstruction but does not close the pala ...
... The space between the restored anterior, superior, and inferior walls of the maxilla can usually be filled with soft tissue (muscle/fat) nasal lining may or may not be necessarily restored. The temporalis flap covers bone effectively in these types of reconstruction but does not close the pala ...
Inferior tibiofibular joint (tibiofibular syndesmosis) — own studies
... system, were made by Aristotle. He reported on 8 pairs of the ribs in humans, and the heart is consisted of 3 ventricles, while all vessels and nerves originate from the heart. According to him the brain was an organ which produced a mucus. Unquestionable authority from ancient times until the middl ...
... system, were made by Aristotle. He reported on 8 pairs of the ribs in humans, and the heart is consisted of 3 ventricles, while all vessels and nerves originate from the heart. According to him the brain was an organ which produced a mucus. Unquestionable authority from ancient times until the middl ...
Q7 Describe the anatomy of the antecubital fossa
... Superior – an imaginary horizontal line connecting the medial and lateral humeral epicondyles Inferior – the apex is directed inferiorly and is formed by the meeting point of the medial and lateral bound ...
... Superior – an imaginary horizontal line connecting the medial and lateral humeral epicondyles Inferior – the apex is directed inferiorly and is formed by the meeting point of the medial and lateral bound ...
Multi-axis passive and active stiffnesses of the glenohumeral joint
... Design. Glenohumeral stiffness along multiple axes was determined in fresh-frozen shoulder specimens under both passive (no simulated muscle contraction) and active (with simulated muscle contraction) conditions. Background. Glenohumeral laxity has been evaluated in various studies with focus on one ...
... Design. Glenohumeral stiffness along multiple axes was determined in fresh-frozen shoulder specimens under both passive (no simulated muscle contraction) and active (with simulated muscle contraction) conditions. Background. Glenohumeral laxity has been evaluated in various studies with focus on one ...
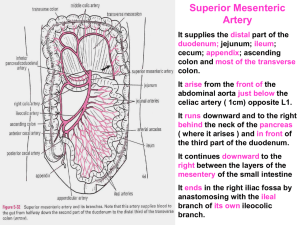
27-As of Mid& hindgut
... It arise from the front of the abdominal aorta just below the celiac artery ( 1cm) opposite L1. It runs downward and to the right behind the neck of the pancreas ( where it arises ) and in front of the third part of the duodenum. It continues downward to the right between the layers of the mesentery ...
... It arise from the front of the abdominal aorta just below the celiac artery ( 1cm) opposite L1. It runs downward and to the right behind the neck of the pancreas ( where it arises ) and in front of the third part of the duodenum. It continues downward to the right between the layers of the mesentery ...
The Anatomy and Physiology of Toothed and Baleen Whales
... approximately 1/3rd of its body’s length. one skull of a Baleen Whale was measured at 5.2 meters and weighed 2,200 pounds. The jaw in this head is greatly arched, allowing the right whale to carry extremely long baleen plates, up to 9 feet long. About 205-270 plates are found on each side of the mou ...
... approximately 1/3rd of its body’s length. one skull of a Baleen Whale was measured at 5.2 meters and weighed 2,200 pounds. The jaw in this head is greatly arched, allowing the right whale to carry extremely long baleen plates, up to 9 feet long. About 205-270 plates are found on each side of the mou ...
Unit VI – The Hip
... on the femur. When viewed schematically these ligaments make a “Z” across the front of the hip capsule. These ligaments serve as “check rings” for the motions at the hip. A portion of the “Z” ligament is taut with flexion or extension of the hip, while other portions are taut during abduction and ab ...
... on the femur. When viewed schematically these ligaments make a “Z” across the front of the hip capsule. These ligaments serve as “check rings” for the motions at the hip. A portion of the “Z” ligament is taut with flexion or extension of the hip, while other portions are taut during abduction and ab ...
Kramer DL, Booth RE, Albert TJ, Balderston RA. Posterior Lumbar
... intramuscular vasculature to redu ce hemorrhage. Delin eation of the pars interarti cularis is an extremely help ful maneuver as it defines the lateralm ost margin of the ca nal bet ween the pedicles. Subpe riostea l remova l of soft tissue ove rlyi ng the pars is facilit ated by ca refully cutting ...
... intramuscular vasculature to redu ce hemorrhage. Delin eation of the pars interarti cularis is an extremely help ful maneuver as it defines the lateralm ost margin of the ca nal bet ween the pedicles. Subpe riostea l remova l of soft tissue ove rlyi ng the pars is facilit ated by ca refully cutting ...
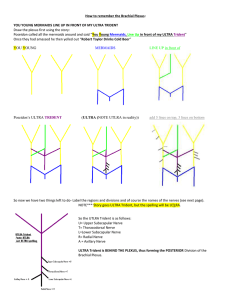
How to remember the Brachial Plexus
... * For the DIVISIONS: note that the initial nemonic has …..Line Up IN FRONT of Poseidon’s ULTRA trident……. So just like the story, the ULTRA Trident is BEHIND THE PLEXUS, thus forming the POSTERIOR Division of the Brachial Plexus. Story for all the nerve names that come off the Brachial Plexus: So al ...
... * For the DIVISIONS: note that the initial nemonic has …..Line Up IN FRONT of Poseidon’s ULTRA trident……. So just like the story, the ULTRA Trident is BEHIND THE PLEXUS, thus forming the POSTERIOR Division of the Brachial Plexus. Story for all the nerve names that come off the Brachial Plexus: So al ...
The Athletic Hip
... femoris muscle of the quadriceps group on the anterior thigh. The normal range for hip extension is 10-30 degrees. Abduction and adduction move the leg away from and toward the midline of the body, respectively, and the hip enjoys approximately 30-50 degrees of abduction and 10-30 degrees of adducti ...
... femoris muscle of the quadriceps group on the anterior thigh. The normal range for hip extension is 10-30 degrees. Abduction and adduction move the leg away from and toward the midline of the body, respectively, and the hip enjoys approximately 30-50 degrees of abduction and 10-30 degrees of adducti ...
CHAPTER 75 FACET JOINTS
... define at any specific intersegmental level but they also change as one moves in a cephalad to a caudad direction. In the upper lumbar segments they are vertical with a predominantly sagittal plane orientation, while in the lower lumbar segments they are somewhat less vertical and are approximately ...
... define at any specific intersegmental level but they also change as one moves in a cephalad to a caudad direction. In the upper lumbar segments they are vertical with a predominantly sagittal plane orientation, while in the lower lumbar segments they are somewhat less vertical and are approximately ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.