
Essential Question: How does the organization of
... 2) Make incisions along the anterior axillary line from your first incision to the inferior border of the axilla. To preserve the thoracotomy tube you inserted earlier, make your incision circumvent it on the medial side. Again, carry your incision down to the rib cage. 3) On the left side, or oppos ...
... 2) Make incisions along the anterior axillary line from your first incision to the inferior border of the axilla. To preserve the thoracotomy tube you inserted earlier, make your incision circumvent it on the medial side. Again, carry your incision down to the rib cage. 3) On the left side, or oppos ...
File
... Mass of striated muscles covered with the mucous membrane Divided into right and left halves by a median septum Three parts: Oral (anterior ⅔) Pharyngeal (posterior ⅓) Root (base) Two surfaces: Dorsal Ventral ...
... Mass of striated muscles covered with the mucous membrane Divided into right and left halves by a median septum Three parts: Oral (anterior ⅔) Pharyngeal (posterior ⅓) Root (base) Two surfaces: Dorsal Ventral ...
Practical class 4 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM ODUCTIVE SYSTEM
... The ejaculatory ducts divide the prostate, although not completely, into 3 lobes - the left, right and the median lobe. The latter has considerable clinical importance because of its anatomical relation with the bladder and its tendency to enlarge in benign senile hypertrophy of the prostate. ...
... The ejaculatory ducts divide the prostate, although not completely, into 3 lobes - the left, right and the median lobe. The latter has considerable clinical importance because of its anatomical relation with the bladder and its tendency to enlarge in benign senile hypertrophy of the prostate. ...
Course Outline
... Synovial membrane lines fibrous capsule. Pouch of synovial membrane passing under tendon of popliteus ...
... Synovial membrane lines fibrous capsule. Pouch of synovial membrane passing under tendon of popliteus ...
Knee Joint
... between tibia & ligamentum patella. 4. Subcutaneous infrapatellar bursa: between tibial tuberosity & skin. 5. Popliteal bursa: between popliteus tendon & capsule. ...
... between tibia & ligamentum patella. 4. Subcutaneous infrapatellar bursa: between tibial tuberosity & skin. 5. Popliteal bursa: between popliteus tendon & capsule. ...
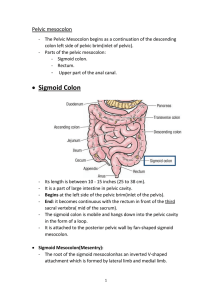
• Sigmoid Colon
... a wedge-shaped space located on each side of the anal canal. The base of the wedge is superficial and formed by the skin. The apex is between Levator ani &Obturator internus muscle. The edge of the wedge is formed by the junction of the medial and lateral walls. - The medial wall is formed by the sl ...
... a wedge-shaped space located on each side of the anal canal. The base of the wedge is superficial and formed by the skin. The apex is between Levator ani &Obturator internus muscle. The edge of the wedge is formed by the junction of the medial and lateral walls. - The medial wall is formed by the sl ...
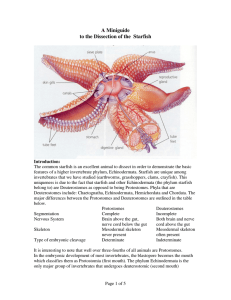
A Miniguide to the Dissection of the Starfish
... Nervous: Nerves coordinate the arm movements for directional locomotion of the starfish. The nerves are difficult to discern during dissection, so we will discuss them only briefly. There is an oral nerve ring around the mouth from which extends five radial nerves along the ventral side of the ambul ...
... Nervous: Nerves coordinate the arm movements for directional locomotion of the starfish. The nerves are difficult to discern during dissection, so we will discuss them only briefly. There is an oral nerve ring around the mouth from which extends five radial nerves along the ventral side of the ambul ...
4-BLOOD SUPPLY OF HEART [Autosaved]
... arteries; (2 branches) To the diaphragmatic surface of the right ventricle. (5) Atrial branches: To the right atrium; anterior and lateral surfaces. Posterior surface of both atria (6)The Artery of the SAN, also supplies both atria. ...
... arteries; (2 branches) To the diaphragmatic surface of the right ventricle. (5) Atrial branches: To the right atrium; anterior and lateral surfaces. Posterior surface of both atria (6)The Artery of the SAN, also supplies both atria. ...
AandPExam3takehomecC7sf7Y
... There are four extrinsic muscles of the tongue: genioglossus, hyoglossus, styoglossus, and palatoglossus. The extrinsic muscles originate from the bone and extend to the tongue. Their main functions are altering the tongue’s position. This allows for protrusion, retraction, and side to side movement ...
... There are four extrinsic muscles of the tongue: genioglossus, hyoglossus, styoglossus, and palatoglossus. The extrinsic muscles originate from the bone and extend to the tongue. Their main functions are altering the tongue’s position. This allows for protrusion, retraction, and side to side movement ...
Lecture Upper Limb I 2010
... arm's main nerves (specifically, spinal roots C5-C7), almost always occurring during birth. Depending on the nature of the damage, the paralysis can either resolve on its own over a period of months, necessitate physical therapy or require surgery. ...
... arm's main nerves (specifically, spinal roots C5-C7), almost always occurring during birth. Depending on the nature of the damage, the paralysis can either resolve on its own over a period of months, necessitate physical therapy or require surgery. ...
Open full article
... Anatomic Variations, but even these authors did not mention percentage of forming of these variations we found8. Variation in the left arm is predicted to cause some clinical symptoms, but now and after many years post-mortem the examination could not be realised. The anomalies in the formation of t ...
... Anatomic Variations, but even these authors did not mention percentage of forming of these variations we found8. Variation in the left arm is predicted to cause some clinical symptoms, but now and after many years post-mortem the examination could not be realised. The anomalies in the formation of t ...
SUPRASCAPULAR NERVE ENTRAPMENT BY PARALABRAL CYST
... from a joint capsule, bursa, ligament, tendon, or subchondral bone. A pseudocyst may result from the extrusion of joint fluid through a labrocapsular tear into adjacent soft tissues. This pathogenesis is similar to that of a meniscal cyst.Although often coincident, ...
... from a joint capsule, bursa, ligament, tendon, or subchondral bone. A pseudocyst may result from the extrusion of joint fluid through a labrocapsular tear into adjacent soft tissues. This pathogenesis is similar to that of a meniscal cyst.Although often coincident, ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 06 Martini Lecture Outline
... These membranous areas are actually the dura mater of the brain, which is a thick membranous material that helps to protect the brain. You can feel the infant’s pulse in the area of the anterior fontanel. Blood vessels lie deep to the fontanel. ...
... These membranous areas are actually the dura mater of the brain, which is a thick membranous material that helps to protect the brain. You can feel the infant’s pulse in the area of the anterior fontanel. Blood vessels lie deep to the fontanel. ...
Structure of the Posterior Abdominal Wall
... facet for articulation with the body of the twelfth thoracic vertebra. The anterior end is pointed and has a small costal cartilage, which is embedded in the musculature of the anterior abdominal wall. In many people it is so short that it fails to protrude beyond the lateral border of the erector s ...
... facet for articulation with the body of the twelfth thoracic vertebra. The anterior end is pointed and has a small costal cartilage, which is embedded in the musculature of the anterior abdominal wall. In many people it is so short that it fails to protrude beyond the lateral border of the erector s ...
The Nervous System Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves
... (white ramus & gray ramus) – carry autonomic motor fibers (ANS) to smooth muscles & glands in ventral body cavity; transmit visceral sensations; only found at T1-L2 spinal nerves ...
... (white ramus & gray ramus) – carry autonomic motor fibers (ANS) to smooth muscles & glands in ventral body cavity; transmit visceral sensations; only found at T1-L2 spinal nerves ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 06 Martini Lecture Outline
... These membranous areas are actually the dura mater of the brain, which is a thick membranous material that helps to protect the brain. You can feel the infant’s pulse in the area of the anterior fontanel. Blood vessels lie deep to the fontanel. ...
... These membranous areas are actually the dura mater of the brain, which is a thick membranous material that helps to protect the brain. You can feel the infant’s pulse in the area of the anterior fontanel. Blood vessels lie deep to the fontanel. ...
Biology - Central Lyon CSD
... school and college students than any other organism. Many of the structures, organs, and systems of the frog are similar to those of man, who is also a vertebrate. At the same time, the frog, an amphibian, is quite different from man. Similarities and differences will be pointed out and noted during ...
... school and college students than any other organism. Many of the structures, organs, and systems of the frog are similar to those of man, who is also a vertebrate. At the same time, the frog, an amphibian, is quite different from man. Similarities and differences will be pointed out and noted during ...
Introduction to the Nervous System
... aspect of the spinal cord and swells as it forms the dorsal root ganglion. 2. The VENTRAL ROOT (motor root) of a spinal nerve arises from the anterolateral aspect of the spinal cord. 3. The SPINAL NERVE itself occupies the space within an intervertebral foramen and is only about one centimeter long ...
... aspect of the spinal cord and swells as it forms the dorsal root ganglion. 2. The VENTRAL ROOT (motor root) of a spinal nerve arises from the anterolateral aspect of the spinal cord. 3. The SPINAL NERVE itself occupies the space within an intervertebral foramen and is only about one centimeter long ...
Pharynx and Larynx
... The digestive and respiratory systems merge briefly in the pharynx, which is subdivided into nasal, oral, and laryngeal parts. The pharyngeal walls basically consist of three strata: a mucosa, a muscularis, and an adventitia. The most superior part, the nasopharynx, is directly continuous with the n ...
... The digestive and respiratory systems merge briefly in the pharynx, which is subdivided into nasal, oral, and laryngeal parts. The pharyngeal walls basically consist of three strata: a mucosa, a muscularis, and an adventitia. The most superior part, the nasopharynx, is directly continuous with the n ...
Pelvic Anatomy Objectives
... 3. Learn the names and locations of the bony landmarks of the os coxae and will be able to specify the ones that can be palpated. a. PSIS, ASIS, ischial tuberosity, sacrum, iliac crest 4. Learn how to correctly orient the pelvic girdle line in the anatomical position. a. The pelvic girdle should be ...
... 3. Learn the names and locations of the bony landmarks of the os coxae and will be able to specify the ones that can be palpated. a. PSIS, ASIS, ischial tuberosity, sacrum, iliac crest 4. Learn how to correctly orient the pelvic girdle line in the anatomical position. a. The pelvic girdle should be ...
Morphology of the Forelimb of the Mole
... triceps (fig. 14) and into it is inserted the infraspinatus muscle. From the spinous process arises the superficial portion of the external head of the triceps and into it inserts the teres minor muscle (fig. 15). The greater tuberosity overhangs a deep fossa which extends upward under the clavicula ...
... triceps (fig. 14) and into it is inserted the infraspinatus muscle. From the spinous process arises the superficial portion of the external head of the triceps and into it inserts the teres minor muscle (fig. 15). The greater tuberosity overhangs a deep fossa which extends upward under the clavicula ...
[ PDF ] - journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences
... base of the mandible till the mastoid process and the skin flaps were raised and reflected laterally. Another horizontal incision is given along the upper border of the clavicle. Platysma a subcutaneous muscle which is also reflected along with the cutaneous nerves lying in the superficial fascia of ...
... base of the mandible till the mastoid process and the skin flaps were raised and reflected laterally. Another horizontal incision is given along the upper border of the clavicle. Platysma a subcutaneous muscle which is also reflected along with the cutaneous nerves lying in the superficial fascia of ...
Skeletal System Notes-Part 2
... Growing bones must also widen as they lengthen. Osteoblasts in the periosteum add bone tissue to the external face of the diaphysis. Osteoclasts in the endosteum remove bone form the inner face of the diaphysis wall. Since these two processes occur at about the same rate, the circumference o ...
... Growing bones must also widen as they lengthen. Osteoblasts in the periosteum add bone tissue to the external face of the diaphysis. Osteoclasts in the endosteum remove bone form the inner face of the diaphysis wall. Since these two processes occur at about the same rate, the circumference o ...
Mediastinum
... Follow the right vagus nerve as it descends in the thorax, first lying posterolateral to the brachiocephalic artery, then lateral to the trachea and medial to the terminal part of the azygos vein. Note that it passes behind the root of the right lung and assists in the formation of the pulmonary pl ...
... Follow the right vagus nerve as it descends in the thorax, first lying posterolateral to the brachiocephalic artery, then lateral to the trachea and medial to the terminal part of the azygos vein. Note that it passes behind the root of the right lung and assists in the formation of the pulmonary pl ...
Posterior Leg Dissection
... above the other tissue which is the tendon of the internal Obturator b. Push your finger through into the pelvis to help you further define where the Tendon of the Internal Obturator c. Be careful as the pudendal vessels and nerve are in this area d. The Sacrospinal ligament is the extension of the ...
... above the other tissue which is the tendon of the internal Obturator b. Push your finger through into the pelvis to help you further define where the Tendon of the Internal Obturator c. Be careful as the pudendal vessels and nerve are in this area d. The Sacrospinal ligament is the extension of the ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.




![4-BLOOD SUPPLY OF HEART [Autosaved]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000391496_1-1cc69f66eb9ccd5c1082faab8bb4d060-300x300.png)













![[ PDF ] - journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007955894_2-e1c257efa5596d9bcec4f688fb06dda4-300x300.png)


