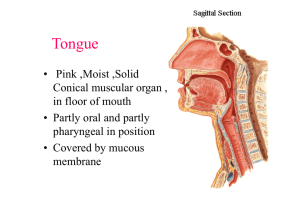
Tongue
... Root • Attached to hyoid and mandible and is in contact inferiorly with geniohyoid and mylohyoid muscles ...
... Root • Attached to hyoid and mandible and is in contact inferiorly with geniohyoid and mylohyoid muscles ...
Dr. H.A.Jaafar Al-Nahrain University
... ciliary muscle consists of meridional and circular fibers of smooth muscle innervated by parasympathetic fibers. It contracts to pull ciliary ring and ciliary processes, relaxing suspensory ligament of lens and allowing it to increase its convexity. ...
... ciliary muscle consists of meridional and circular fibers of smooth muscle innervated by parasympathetic fibers. It contracts to pull ciliary ring and ciliary processes, relaxing suspensory ligament of lens and allowing it to increase its convexity. ...
SO Poštulková Odborná angličtina 1
... hour about 1 billion cells in the human body must be replaced. The adult body is made up of 206 bones, 600 muscles, and 22 internal organs. The human body is made to stand erect, walk on two feet, use the arms to carry and lift, and has opposable thumbs (able to grasp). The head is composed of the h ...
... hour about 1 billion cells in the human body must be replaced. The adult body is made up of 206 bones, 600 muscles, and 22 internal organs. The human body is made to stand erect, walk on two feet, use the arms to carry and lift, and has opposable thumbs (able to grasp). The head is composed of the h ...
Chapter 2 Suffixes and Combining Forms Made Easy 1 2 Suffixes
... 2 Suffixes and Combining Forms Made Easy Student Objectives After completing Chapter 1, the student will be able to do the following: ...
... 2 Suffixes and Combining Forms Made Easy Student Objectives After completing Chapter 1, the student will be able to do the following: ...
Pharynx - mcstmf
... Ethmoid Sinuses The ethmoidal sinuses are anterior, middle, and posterior and they are contained within the ethmoid bone between the nose and the orbit. They are separated from the latter by a thin plate of bone so that infection can readily spread from the sinuses into the orbit. The anteri ...
... Ethmoid Sinuses The ethmoidal sinuses are anterior, middle, and posterior and they are contained within the ethmoid bone between the nose and the orbit. They are separated from the latter by a thin plate of bone so that infection can readily spread from the sinuses into the orbit. The anteri ...
Pfeiffer_5_IM_Chapter11
... 3. Sternoclavicular Joint Injuries. The SC joint is formed by the union of the proximal end of the clavicle and the manubrium of the sternum. The SC joint is supported by several ligaments (see Figure 11.3 on page 152) that include the joint capsule, the SC ligaments, the interclavicular and costocl ...
... 3. Sternoclavicular Joint Injuries. The SC joint is formed by the union of the proximal end of the clavicle and the manubrium of the sternum. The SC joint is supported by several ligaments (see Figure 11.3 on page 152) that include the joint capsule, the SC ligaments, the interclavicular and costocl ...
pelvis-and-fetal-skull2
... lies close to the maternal anal opening. Once the head is born, show the next step, restitution. Here the neck untwists and restitutes back through 45˚(1/8th of a circle) to the original position in the pelvis. Now show the external rotation. Rotation of the head by further 45˚(1/8th of a circle) in ...
... lies close to the maternal anal opening. Once the head is born, show the next step, restitution. Here the neck untwists and restitutes back through 45˚(1/8th of a circle) to the original position in the pelvis. Now show the external rotation. Rotation of the head by further 45˚(1/8th of a circle) in ...
Italian Journal of Anatomy and Embryology
... and pubic symphysis morphology (Reverte-Coma, 1991). Adult individuals were classified by age in either 25-40 year-old or 41-65 year-old. Only atlas vertebrae from adult skeletons with a clear-cut age and gender classification and complete cervical spine were used to measure vertebral TF anteroposte ...
... and pubic symphysis morphology (Reverte-Coma, 1991). Adult individuals were classified by age in either 25-40 year-old or 41-65 year-old. Only atlas vertebrae from adult skeletons with a clear-cut age and gender classification and complete cervical spine were used to measure vertebral TF anteroposte ...
Tongue
... Root • Attached to hyoid and mandible and is in contact inferiorly with geniohyoid and mylohyoid muscles ...
... Root • Attached to hyoid and mandible and is in contact inferiorly with geniohyoid and mylohyoid muscles ...
Chapter 22: The Shoulder Complex
... GIRD - Glenohumeral internal rotation deficit Other terms Superior labrum anterior posterior (SLAP) lesion - anteroposterior tear in the superior glenoid labrum Bankart lesion - a permanent anterior defect on the labrum following the detached labrum and capsule after dislocation Hill-Sachs Lesion - ...
... GIRD - Glenohumeral internal rotation deficit Other terms Superior labrum anterior posterior (SLAP) lesion - anteroposterior tear in the superior glenoid labrum Bankart lesion - a permanent anterior defect on the labrum following the detached labrum and capsule after dislocation Hill-Sachs Lesion - ...
SALC07 Biological Sciences Head & Neck 4: Normal Swallow
... Commonly divided into 4 stages: Pre-oral stage Oral stage (Oral preparation and oral ...
... Commonly divided into 4 stages: Pre-oral stage Oral stage (Oral preparation and oral ...
resting expiratory level
... • expanding the volume of the lungs. • Lung volume can be expanded: • In all three dimensions • With two primary muscle mechanisms ...
... • expanding the volume of the lungs. • Lung volume can be expanded: • In all three dimensions • With two primary muscle mechanisms ...
Lab 5 - APPENDICULAR SKELETON AND ARTICULATIONS
... You should also be able to explain the articulation of the skull with the vertebral column, using such terms as occiptal bone, occipital condyle, atlas, and axis, and how these articulations allow the head to rock and turn. (consult lab and lecture texts). ...
... You should also be able to explain the articulation of the skull with the vertebral column, using such terms as occiptal bone, occipital condyle, atlas, and axis, and how these articulations allow the head to rock and turn. (consult lab and lecture texts). ...
Our Human Body - Classroom Activities 1-13
... have recorded from Part 2 to write labels, and an explanation of how that body part works, around the outside of the body outline. The posters should be hung around the room. Part 4: Using their model-poster as a prop each group should prepare a short presentation about their body part or system, an ...
... have recorded from Part 2 to write labels, and an explanation of how that body part works, around the outside of the body outline. The posters should be hung around the room. Part 4: Using their model-poster as a prop each group should prepare a short presentation about their body part or system, an ...
FORM B
... c) lumen - the outside lining of an organ d) juxtaspinal - next to the spine e) idiopathic - on unknown cause 89) What is Dr. G's e-mail address? a) [email protected] b) [email protected] c) [email protected] d) [email protected] e) [email protected] 90) When i ...
... c) lumen - the outside lining of an organ d) juxtaspinal - next to the spine e) idiopathic - on unknown cause 89) What is Dr. G's e-mail address? a) [email protected] b) [email protected] c) [email protected] d) [email protected] e) [email protected] 90) When i ...
Summer 02
... d) auscultation - to listen to the sounds within the body e) atresia - congenital absence of a body opening 3) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) bifurcate - to split into two b) bradycardia - slow heart rate c) cicatrix - a scar d) claudication - a popping sound in a joint e) cephalagia - a headache 4) ...
... d) auscultation - to listen to the sounds within the body e) atresia - congenital absence of a body opening 3) Choose the INCORRECT match. a) bifurcate - to split into two b) bradycardia - slow heart rate c) cicatrix - a scar d) claudication - a popping sound in a joint e) cephalagia - a headache 4) ...
Posterior pharyngeal wall
... This extends from base of the skull to the hard palate and communicates anteriorly with the nasal cavity through the posterior nares (choanae). At the junction of the roof and posterior wall, there is a small of lymphoid tissue called the nasopharyngeal tonsil (adenoid). In the lateral wall there ar ...
... This extends from base of the skull to the hard palate and communicates anteriorly with the nasal cavity through the posterior nares (choanae). At the junction of the roof and posterior wall, there is a small of lymphoid tissue called the nasopharyngeal tonsil (adenoid). In the lateral wall there ar ...
Biology B - Introduction Lesson
... team. They form specialized groups called tissues. A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. Humans are made of four main kinds of tissues. They include epithelial tissue, nerve tissue, connective tissue, and muscle tissue. Groups of cells that work toge ...
... team. They form specialized groups called tissues. A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. Humans are made of four main kinds of tissues. They include epithelial tissue, nerve tissue, connective tissue, and muscle tissue. Groups of cells that work toge ...
Biology B - Introduction Lesson
... team. They form specialized groups called tissues. A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. Humans are made of four main kinds of tissues. They include epithelial tissue, nerve tissue, connective tissue, and muscle tissue. Groups of cells that work toge ...
... team. They form specialized groups called tissues. A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. Humans are made of four main kinds of tissues. They include epithelial tissue, nerve tissue, connective tissue, and muscle tissue. Groups of cells that work toge ...
SCROTUM & PROSTATE - Hastaneciyiz's Blog
... a. Attached to neck of urinary bladder b. Prostatic urethra enters middle of base close to anterior surface ...
... a. Attached to neck of urinary bladder b. Prostatic urethra enters middle of base close to anterior surface ...
scrotum & prostate - Orange Coast College
... a. Attached to neck of urinary bladder b. Prostatic urethra enters middle of base close to anterior surface ...
... a. Attached to neck of urinary bladder b. Prostatic urethra enters middle of base close to anterior surface ...
Sports Injuries in the Aging Athlete
... stress the need for a CLOSED MRI unless you are claustrophobic ...
... stress the need for a CLOSED MRI unless you are claustrophobic ...
Prenatal Development Timeline
... Telopharyngeal bodies Alimentary epithelium invades stroma of liver Alimentary epthelium proliferates in primordia of stomach, liver, and dorsal pancreas First part of pancreas Gastric portion of foregut elongates (25 to 28 somites) Hepatic primordium with abundant vascular plexus Omental bursa Orop ...
... Telopharyngeal bodies Alimentary epithelium invades stroma of liver Alimentary epthelium proliferates in primordia of stomach, liver, and dorsal pancreas First part of pancreas Gastric portion of foregut elongates (25 to 28 somites) Hepatic primordium with abundant vascular plexus Omental bursa Orop ...
Development of the mandible
... Meckel’s cartilage has a close, relationship to the mandibular nerve, at the junction between poximal and middle thirds, where the mandibular nerve divides into the lingual and inferior alveolar nerve. The lingual nerve passes forward, on the medial side of the cartilage, while the inferior alverola ...
... Meckel’s cartilage has a close, relationship to the mandibular nerve, at the junction between poximal and middle thirds, where the mandibular nerve divides into the lingual and inferior alveolar nerve. The lingual nerve passes forward, on the medial side of the cartilage, while the inferior alverola ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.