HSS 1010
... – Facing forward – Arms hanging at the sides – Palms facing forward and the thumbs outward ...
... – Facing forward – Arms hanging at the sides – Palms facing forward and the thumbs outward ...
Medial Cutaneous Nerve of Axilla
... The variant branch of the medial cord of brachial plexus encountered in the present investigation is a rare anatomical entity. It can be justifiably designated as the medial cutaneous nerve of the axilla (MCNAx) (root value- C8, 1) in the view of its distribution to the upper part of the medial wall ...
... The variant branch of the medial cord of brachial plexus encountered in the present investigation is a rare anatomical entity. It can be justifiably designated as the medial cutaneous nerve of the axilla (MCNAx) (root value- C8, 1) in the view of its distribution to the upper part of the medial wall ...
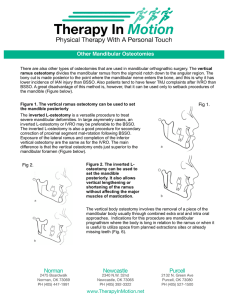
Other Mandibular Osteotomies
... Indications include leveling the occlusal plane, changing the anteroposterior position of the teeth, correcting asymmetries and changing the axial angulation of the teeth (Fig. 5). ...
... Indications include leveling the occlusal plane, changing the anteroposterior position of the teeth, correcting asymmetries and changing the axial angulation of the teeth (Fig. 5). ...
SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE NASOPHARYNX
... -travels through the parotid gland, passes between the ramus of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, passes either deep or superficial to the lateral pterygoid muscle and enters the ...
... -travels through the parotid gland, passes between the ramus of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, passes either deep or superficial to the lateral pterygoid muscle and enters the ...
Practical Class 4 BLOOD SUPPL BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE TRUNK
... The paired visceral branches of the thoracic aorta are the bronchial arteries which form part of the systemic circulation to the lungs (remind yourself of the distinction between the pulmonary and systemic circulations). In a previous practical you should have identified the bronchial arteries as th ...
... The paired visceral branches of the thoracic aorta are the bronchial arteries which form part of the systemic circulation to the lungs (remind yourself of the distinction between the pulmonary and systemic circulations). In a previous practical you should have identified the bronchial arteries as th ...
Upper Cross System Head Injuries & Neck Injuries
... – Arachnoid: The subarachnoid space exists between arachnoid and pia mater and is C.S.F. and passage for veins in the cranial cavity(veins in this area) – Pia Mater: a thin and “invisible” covering attached intimately to the neural structures ...
... – Arachnoid: The subarachnoid space exists between arachnoid and pia mater and is C.S.F. and passage for veins in the cranial cavity(veins in this area) – Pia Mater: a thin and “invisible” covering attached intimately to the neural structures ...
07 sacral plexus femoral and sciatic nerves
... experienced in the posterior aspect of the thigh, the posterior and lateral sides of the leg, and the lateral part of the foot. ...
... experienced in the posterior aspect of the thigh, the posterior and lateral sides of the leg, and the lateral part of the foot. ...
Fehrenbach: Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck
... Both statements are true. Muscles may differ in size and details of their attachments. Joints, vessels, nerves, glands, lymph nodes, fasciae, and spaces of an individual can vary in size, location, and even presence. Both statements are true. Muscles may differ in size and details of their attachmen ...
... Both statements are true. Muscles may differ in size and details of their attachments. Joints, vessels, nerves, glands, lymph nodes, fasciae, and spaces of an individual can vary in size, location, and even presence. Both statements are true. Muscles may differ in size and details of their attachmen ...
Document
... outer border of the first rib, and ends normally at the inferior border of teres major, where it becomes the brachial artery. At first deep, it subsequently becomes superficial, when it is covered only by the skin and fasciae/ pectoralis minor crosses it and so divides it into three parts which are ...
... outer border of the first rib, and ends normally at the inferior border of teres major, where it becomes the brachial artery. At first deep, it subsequently becomes superficial, when it is covered only by the skin and fasciae/ pectoralis minor crosses it and so divides it into three parts which are ...
incomplete formation of posterior cord of brachial plexus: a case report
... trunks.2 The cords branch out to supply the flexor and the extensor compartments of upper limb. The branches which arise from the roots and the trunks are seen above the clavicle and these are called as supraclavicular and the branches which arise mainly from the cords are seen below the clavicle he ...
... trunks.2 The cords branch out to supply the flexor and the extensor compartments of upper limb. The branches which arise from the roots and the trunks are seen above the clavicle and these are called as supraclavicular and the branches which arise mainly from the cords are seen below the clavicle he ...
lecture 8 elbow
... Ulnar collateral ligament (medial) – fan shaped Radial collateral ligaments (lateral) cord like Ulna nerve passes through the cubital tunnel ...
... Ulnar collateral ligament (medial) – fan shaped Radial collateral ligaments (lateral) cord like Ulna nerve passes through the cubital tunnel ...
Wrist & Hand - members.iinet.com.au
... caption: “At the lower end of the forearm there is an extensor retinaculum. Septa attach the retinaculum to the radius and ulna forming six osseofascial tunnels for the extensor tendons”. List the tendons corresponding to each of the numbered tunnels above. (Oct 00) What is the arrangement of struct ...
... caption: “At the lower end of the forearm there is an extensor retinaculum. Septa attach the retinaculum to the radius and ulna forming six osseofascial tunnels for the extensor tendons”. List the tendons corresponding to each of the numbered tunnels above. (Oct 00) What is the arrangement of struct ...
PEC Block for Breast Surgery - Is it a Useful Technique? Juan
... The pectoral nerves are the main branches of the brachial plexus that provide motor innervation to pectoral muscles, 2 principal nerves are described, Lateral Pectoral Nerve(LPN) and the Medial Pectoral nerve (MPN) The LPNarises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, and through it from the f ...
... The pectoral nerves are the main branches of the brachial plexus that provide motor innervation to pectoral muscles, 2 principal nerves are described, Lateral Pectoral Nerve(LPN) and the Medial Pectoral nerve (MPN) The LPNarises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, and through it from the f ...
pdf
... and finish in the anterior wall of the pharynx, where they innervate its muscles, as the inferior constrictor of the pharynx. On the other hand, the superior laryngeal nerve, which innervates the cricothyroid muscle, begins in the inferior part of the inferior vagus node, and runs inferiorly, anteri ...
... and finish in the anterior wall of the pharynx, where they innervate its muscles, as the inferior constrictor of the pharynx. On the other hand, the superior laryngeal nerve, which innervates the cricothyroid muscle, begins in the inferior part of the inferior vagus node, and runs inferiorly, anteri ...
Exam questions on human anatomy
... 12. Orbit: walls, foramina, fissures and canals and its contents. Connection to another region of the skull. 13. Bone nasal cavity: the walls, the nasal meatus and connection with paranasal sines and orbit. ...
... 12. Orbit: walls, foramina, fissures and canals and its contents. Connection to another region of the skull. 13. Bone nasal cavity: the walls, the nasal meatus and connection with paranasal sines and orbit. ...
SKULL ( NORMA LATERALIS )
... infratemporal surface of the greater wing of the sphenoid and small part of the squamous temporal bone. (b). Floor is open. (c ). Medial wall is formed by the lateral plate and the pyramidal process of the palatine bone. (d). Lateral wall is formed by the ramus of the mandible. The foramen ovale and ...
... infratemporal surface of the greater wing of the sphenoid and small part of the squamous temporal bone. (b). Floor is open. (c ). Medial wall is formed by the lateral plate and the pyramidal process of the palatine bone. (d). Lateral wall is formed by the ramus of the mandible. The foramen ovale and ...
ch07_answer_key - ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
... 20. The pelvic girdle connects the bones of the lower limbs to the axial skeleton. 21. The pelvic girdle, sacrum, and coccyx form the pelvis. 22. Each lower limb consists of a femur, tibia, fibula, patella, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges. 23. The femur and tibia articulate with each other at th ...
... 20. The pelvic girdle connects the bones of the lower limbs to the axial skeleton. 21. The pelvic girdle, sacrum, and coccyx form the pelvis. 22. Each lower limb consists of a femur, tibia, fibula, patella, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges. 23. The femur and tibia articulate with each other at th ...
Distribution of terminal nerve entry points to the flexor and extensor
... The motor points of the skeletal muscles, mainly of interest to anatomists and physiologists, have recently attracted much attention from researchers in the field of functional electrical stimulation. The muscle motor point has been defined as the entry point of the motor nerve branch into the epimy ...
... The motor points of the skeletal muscles, mainly of interest to anatomists and physiologists, have recently attracted much attention from researchers in the field of functional electrical stimulation. The muscle motor point has been defined as the entry point of the motor nerve branch into the epimy ...
the Nervous System
... part of the finger or thumb where the fingerprint is taken) and sides of the finger. There are two such nerves to each finger and thumb in the hand. Damage to this nerve reduces the sensation. If the nerve is not repaired, you will have a permanent numb patch on your finger, and there may be a tende ...
... part of the finger or thumb where the fingerprint is taken) and sides of the finger. There are two such nerves to each finger and thumb in the hand. Damage to this nerve reduces the sensation. If the nerve is not repaired, you will have a permanent numb patch on your finger, and there may be a tende ...
Everything you wanted to know to finish up on the leg and foot
... popliteal fossa to more distal calf (5-8 cm proximal to ankle) • Formed from – Communicating branch of lateral sural cutaneous nerve from: – Medial sural cutaneous nerve from: ...
... popliteal fossa to more distal calf (5-8 cm proximal to ankle) • Formed from – Communicating branch of lateral sural cutaneous nerve from: – Medial sural cutaneous nerve from: ...
The Nervous System Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves
... • 31 pair of nerves – each nerve forms from union of dorsal/ventral root of spinal cord segment & exits between vertebra at IVF • 8 pair cervical spinal nerves – 1st cervical nerve exits between occipital bone & C1, 8th cervical nerve exits the IVF between C7T1 • 12 pair thoracic spinal nerves • 5 p ...
... • 31 pair of nerves – each nerve forms from union of dorsal/ventral root of spinal cord segment & exits between vertebra at IVF • 8 pair cervical spinal nerves – 1st cervical nerve exits between occipital bone & C1, 8th cervical nerve exits the IVF between C7T1 • 12 pair thoracic spinal nerves • 5 p ...
The Skeleton: Part B
... • Orientation of articular facets locks lumbar vertebrae together so as to prevent rotation Sacrum and Coccyx • Sacrum • 5 fused vertebrae (S1–S5) • Forms posterior wall of pelvis • Articulates with L5 superiorly, and with auricular surfaces of the hip bones laterally ...
... • Orientation of articular facets locks lumbar vertebrae together so as to prevent rotation Sacrum and Coccyx • Sacrum • 5 fused vertebrae (S1–S5) • Forms posterior wall of pelvis • Articulates with L5 superiorly, and with auricular surfaces of the hip bones laterally ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.