CHAPTER 3
... 3-1B). Furthermore, capitular and costotransverse joints do not form. In other words, the head of such a cervical "rib" is fused to the body of the vertebra, and the "tubercle" of such a cervical "rib" is fused to the tip of the transverse process. The gap between the neck of this cervical costal pr ...
... 3-1B). Furthermore, capitular and costotransverse joints do not form. In other words, the head of such a cervical "rib" is fused to the body of the vertebra, and the "tubercle" of such a cervical "rib" is fused to the tip of the transverse process. The gap between the neck of this cervical costal pr ...
Anatomical Study of the Superior Gluteal Artery
... artery was classified into four types, the vertical, the horizontal, the descending, and the penetrating main branches. The average external diameter of the pedicle and the main perforator of the horizontal main branches were the largest (2.7 + 0.6 mm and 1.2 + 0.2 mm, respectively). These perforato ...
... artery was classified into four types, the vertical, the horizontal, the descending, and the penetrating main branches. The average external diameter of the pedicle and the main perforator of the horizontal main branches were the largest (2.7 + 0.6 mm and 1.2 + 0.2 mm, respectively). These perforato ...
OSU Anatomy Outline
... OSU Anatomy of the Foot CD Text OSU Anatomy of the Foot CD Text.....................................................................10 Introductory Information ......................................................................................10 Course Syllabus ................................... ...
... OSU Anatomy of the Foot CD Text OSU Anatomy of the Foot CD Text.....................................................................10 Introductory Information ......................................................................................10 Course Syllabus ................................... ...
Bilateral asymmetry of the highly bifurcated brachial artery variation
... common, the bilateral occurrence of different forms is rare, as mentioned above. If we take into account that the observed and described bifurcation Types (II and III) are much less common than Type I, their bilateral occurrence might be considered as extremely rare. According to the current embryol ...
... common, the bilateral occurrence of different forms is rare, as mentioned above. If we take into account that the observed and described bifurcation Types (II and III) are much less common than Type I, their bilateral occurrence might be considered as extremely rare. According to the current embryol ...
Acland`s DVD Atlas of Human Anatomy Transcript for Volume 3
... The upper articular processes of lumbar vertebra face inward, the lower ones face outward. Because of this arrangement, there’s almost no rotation between lumbar vertebrae. The movements that can occur in the lumbar spine are flexion, and extension, and lateral flexion to either side. ...
... The upper articular processes of lumbar vertebra face inward, the lower ones face outward. Because of this arrangement, there’s almost no rotation between lumbar vertebrae. The movements that can occur in the lumbar spine are flexion, and extension, and lateral flexion to either side. ...
02 – Bony Anatomy of the Skull
... Temporal Bone: Supine; locate the mastoid process by placing your fingers behind the ear lobe. The zygomatic arch can be palpated by placing your fingers anterior to the external auditory meatus. Palpate anteriorly along the arch with your finger and thumb. The flat squamous portion can be palpated ...
... Temporal Bone: Supine; locate the mastoid process by placing your fingers behind the ear lobe. The zygomatic arch can be palpated by placing your fingers anterior to the external auditory meatus. Palpate anteriorly along the arch with your finger and thumb. The flat squamous portion can be palpated ...
Knee Replacement Surgery
... The knee is a vulnerable joint that bears a great deal of stress from everyday activities such as lifting and kneeling, and from high-impact activities such as jogging and aerobics. The knee is formed by the following parts: tibia - shin bone or larger bone of the lower leg. femur - thighbone or ...
... The knee is a vulnerable joint that bears a great deal of stress from everyday activities such as lifting and kneeling, and from high-impact activities such as jogging and aerobics. The knee is formed by the following parts: tibia - shin bone or larger bone of the lower leg. femur - thighbone or ...
External Acoustic Meatus.
... relationship to the middle ear. The facial nerve comprises a larger part, which supplies the muscles of facial expression, and a smaller part termed the nervus intermedius, which contains taste fibers for the anterior two thirds of the tongue, secretomotor fibers for the lacrimal and salivary glands ...
... relationship to the middle ear. The facial nerve comprises a larger part, which supplies the muscles of facial expression, and a smaller part termed the nervus intermedius, which contains taste fibers for the anterior two thirds of the tongue, secretomotor fibers for the lacrimal and salivary glands ...
Radial Artery
... into dorsal metacarpal veins, which unite to form a dorsal venous arch or network. Dorsal venous network lies on the dorsum of the hand, in the subcutanous tissue, proximal to the metacarpophalangeal joints Drains into the cephalic vein laterally, and basilic vein medially ...
... into dorsal metacarpal veins, which unite to form a dorsal venous arch or network. Dorsal venous network lies on the dorsum of the hand, in the subcutanous tissue, proximal to the metacarpophalangeal joints Drains into the cephalic vein laterally, and basilic vein medially ...
Mollusks and Segmented Worms
... • Eggs and sperm are released at the same time into the water where external fertilization takes place. ...
... • Eggs and sperm are released at the same time into the water where external fertilization takes place. ...
NBCE Mock Board Questions Spinal Anatomy
... The following statements concerning the spinal cord are correct EXCEPT: A. The anterior and posterior gray columns on the two sides are united by a gray commissure. B. The terminal ventricle is the expanded lower end of the central canal. C. The larger nerve cell bodies in the anterior gray horns gi ...
... The following statements concerning the spinal cord are correct EXCEPT: A. The anterior and posterior gray columns on the two sides are united by a gray commissure. B. The terminal ventricle is the expanded lower end of the central canal. C. The larger nerve cell bodies in the anterior gray horns gi ...
Ankle_Foot
... Included in the joint are the medial and lateral malleolus of tibia (med) and fibula (lat) that grip the talus firmly – Don’t forget distal Tibio-Fibular Joint and its importance Note position of medial + lateral malleolus Dorsiflexion (25 degrees) and plantarflexion (50) only ...
... Included in the joint are the medial and lateral malleolus of tibia (med) and fibula (lat) that grip the talus firmly – Don’t forget distal Tibio-Fibular Joint and its importance Note position of medial + lateral malleolus Dorsiflexion (25 degrees) and plantarflexion (50) only ...
Kinesiology of the Upper Extremity
... Undergoes flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, and medial/lateral rotation Abduction occurs with lateral rotation and flexion also occurs with simultaneous rotation. The direction of this rotation is unclear, but these rotations are necessary to help preserve the subcromial space. Translation acc ...
... Undergoes flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, and medial/lateral rotation Abduction occurs with lateral rotation and flexion also occurs with simultaneous rotation. The direction of this rotation is unclear, but these rotations are necessary to help preserve the subcromial space. Translation acc ...
Supplementary Text S2.
... The positions of the seven areas sensitive to visual field location found in each subject are described below in relation to sulcal and gyral landmarks on the undistorted cortical surface (See also Figure S5). MIPS ...
... The positions of the seven areas sensitive to visual field location found in each subject are described below in relation to sulcal and gyral landmarks on the undistorted cortical surface (See also Figure S5). MIPS ...
Read the coroner`s report on the 2012 dog attack death of a 30
... INJURY L is a group of three horizontally oriented elliptical full-thickness lacerations surrounded by erythema that are approximately 1 1/2 inches above the lateral aspect of the right eyebrow. From superior to inferior they are 0.3 cm, 0.2 cm and 0.3 cm. They are each separated by approximately 0. ...
... INJURY L is a group of three horizontally oriented elliptical full-thickness lacerations surrounded by erythema that are approximately 1 1/2 inches above the lateral aspect of the right eyebrow. From superior to inferior they are 0.3 cm, 0.2 cm and 0.3 cm. They are each separated by approximately 0. ...
Functional Anatomy of the Shoulder Complex
... overriding the acromion (Fig. 2). The joint is important because it contributes to total arm movement in addition to transmitting forces between the clavicle and the acromion.412 The acromioclavicular joint has a capsule and a superior acromioclavicular ligament that strengthen the upper aspect of t ...
... overriding the acromion (Fig. 2). The joint is important because it contributes to total arm movement in addition to transmitting forces between the clavicle and the acromion.412 The acromioclavicular joint has a capsule and a superior acromioclavicular ligament that strengthen the upper aspect of t ...
The small intestine
... - The long free edge of the fold encloses the mobile intestine. - The short root of the fold is continuous with the parietal peritoneum on the posterior abdominal wall - Along a line that extends downward and to the right from the left side of the second lumbar vertebra to the region of the right sa ...
... - The long free edge of the fold encloses the mobile intestine. - The short root of the fold is continuous with the parietal peritoneum on the posterior abdominal wall - Along a line that extends downward and to the right from the left side of the second lumbar vertebra to the region of the right sa ...
Jejunum and Ileum Location and Description
... - The long free edge of the fold encloses the mobile intestine. - The short root of the fold is continuous with the parietal peritoneum on the posterior abdominal wall - Along a line that extends downward and to the right from the left side of the second lumbar vertebra to the region of the right sa ...
... - The long free edge of the fold encloses the mobile intestine. - The short root of the fold is continuous with the parietal peritoneum on the posterior abdominal wall - Along a line that extends downward and to the right from the left side of the second lumbar vertebra to the region of the right sa ...
19-Pleura & Lungs
... vertebral bodies & back of sternum 2. Diaphragmatic pleura Covers the thoracic surface of the diaphragm ...
... vertebral bodies & back of sternum 2. Diaphragmatic pleura Covers the thoracic surface of the diaphragm ...
Clinical and Functional Anatomy of the Urethral Sphincter
... smooth muscle of the IUS and these striated muscles surrounding the IUS acts to control the removal of fluids from the body. ...
... smooth muscle of the IUS and these striated muscles surrounding the IUS acts to control the removal of fluids from the body. ...
Lower limb muscle activity during gait
... High-heeled shoes are prominent in today’s society and are worn on special occasions as well as with more casual outfits. Certain known kinematic changes occur when walking in shoes with high heels vs. lower heels as well as changes in the centre of mass and a reduction in the base of support. Altho ...
... High-heeled shoes are prominent in today’s society and are worn on special occasions as well as with more casual outfits. Certain known kinematic changes occur when walking in shoes with high heels vs. lower heels as well as changes in the centre of mass and a reduction in the base of support. Altho ...
Lecture 16: Wrist and Hand
... o if damaged: weak abduction at shoulder joint, sensory loss, atrophy o injury can happen during surgery Musculocutaneous: flexors of arm o well protected, only likely to get injured w/ surgery o functional loss: weak flexion at elbow joint (anterior compartment), minimal sensory loss (because bec ...
... o if damaged: weak abduction at shoulder joint, sensory loss, atrophy o injury can happen during surgery Musculocutaneous: flexors of arm o well protected, only likely to get injured w/ surgery o functional loss: weak flexion at elbow joint (anterior compartment), minimal sensory loss (because bec ...
By: Gary Gray, PT
... - FMR facilitating superior segment right rotation and inferior segment left rotation Discussion of FMR progressions with same position as above, with left hand driving in the transverse plane, with FMR facilitating lateral flexion to the left and rotation to the right. Getting Type I and Type II mo ...
... - FMR facilitating superior segment right rotation and inferior segment left rotation Discussion of FMR progressions with same position as above, with left hand driving in the transverse plane, with FMR facilitating lateral flexion to the left and rotation to the right. Getting Type I and Type II mo ...
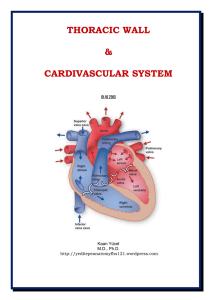
Dr.Kaan Yücel yeditepeanatomyfhs121.wordpress.com Thoracic
... The thorax is the part of the body between the neck and abdomen. Posterior surface is formed by the 12 thoracic vertebræ and the posterior parts of the ribs. Anterior surface is formed by the sternum and costal cartilages. Lateral surfaces are formed by the ribs, separated from each other by the int ...
... The thorax is the part of the body between the neck and abdomen. Posterior surface is formed by the 12 thoracic vertebræ and the posterior parts of the ribs. Anterior surface is formed by the sternum and costal cartilages. Lateral surfaces are formed by the ribs, separated from each other by the int ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.