Week 2 Notes - UWI St. Augustine
... • During development the diaphragm is displaced inferiorly to the lower thoracic aperture. It drags the phrenic nerve along with it. Referred Pain: Chest pain, lung pain, or pain in the diaphragm may be felt in the left shoulder. This is because the sensory origins of the phrenic nerve (C3-C5) also ...
... • During development the diaphragm is displaced inferiorly to the lower thoracic aperture. It drags the phrenic nerve along with it. Referred Pain: Chest pain, lung pain, or pain in the diaphragm may be felt in the left shoulder. This is because the sensory origins of the phrenic nerve (C3-C5) also ...
Structures of the lymphatic system
... Nodes filter lymph fluid of harmful substances Also produce lymphocytes (WBC) and antibiotics Swollen lymph nodes may mean there is a disease process Short tube that receives all of the purified lymph from the right side of the head and neck, right chest, and right arm Empties into the right subclav ...
... Nodes filter lymph fluid of harmful substances Also produce lymphocytes (WBC) and antibiotics Swollen lymph nodes may mean there is a disease process Short tube that receives all of the purified lymph from the right side of the head and neck, right chest, and right arm Empties into the right subclav ...
ch07-axial-skeleton
... muscles and for muscles of the neck and pharynx The hyoid bone also helps to keep the larynx (voice box) open at all times Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ...
... muscles and for muscles of the neck and pharynx The hyoid bone also helps to keep the larynx (voice box) open at all times Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ...
Sacral Base L + R
... not follow an injury Direct stimuli initiates trigger points by causing abnormal, continuous input from the muscle spindle, leading to reflex tension in the associated muscle ...
... not follow an injury Direct stimuli initiates trigger points by causing abnormal, continuous input from the muscle spindle, leading to reflex tension in the associated muscle ...
Chapter 9 Test Review
... Give examples of chemoreceptors Describe and give examples of baroreceptors Know the location of chemoreceptors Describe olfactory glands Know the primary taste sensations Know the location of the hearing receptors Know the location and function of the lacrimal glands Know the function (direction of ...
... Give examples of chemoreceptors Describe and give examples of baroreceptors Know the location of chemoreceptors Describe olfactory glands Know the primary taste sensations Know the location of the hearing receptors Know the location and function of the lacrimal glands Know the function (direction of ...
Document
... •Distal: farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk ...
... •Distal: farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk ...
Objectives
... auditory meatus, behind the ramus of the mandible and in front of sternocleidomastoid muscle. Parts of the glands: The facial nerve divides the gland into superficial and deep lobes. Parotid duct: - It emerges from the anterior border of the gland and passes over the lateral surface of masseter. - I ...
... auditory meatus, behind the ramus of the mandible and in front of sternocleidomastoid muscle. Parts of the glands: The facial nerve divides the gland into superficial and deep lobes. Parotid duct: - It emerges from the anterior border of the gland and passes over the lateral surface of masseter. - I ...
Powerpoint - Zill Anatomy Web Pages
... layers -infection from head (tonsillitis) can spread to mediastinum ...
... layers -infection from head (tonsillitis) can spread to mediastinum ...
Chapter 8 PowerPoint - Hillsborough Community College
... • Rotation: turning of bone around its own long axis, toward midline or away from it – Medial: rotation toward midline – Lateral: rotation away from midline – Examples • Rotation between C1 and C2 vertebrae • Rotation of humerus and femur ...
... • Rotation: turning of bone around its own long axis, toward midline or away from it – Medial: rotation toward midline – Lateral: rotation away from midline – Examples • Rotation between C1 and C2 vertebrae • Rotation of humerus and femur ...
Chapter 5 The Human Body
... – Full distance that a joint can be moved – Flexion • Moving a distal part of an extremity toward the trunk ...
... – Full distance that a joint can be moved – Flexion • Moving a distal part of an extremity toward the trunk ...
ANATOMY 1. Muscle contraction is initiated by binding of calcium
... Questions 9-11. A 5 year-old male was brought to a hospital because of pain and swelling of the right arm. On examination, the patient’s right arm was very edematous, with a noticeable hematoma on its posterior aspect. The wrist joint immediately assumed a flexed position that the patient was unable ...
... Questions 9-11. A 5 year-old male was brought to a hospital because of pain and swelling of the right arm. On examination, the patient’s right arm was very edematous, with a noticeable hematoma on its posterior aspect. The wrist joint immediately assumed a flexed position that the patient was unable ...
Significance of anatomical variations of the lateral circumflex femoral
... The blood supply of the TFL flap has been described as being through the lateral circumflex artery (LCFA) of the profunda femoris artery (PFA) [13, 15, 28]. LCFA is routinely a lateral branch of PFA, near the root. It inclines between the anterior and the posterior division of the femoral nerve, pos ...
... The blood supply of the TFL flap has been described as being through the lateral circumflex artery (LCFA) of the profunda femoris artery (PFA) [13, 15, 28]. LCFA is routinely a lateral branch of PFA, near the root. It inclines between the anterior and the posterior division of the femoral nerve, pos ...
Grade Five Big Idea 14 Human Body 2014 T. Guide.tx
... Ask: What do know about the organs in the human body and their functions? Click on the hyperlink Body a Building and explore organs in the body systems. Ask how do think organs in the body form? ...
... Ask: What do know about the organs in the human body and their functions? Click on the hyperlink Body a Building and explore organs in the body systems. Ask how do think organs in the body form? ...
File
... Anal Sphincters: part of circular muscle coat and has an involuntary internal sphincter & a voluntary external sphincter. A. Internal sphincter: is formed from a thickening of smooth muscle of circular coat at upper end of anal canal. It is enclosed by a sheath of striped muscle that forms voluntary ...
... Anal Sphincters: part of circular muscle coat and has an involuntary internal sphincter & a voluntary external sphincter. A. Internal sphincter: is formed from a thickening of smooth muscle of circular coat at upper end of anal canal. It is enclosed by a sheath of striped muscle that forms voluntary ...
Document
... • The bones that create the architecture of the thoracic cage include the sternum, the ribs, and the thoracic vertebrae. • The sternum: The sternum is a flat, long bone that forms the medial and anterior part of the thoracic cage. It has three parts: – Manubrium: The manubrium forms the upper part o ...
... • The bones that create the architecture of the thoracic cage include the sternum, the ribs, and the thoracic vertebrae. • The sternum: The sternum is a flat, long bone that forms the medial and anterior part of the thoracic cage. It has three parts: – Manubrium: The manubrium forms the upper part o ...
Foot/Ankle - ProvidencePanthersSportsMedicine
... As foot flattens, plantar fascia is stretched & pulled where it attaches to calcaneus calcaneus reacts by forming spur of bony material ...
... As foot flattens, plantar fascia is stretched & pulled where it attaches to calcaneus calcaneus reacts by forming spur of bony material ...
Chapter 5 Study Guide
... 9. Shoulder girdle bone that articulates anteriorly with the sternum 10. Socket in the scapula for the arm bone 11. Process above the glenoid cavity that permits muscle attachment 12. Commonly called the collarbone 13. Distal medial process of the humerus; joins the ulna 14. Medial bone of the forea ...
... 9. Shoulder girdle bone that articulates anteriorly with the sternum 10. Socket in the scapula for the arm bone 11. Process above the glenoid cavity that permits muscle attachment 12. Commonly called the collarbone 13. Distal medial process of the humerus; joins the ulna 14. Medial bone of the forea ...
Digestive System
... It’s the longest porCon of the gland and runs from the neck to the tail. It’s slightly triangular in cross secCon, becoming thinner and less broad toward the tail. The Anterosuperior surface is per ...
... It’s the longest porCon of the gland and runs from the neck to the tail. It’s slightly triangular in cross secCon, becoming thinner and less broad toward the tail. The Anterosuperior surface is per ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 25 Martini lecture Outline
... becomes thick and round and is called the round ligament The round ligament used to be the fetal umbilical vein The falciform ligament spreads on the surface of the liver attaching to the inferior side of the diaphragm This spreading ligament is called the coronary ligament ...
... becomes thick and round and is called the round ligament The round ligament used to be the fetal umbilical vein The falciform ligament spreads on the surface of the liver attaching to the inferior side of the diaphragm This spreading ligament is called the coronary ligament ...
1) The Larynx - Dr. Hiwa Embryology of Larynx Anatomy of the Larynx
... o Open & close glottis: (lateral & post. cricoarytenoid muscles, transverse & oblique arytenoids). o Control the tension of vocal ligaments: (thyroarytenoids, vocalis and cricothyroids). o Alter the shape of the inlet of the larynx: (aryepiglotticus and the thyroepiglotticus). o Except transverse ar ...
... o Open & close glottis: (lateral & post. cricoarytenoid muscles, transverse & oblique arytenoids). o Control the tension of vocal ligaments: (thyroarytenoids, vocalis and cricothyroids). o Alter the shape of the inlet of the larynx: (aryepiglotticus and the thyroepiglotticus). o Except transverse ar ...
Navigating Anorectal Anatomy
... • Circular layer of rectum becomes internal anal sphincter • Longitudinal layer of rectum becomes intersphincteric fascial plane • External anal sphincter is composed of three parts • Levator ani contributes puborectalis, which is continuous with deep external anal sphincter • Tube within a tube • I ...
... • Circular layer of rectum becomes internal anal sphincter • Longitudinal layer of rectum becomes intersphincteric fascial plane • External anal sphincter is composed of three parts • Levator ani contributes puborectalis, which is continuous with deep external anal sphincter • Tube within a tube • I ...
Planul
... LESSON 2. The shoulder (pectoral) girdle region. Infraclavicular, deltoid, scapular, axillary regions and shoulder joint. Surgical anatomy of vessels and nerves. Spaces, ways of spreading of pus, evolution of phlegmons and hematomas (incisions performed to drain collections). Collateral blood circul ...
... LESSON 2. The shoulder (pectoral) girdle region. Infraclavicular, deltoid, scapular, axillary regions and shoulder joint. Surgical anatomy of vessels and nerves. Spaces, ways of spreading of pus, evolution of phlegmons and hematomas (incisions performed to drain collections). Collateral blood circul ...
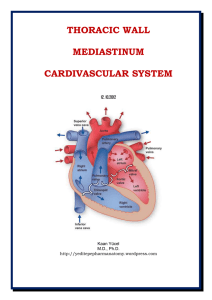
Dr.Kaan Yücel yeditepepharmanatomy.wordpress.com Thoracic
... from the body through the superior vena cava (SVC) and inferior vena cava (IVC) and pumps it through the pulmonary trunk and arteries to the lungs for oxygenation. The left side of the heart (left heart) receives welloxygenated (arterial) blood from the lungs through the pulmonary veins and pumps it ...
... from the body through the superior vena cava (SVC) and inferior vena cava (IVC) and pumps it through the pulmonary trunk and arteries to the lungs for oxygenation. The left side of the heart (left heart) receives welloxygenated (arterial) blood from the lungs through the pulmonary veins and pumps it ...
Right sided Colectomies: A stepwise approach
... region. Step IV. The hand port is inserted trough the Pfannenstiehl. The surgeon inserts the left hand in the hand port. Optics are inserted trough the umbilical port. Using the right hand, an ultrasonic dissector is introduced trough the epigastric port. Step V. At the level of the pyloric muscle, ...
... region. Step IV. The hand port is inserted trough the Pfannenstiehl. The surgeon inserts the left hand in the hand port. Optics are inserted trough the umbilical port. Using the right hand, an ultrasonic dissector is introduced trough the epigastric port. Step V. At the level of the pyloric muscle, ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.