Vertebral Column and Thoracic Cage Lab
... 15. The joint between a coxa of the pelvis and the sacrum is called the _______________ joint. 16. The upper, anterior margin of the sacrum that projects forward is called the ________________. 17. An opening called the _________________ exists at the tip of the sacral canal. ...
... 15. The joint between a coxa of the pelvis and the sacrum is called the _______________ joint. 16. The upper, anterior margin of the sacrum that projects forward is called the ________________. 17. An opening called the _________________ exists at the tip of the sacral canal. ...
PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE POP
... The vagina can be anatomically divided into the proximal, middle, and distal regions. The proximal segment, called the vault or cuff, is stabilized by the parametrium, which includes the cardinal and uterosacral ligaments. Uterine and vault prolapse are both associated with damage to these support ...
... The vagina can be anatomically divided into the proximal, middle, and distal regions. The proximal segment, called the vault or cuff, is stabilized by the parametrium, which includes the cardinal and uterosacral ligaments. Uterine and vault prolapse are both associated with damage to these support ...
3rd Nine Weeks 2016-2017
... posterior. Obj: Identify different muscles of the anterior and posterior aspect of the cat. Lesson: Lab- Cat DissectionStudy their cat for the Cat Practical ...
... posterior. Obj: Identify different muscles of the anterior and posterior aspect of the cat. Lesson: Lab- Cat DissectionStudy their cat for the Cat Practical ...
term 2 answers to questions - Hatzalah of Miami-Dade
... 21. III and IV run in the lateral wall and VI runs within the sinus lying on the lateral aspect of the internal carotid artery. ...
... 21. III and IV run in the lateral wall and VI runs within the sinus lying on the lateral aspect of the internal carotid artery. ...
13-The anal triangle2008-03
... It is the region of the trunk inferior to the pelvic diaphragm (levator ani & coccygei) ...
... It is the region of the trunk inferior to the pelvic diaphragm (levator ani & coccygei) ...
Investigating Animal Diversity
... member of the phylum Cnidaria. If it is bilaterally symmetric, as most animals are, more information is required to narrow down the choices. Assuming your unknown is a bilaterally symmetrical animal, you will now need information about its embryological development. The previous lab topic shows the ...
... member of the phylum Cnidaria. If it is bilaterally symmetric, as most animals are, more information is required to narrow down the choices. Assuming your unknown is a bilaterally symmetrical animal, you will now need information about its embryological development. The previous lab topic shows the ...
24. para.lymph1242010-10-01 03:411.5 MB
... nasal part of the pharynx. 2-The greater; lesser palatine ns. They supply the mucous membrane of the palate, tonsil and nasal cavity. 3- The nasal & nasopalatine ns: They enter the nose through the sphenopalatine foramen and supply the mucous membrane and glands of the nasal cavity. ...
... nasal part of the pharynx. 2-The greater; lesser palatine ns. They supply the mucous membrane of the palate, tonsil and nasal cavity. 3- The nasal & nasopalatine ns: They enter the nose through the sphenopalatine foramen and supply the mucous membrane and glands of the nasal cavity. ...
Knee Injuries
... -Program will be created by Physical Therapist or Athletic Trainer -Depending on level of sprain, recovery may take 2 weeks to several months ...
... -Program will be created by Physical Therapist or Athletic Trainer -Depending on level of sprain, recovery may take 2 weeks to several months ...
An Overview - Association of Surgical Technologists
... ninth costal cartilage and continues downward and ...
... ninth costal cartilage and continues downward and ...
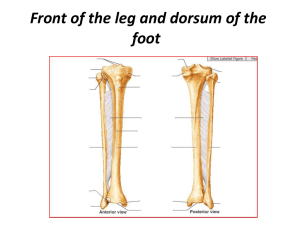
Front of the leg and dorsum of the foot
... both muscles, then it descend between it and extensor digitorum longus m. pierce the deep fascia in the distal 1/3 of the leg and divides into medial and intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerves. ...
... both muscles, then it descend between it and extensor digitorum longus m. pierce the deep fascia in the distal 1/3 of the leg and divides into medial and intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerves. ...
INSYS 300 -
... Intelligent Reasoning! Knowledge-base Ontology Semantic Networks Uncertainty(impreciseness)-handling ...
... Intelligent Reasoning! Knowledge-base Ontology Semantic Networks Uncertainty(impreciseness)-handling ...
lower_ext_ppt.aug_o7
... 1. To teach clinically relevant gross anatomy 2. To make it easier to understand gross anatomy 3. To introduce a clinical lexicon ...
... 1. To teach clinically relevant gross anatomy 2. To make it easier to understand gross anatomy 3. To introduce a clinical lexicon ...
The Respiratory System
... • About 2.5 cm in diameter • Contains tracheal cartilage • Each cartilage ring is actually C-shaped, not a complete ring • Connecting one cartilage ring to another are annular ligaments ...
... • About 2.5 cm in diameter • Contains tracheal cartilage • Each cartilage ring is actually C-shaped, not a complete ring • Connecting one cartilage ring to another are annular ligaments ...
HuP 191B – Advanced Assessment of Upper Extremity Injuries
... – Median nerve from lateral and medial cord – Ulnar nerve from medial cord – Axillary and radial nerves from posterior cord ...
... – Median nerve from lateral and medial cord – Ulnar nerve from medial cord – Axillary and radial nerves from posterior cord ...
CS sacrum TOMF 2013 - Tucson Osteopathic Medical Foundation
... GLUTEUS MINIMUS This is not found behind as I had thought at first, but about two and a half inches down and out from the anterior superior spine of the ilium. This and the gluteus medius are common causes for pain on the lateral part of the pelvis, after a long drive in a car in a sitting position ...
... GLUTEUS MINIMUS This is not found behind as I had thought at first, but about two and a half inches down and out from the anterior superior spine of the ilium. This and the gluteus medius are common causes for pain on the lateral part of the pelvis, after a long drive in a car in a sitting position ...
anatomy of pleura
... The parietal and visceral layers are separated from one another by a slitlike space called pleural cavity Clinicians use the term pleural space instead of the anatomic term pleural cavity Pleural cavity contains thin film of tissue fluid called pleural fluid Fluid permits the two layers to move on e ...
... The parietal and visceral layers are separated from one another by a slitlike space called pleural cavity Clinicians use the term pleural space instead of the anatomic term pleural cavity Pleural cavity contains thin film of tissue fluid called pleural fluid Fluid permits the two layers to move on e ...
ANATOMY OF FEMALE GENITAL ORGANS
... exocervix and the endocervix is the squamocolumnar junction, which is visible through a colposcope. The squamocolumnar junction is the most common primary site within the cervix. The cervix projects into the vagina, and the circular trough formed at the upper end of the vagina around the cervix is t ...
... exocervix and the endocervix is the squamocolumnar junction, which is visible through a colposcope. The squamocolumnar junction is the most common primary site within the cervix. The cervix projects into the vagina, and the circular trough formed at the upper end of the vagina around the cervix is t ...
Chapter 8: The Appendicular Skeleton
... Cup-shaped, lateral depression Articulates with humerus Forms shoulder joint ...
... Cup-shaped, lateral depression Articulates with humerus Forms shoulder joint ...
The plantaris muscle: anatomy, injury, imaging, and treatment Andreo A. Spina, DC*
... distal hand of the practitioner covers the heel while the forearm is applied against the plantar aspect of the foot, allowing a simultaneous resistance to plantarflexion of the foot and flexion of the knee. The muscle is palpated in the popliteal fossa, medial and superior to the lateral head of the ...
... distal hand of the practitioner covers the heel while the forearm is applied against the plantar aspect of the foot, allowing a simultaneous resistance to plantarflexion of the foot and flexion of the knee. The muscle is palpated in the popliteal fossa, medial and superior to the lateral head of the ...
Embryology Respiratory System د.ايناس فاضل كاظم
... In the head/neck region, the pharynx forms a major arched cavity within the phrayngeal arches. The lungs go through 4 distinct histological phases of development and in late fetal development thyroid hormone, respiratory motions and amniotic fluid are thought to have a role in lung maturation. The t ...
... In the head/neck region, the pharynx forms a major arched cavity within the phrayngeal arches. The lungs go through 4 distinct histological phases of development and in late fetal development thyroid hormone, respiratory motions and amniotic fluid are thought to have a role in lung maturation. The t ...
Ultrasound of Brachial Plexus : Technique, Mapping and
... The fifth and sixth rami unite at the lateral border of scalenus medius as the upper trunk; the eighth cervical and first thoracic rami join behind scalenus anterior as the lower trunk; the seventh cervical ramus becomes the middle trunk. The three trunks incline laterally, and either just above or ...
... The fifth and sixth rami unite at the lateral border of scalenus medius as the upper trunk; the eighth cervical and first thoracic rami join behind scalenus anterior as the lower trunk; the seventh cervical ramus becomes the middle trunk. The three trunks incline laterally, and either just above or ...
lateral nasal wall comprising narrow, mucosal lined channels and
... This nasal cycle is a normal physiological mechanism that is present to some extent in all of us but noticed only by some people. Nasal epithelium is a pseudostratifi ed columnar ciliated mucous membrane continuous throughout the sinuses. The epithelium contains goblet cells, which produce mucus, an ...
... This nasal cycle is a normal physiological mechanism that is present to some extent in all of us but noticed only by some people. Nasal epithelium is a pseudostratifi ed columnar ciliated mucous membrane continuous throughout the sinuses. The epithelium contains goblet cells, which produce mucus, an ...
The Skeletal System - αριστοτελειο πανεπιστημιο θεσσαλονικης
... The wrist, or carpus, consists of 8 small bones called the carpal bones that are tightly bound by ligaments. These bone are arranged in two rows of four bones each. The top row (the row closest to the forearm) from the lateral (thumb) side to the medial side contains the scaphoid, lunate, triquetral ...
... The wrist, or carpus, consists of 8 small bones called the carpal bones that are tightly bound by ligaments. These bone are arranged in two rows of four bones each. The top row (the row closest to the forearm) from the lateral (thumb) side to the medial side contains the scaphoid, lunate, triquetral ...
File
... •Distal: farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk ...
... •Distal: farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk ...
Anatomical terminology

Anatomical terminology is used by anatomists and zoologists, in scientific journals, textbooks, and by doctors and other health professionals. Anatomical terminology contains a variety of unique and possibly confusing terms to describe the anatomical location and action of different structures. By using this terminology, anatomists hope to be more precise and reduce errors and ambiguity. For example, is a scar ""above the wrist"" located on the forearm two or three inches away from the hand? Or is it at the base of the hand? Is it on the palm-side or back-side? By using precise anatomical terminology, ambiguity is eliminated.Anatomical terms derive from Ancient Greek and Latin words, and because these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the meaning of their words does not change. The current international standard is the Terminologia Anatomica.