FastGene Taq DNA Polymerase
... Taq DNA polymerase in an existing protocol. The final MgCl2 concentration may need to be optimized to account for differences in buffer formulation. • Both Buffer A and Buffer B contain MgCl2 at a final concentration of 1.5 mM. • Buffer A is recommended as first approach and for applications requi ...
... Taq DNA polymerase in an existing protocol. The final MgCl2 concentration may need to be optimized to account for differences in buffer formulation. • Both Buffer A and Buffer B contain MgCl2 at a final concentration of 1.5 mM. • Buffer A is recommended as first approach and for applications requi ...
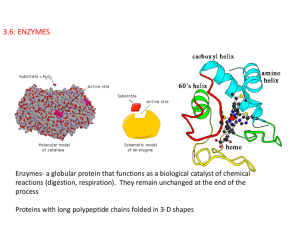
Enzymes: Introduction notes
... – for substrate acted upon – for reaction catalyzed Example: Proteases are a whole class of enzymes that all catalyze hydrolysis of peptide bonds: ...
... – for substrate acted upon – for reaction catalyzed Example: Proteases are a whole class of enzymes that all catalyze hydrolysis of peptide bonds: ...
Molecular Cloning and Nucleotide Sequence of the 3
... The 3-IMDH gene of C. utilis was cloned and its nucleotide sequence was determined. This is the first report of the nucleotide sequence of a functional gene of C. utilis as far as we know. The sequence of 2209 bp was an alignment of four restriction fragments determined separately. The sequences of ...
... The 3-IMDH gene of C. utilis was cloned and its nucleotide sequence was determined. This is the first report of the nucleotide sequence of a functional gene of C. utilis as far as we know. The sequence of 2209 bp was an alignment of four restriction fragments determined separately. The sequences of ...
Genotyping of urinary samples stored with EDTA for
... Figures 2A and 2B show a similar trend of average detection rate sharply decreasing from day 0 to day 9 followed by a slight additional decrease, except in female subjects’ urinary DNA preserved with EDTA. What is the source of this degradation, and how can the gender differences be explained? After ...
... Figures 2A and 2B show a similar trend of average detection rate sharply decreasing from day 0 to day 9 followed by a slight additional decrease, except in female subjects’ urinary DNA preserved with EDTA. What is the source of this degradation, and how can the gender differences be explained? After ...
enzymes - Yengage
... derivatives of vitamins Bound reversibly by weak non-covalent bonds to active site and released during the reaction separated easily from enzyme by dialysis Affinity for the enzyme is similar to substrate chemically changed by catalysis considered as co-substrate Function: carriers of various ...
... derivatives of vitamins Bound reversibly by weak non-covalent bonds to active site and released during the reaction separated easily from enzyme by dialysis Affinity for the enzyme is similar to substrate chemically changed by catalysis considered as co-substrate Function: carriers of various ...
Regulation of enzyme activity
... E- Concentration of substrates, coenzymes and metal ion activator The susceptibility of the enzyme to degradation depends on its conformation. Presence of substrate, coenzyme or metal ion activator causes changes in the enzyme conformation decreasing its rate of degradation. ...
... E- Concentration of substrates, coenzymes and metal ion activator The susceptibility of the enzyme to degradation depends on its conformation. Presence of substrate, coenzyme or metal ion activator causes changes in the enzyme conformation decreasing its rate of degradation. ...
Decoding the message_2 - Molecular-Biology-Resource
... Review base pairing in DNA (A with T and G with C) vs. RNA (A with U and G with C) This activity can also be done backwards (from translation to transcription); students will learn how to determine the DNA sequences for a polypeptide/protein This activity drastically simplifies how protein synthesis ...
... Review base pairing in DNA (A with T and G with C) vs. RNA (A with U and G with C) This activity can also be done backwards (from translation to transcription); students will learn how to determine the DNA sequences for a polypeptide/protein This activity drastically simplifies how protein synthesis ...
HOW DO ENZYMES - R
... neutralize the strong acids and enzymes in the stomach juices, so that the small intestine is protected against being digested itself. In the small intestine the final breakdown of proteins is done by good bacteria. The brokendown proteins, and the nutrients that the enzymes have already broken down ...
... neutralize the strong acids and enzymes in the stomach juices, so that the small intestine is protected against being digested itself. In the small intestine the final breakdown of proteins is done by good bacteria. The brokendown proteins, and the nutrients that the enzymes have already broken down ...
Folate and DNA methylation during in utero development and aging
... dinucleotides occur at low abundance throughout the human DNA genome and tend to concentrate in regions known as CpG islands found in the promoter regions of genes. A CpG island is a region of DNA with more than 200 bp, a high G-C content and an observed/expected ratio of CpGs greater than 0.6 [2]. ...
... dinucleotides occur at low abundance throughout the human DNA genome and tend to concentrate in regions known as CpG islands found in the promoter regions of genes. A CpG island is a region of DNA with more than 200 bp, a high G-C content and an observed/expected ratio of CpGs greater than 0.6 [2]. ...
Griffith_155
... weights calculated from the sequences of the enzymes (e.g., 34,466 for the B. cereus PI-PLC). The value is higher than that observed by gel filtration ...
... weights calculated from the sequences of the enzymes (e.g., 34,466 for the B. cereus PI-PLC). The value is higher than that observed by gel filtration ...
Rapid DNA Extraction from Plant Seeds for PCR
... storage carbohydrates and polyphenols can interfere with successful amplification of DNA prepared from seeds. Until now, cumbersome preparation steps were needed to purify analytical amounts of seed DNA. EPICENTRE’s new QuickExtract™ Seed DNA Extraction Solution facilitates the extraction of PCR-rea ...
... storage carbohydrates and polyphenols can interfere with successful amplification of DNA prepared from seeds. Until now, cumbersome preparation steps were needed to purify analytical amounts of seed DNA. EPICENTRE’s new QuickExtract™ Seed DNA Extraction Solution facilitates the extraction of PCR-rea ...
Chapter 15 Enzymes
... • An example is trypsin, a digestive enzyme. • It is synthesized and stored as trypsinogen, which has no enzyme activity. • It becomes active only after a six-amino acid fragment is hydrolyzed and removed from the N-terminal end of its chain. • Removal of this small fragment changes not only the pri ...
... • An example is trypsin, a digestive enzyme. • It is synthesized and stored as trypsinogen, which has no enzyme activity. • It becomes active only after a six-amino acid fragment is hydrolyzed and removed from the N-terminal end of its chain. • Removal of this small fragment changes not only the pri ...
Intrastrand Self-complementary Sequences in Bacillus subtilis DNA
... chromosome. Molecules of DNA which are retained by hydroxyapatite (e.g. HA HII) need not be perfectly helical but can have single-stranded tails or loops (Wilson & Thomas, 1973). To determine whether the DNA sequence responsible for the transforming activity resides in the base-paired or single-stra ...
... chromosome. Molecules of DNA which are retained by hydroxyapatite (e.g. HA HII) need not be perfectly helical but can have single-stranded tails or loops (Wilson & Thomas, 1973). To determine whether the DNA sequence responsible for the transforming activity resides in the base-paired or single-stra ...
Enzyme Optimum pH - Sir Sabir Hussain
... o According to this model; as one specific key can open only a specific lock in the same manner a specific enzyme can transform only one substrate into product(s) o According to this model, the active site is a rigid structure and there is no modification or flexibility in the active site before, du ...
... o According to this model; as one specific key can open only a specific lock in the same manner a specific enzyme can transform only one substrate into product(s) o According to this model, the active site is a rigid structure and there is no modification or flexibility in the active site before, du ...
Lecture * 4 The Kinetics of Enzyme
... intercept of Km/Vm. • This plot is used to determine Vm more accurately. ...
... intercept of Km/Vm. • This plot is used to determine Vm more accurately. ...