
Enzyme Class
... which functions as a biological catalyst, speeding up reaction rate by lowering activation energy without being affected by the reaction it catalyse ...
... which functions as a biological catalyst, speeding up reaction rate by lowering activation energy without being affected by the reaction it catalyse ...
PDF
... first during the differentiation period. Concerning the nucleic acids there is an increase in amount of DNA, which tolerably closely follows the course of histogenesis (Agrell, 1952). There is also an obvious inverse variation in amount of DNA and PNA. This inverse change strongly suggests a mutual ...
... first during the differentiation period. Concerning the nucleic acids there is an increase in amount of DNA, which tolerably closely follows the course of histogenesis (Agrell, 1952). There is also an obvious inverse variation in amount of DNA and PNA. This inverse change strongly suggests a mutual ...
Small-molecule metabolism: an enzyme mosaic
... rhamnulokinase (rhaB) and rhamnulose1-phosphate aldolase (rhaD), and L-ribulokinase (araB) and L-ribulose phosphate 4-epimerase (araD) in Fig. 3, are very rare. If duplication of large portions of the bacterial chromosome takes place, and all the genes in a duplicated portion were used to form a new ...
... rhamnulokinase (rhaB) and rhamnulose1-phosphate aldolase (rhaD), and L-ribulokinase (araB) and L-ribulose phosphate 4-epimerase (araD) in Fig. 3, are very rare. If duplication of large portions of the bacterial chromosome takes place, and all the genes in a duplicated portion were used to form a new ...
Base excision repair
... of Rad50 dimers. Inactive ATM dimers are recruited to the DSBs through interaction with the carboxyl terminus of Nbs1, and by a less ...
... of Rad50 dimers. Inactive ATM dimers are recruited to the DSBs through interaction with the carboxyl terminus of Nbs1, and by a less ...
FOR ENZYMES THE LIMITS FOR LIFE DEFINE THE LIMITS
... This low rate of 0.4 s–1 is a misleading assessment of this enzyme’s activity. That is, the enzyme cannot repair more damaged nucleotides than exist. Unlike other enzymes that have access to a steady concentration of substrate molecules, photolyase must search for the infrequent damaged site. It bin ...
... This low rate of 0.4 s–1 is a misleading assessment of this enzyme’s activity. That is, the enzyme cannot repair more damaged nucleotides than exist. Unlike other enzymes that have access to a steady concentration of substrate molecules, photolyase must search for the infrequent damaged site. It bin ...
Enzymatic
... 43. Based off of your observations of the enzyme shown, which of the following is true? A. The denaturation of the enzyme DOES NOT affect the enzyme’s function. B. The denaturation of this enzyme by pH changes is irreversible. In other words, restoring the pH to an optimal level DOES NOT fix the enz ...
... 43. Based off of your observations of the enzyme shown, which of the following is true? A. The denaturation of the enzyme DOES NOT affect the enzyme’s function. B. The denaturation of this enzyme by pH changes is irreversible. In other words, restoring the pH to an optimal level DOES NOT fix the enz ...
ENZYMES - PROBLEMS - Chemistry@Elmhurst
... Normally folic acid is synthesized in two steps in bacteria by the top reaction on the left. If a sulfa drug is used, the first enzyme is not to specific and can use the sulfonamide in the first reaction. This reaction produces the product containing pteridine and the sulfa drug. The next and final ...
... Normally folic acid is synthesized in two steps in bacteria by the top reaction on the left. If a sulfa drug is used, the first enzyme is not to specific and can use the sulfonamide in the first reaction. This reaction produces the product containing pteridine and the sulfa drug. The next and final ...
Stability, catalytic versatility and evolution of the
... stable in order to maintain their native structures but also have to be flexible to allow conformational changes during catalysis. These opposing requirements are particularly striking for enzymes from extremophiles, which must be both stable and active under extreme conditions of salt, pH and tempe ...
... stable in order to maintain their native structures but also have to be flexible to allow conformational changes during catalysis. These opposing requirements are particularly striking for enzymes from extremophiles, which must be both stable and active under extreme conditions of salt, pH and tempe ...
DNA recognition code of transcription factors
... very close to the DNA a small residue can easily fit in but a bulky residue may not. The stereochemical charts of the HTH, PH, AF and C4 families have been deduced. Stereochemical rules will be determined in the near future for other families, such as MybLexA [the protein structures have been determ ...
... very close to the DNA a small residue can easily fit in but a bulky residue may not. The stereochemical charts of the HTH, PH, AF and C4 families have been deduced. Stereochemical rules will be determined in the near future for other families, such as MybLexA [the protein structures have been determ ...
Lack of homology between two haloacetate dehalogenase genes
... multiple mutations on either gene copy, which results in the creation of a modified enzyme (Rigby et al., 1974). If gene duplication is important in evolution, we would expect to find two similar enzymes in a cell at some stage of the evolutionary process. The nylon-oligomer-degrading enzymes found ...
... multiple mutations on either gene copy, which results in the creation of a modified enzyme (Rigby et al., 1974). If gene duplication is important in evolution, we would expect to find two similar enzymes in a cell at some stage of the evolutionary process. The nylon-oligomer-degrading enzymes found ...
Detection of Cow Milk in Water Buffalo Cheese by SYBR Green Real
... preservation period. DNA was found in all experimental samples. Real time amplification of DNA from governing liquid proved the method’s actual applicability for species detection purposes. Hot-start PCR and fluorescence signal acquisition were optimal at 56oC, allowing SYBR Green I-based real-time ...
... preservation period. DNA was found in all experimental samples. Real time amplification of DNA from governing liquid proved the method’s actual applicability for species detection purposes. Hot-start PCR and fluorescence signal acquisition were optimal at 56oC, allowing SYBR Green I-based real-time ...
Metabolism 2 PDF
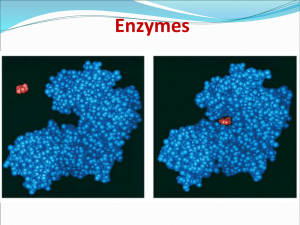
... • 4. Changes shape as substrate binds to it, so that it fits even more snugly around reactant (= induced fit, fig 8.16) • 5. Brings chemical groups of active site into position to enhance catalyzing the rxn • 6. Enzymes return to their original conformation after releasing converted substrate ⇒ they ...
... • 4. Changes shape as substrate binds to it, so that it fits even more snugly around reactant (= induced fit, fig 8.16) • 5. Brings chemical groups of active site into position to enhance catalyzing the rxn • 6. Enzymes return to their original conformation after releasing converted substrate ⇒ they ...
video slide
... • 4. Changes shape as substrate binds to it, so that it fits even more snugly around reactant (= induced fit, fig 8.16) • 5. Brings chemical groups of active site into position to enhance catalyzing the rxn • 6. Enzymes return to their original conformation after releasing converted substrate they ...
... • 4. Changes shape as substrate binds to it, so that it fits even more snugly around reactant (= induced fit, fig 8.16) • 5. Brings chemical groups of active site into position to enhance catalyzing the rxn • 6. Enzymes return to their original conformation after releasing converted substrate they ...
enzymology
... This type of control in cells is exercised at the gene level. If the gene for that enzyme is activated then enzyme synthesis takes place and the process is called enzyme induction. On the contrary, if enzyme synthesis is inhibited it is called repression. This type of control mechanism is operative ...
... This type of control in cells is exercised at the gene level. If the gene for that enzyme is activated then enzyme synthesis takes place and the process is called enzyme induction. On the contrary, if enzyme synthesis is inhibited it is called repression. This type of control mechanism is operative ...
ENZYMES AS CATALYSTS ROLE OF COENZYMES AND METALS
... A. The rearrangements of covalent bonds during an enzyme-catalyzed reaction • Catalytic functional groups on an enzyme may form a transient covalent bond with a substrate. • These interactions lower the activation energy by providing an alternative, lowerenergy reaction path. B. The noncovalent inte ...
... A. The rearrangements of covalent bonds during an enzyme-catalyzed reaction • Catalytic functional groups on an enzyme may form a transient covalent bond with a substrate. • These interactions lower the activation energy by providing an alternative, lowerenergy reaction path. B. The noncovalent inte ...






















![K m + [S]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008289247_1-97eed219b6e242b1a447e591c5c01f05-300x300.png)