Pinpointing dynamic coupling in enzymes for efficient drug design
... contradictory results demonstrate the delicate nature of motional coupling to catalysis. We have refined this global picture of motional coupling by isotopically labeling specific segments of an enzyme and therefore experimentally determining which parts of the enzyme show motional coupling [19] . T ...
... contradictory results demonstrate the delicate nature of motional coupling to catalysis. We have refined this global picture of motional coupling by isotopically labeling specific segments of an enzyme and therefore experimentally determining which parts of the enzyme show motional coupling [19] . T ...
Introduction to Molecular Systematics
... • Proteins are the structures and enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions that are essential for the function of an organism • DNA code is read and converted to protein in two steps – Transcription: DNA is copied to messenger RNA – Translation: messenger RNA is template for protein ...
... • Proteins are the structures and enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions that are essential for the function of an organism • DNA code is read and converted to protein in two steps – Transcription: DNA is copied to messenger RNA – Translation: messenger RNA is template for protein ...
Enzymes
... • An enzyme allows a reaction to proceed rapidly under conditions prevailing in the cell by providing an alternate reaction pathway with a lower free energy of activation . • The enzyme does not change the free energies of the reactants or products and, therefore, does not change the equilibrium of ...
... • An enzyme allows a reaction to proceed rapidly under conditions prevailing in the cell by providing an alternate reaction pathway with a lower free energy of activation . • The enzyme does not change the free energies of the reactants or products and, therefore, does not change the equilibrium of ...
Chapter 6 Enzymes
... 1850's Louis Pasteur something in yeast that ferments things 1897 Buchner proved that yeast extracts, not live yeast could ferment sugar term Enzyme coined by Fredrick Kuhne 1st isolated was urease by Sumner 1926 - proved were protein not until 1930's that widely accepted A. Most enzymes are protein ...
... 1850's Louis Pasteur something in yeast that ferments things 1897 Buchner proved that yeast extracts, not live yeast could ferment sugar term Enzyme coined by Fredrick Kuhne 1st isolated was urease by Sumner 1926 - proved were protein not until 1930's that widely accepted A. Most enzymes are protein ...
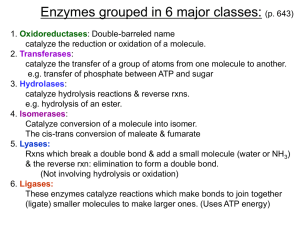
BCMB 3100 – Chapters 6,7,8 Enzyme Basics • Six Classes (IUBMB
... • Catalyze lysis of a substrate, generating a double bond in a nonhydrolytic, nonoxidative elimination (i.e. nonhydrolytic & nonoxidative lysis that yields a double bond) ...
... • Catalyze lysis of a substrate, generating a double bond in a nonhydrolytic, nonoxidative elimination (i.e. nonhydrolytic & nonoxidative lysis that yields a double bond) ...
Enzymes | Principles of Biology from Nature Education
... the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme. Denatured enzymes are no longer able to catalyze biochemical reactions. This is one of the reasons an extremely high fever can be dangerous — the increased temperature over an extended period of time can denature human proteins. However, moderate fever ...
... the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme. Denatured enzymes are no longer able to catalyze biochemical reactions. This is one of the reasons an extremely high fever can be dangerous — the increased temperature over an extended period of time can denature human proteins. However, moderate fever ...
Anabaena - Oxford Academic
... ensures that glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate via aldolase will also re-enter the cycle rather than be metabolized to pyruvate. Thus glucose 6-phosphate can be completely oxidized to CO, with the concomitant production of maximal amounts of NADPH. This is in keeping with the observations of BBhme [5], in ...
... ensures that glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate via aldolase will also re-enter the cycle rather than be metabolized to pyruvate. Thus glucose 6-phosphate can be completely oxidized to CO, with the concomitant production of maximal amounts of NADPH. This is in keeping with the observations of BBhme [5], in ...
Mapping Enzyme Active Sites in Complex Proteomes
... cysteine nucleophile C32,13 while ALDH1 and ECH1 were modified on carboxylate residues that function as catalytic bases/ acids in these enzymes (E26914 and D204,15 respectively). The labeling sites in DDH, D176 and Y180, are both conserved, and the latter has been shown to be important for catalysis ...
... cysteine nucleophile C32,13 while ALDH1 and ECH1 were modified on carboxylate residues that function as catalytic bases/ acids in these enzymes (E26914 and D204,15 respectively). The labeling sites in DDH, D176 and Y180, are both conserved, and the latter has been shown to be important for catalysis ...
Lecture 4| Enzyme Catalysis: Structural basis and energetics of
... Effect of pH on enzyme catalysis • When the rate-‐limi(ng component of the cataly(c process involves a (tratable residue, the measured ac(vity of the enzyme depends on pH and the ioniza(on status of ...
... Effect of pH on enzyme catalysis • When the rate-‐limi(ng component of the cataly(c process involves a (tratable residue, the measured ac(vity of the enzyme depends on pH and the ioniza(on status of ...
APenzymes
... each enzyme works with a specific substrate chemical fit between active site & substrate H bonds & ionic bonds ...
... each enzyme works with a specific substrate chemical fit between active site & substrate H bonds & ionic bonds ...
Advanced primer design
... The GC content of nucleic acids can vary for different creatures, or it can differ depending on whether the nucleic acid is derived from prokaryotic cell or non-prokaryotic cell. Those with a low GC content is said to be AT rich, and those with a high GC content is said to be GC rich. bp: Abbreviati ...
... The GC content of nucleic acids can vary for different creatures, or it can differ depending on whether the nucleic acid is derived from prokaryotic cell or non-prokaryotic cell. Those with a low GC content is said to be AT rich, and those with a high GC content is said to be GC rich. bp: Abbreviati ...
A Novel Assay for DNA-Dependent DNA Polymerase Activity
... 30mM followed by 25ul of 90mM NaH2PO4 containing 4 pMol of biotinylated capture probe. The microtiter plate is agitated throughout the 45 minute capture period. Note that re-annealing of sister strands (C) competes with capture and immobilization of the Ru-labeled species at the surface of the elect ...
... 30mM followed by 25ul of 90mM NaH2PO4 containing 4 pMol of biotinylated capture probe. The microtiter plate is agitated throughout the 45 minute capture period. Note that re-annealing of sister strands (C) competes with capture and immobilization of the Ru-labeled species at the surface of the elect ...
The serC-aroA operon of Escherichia coli
... be readily observed in the 'high-activity' crude extracts. Unfortunately, in wild type E. coli there is an abundant protein which co-migrates with EPSP synthase. This has been identified as elongation factor Tu which has an Mr of 43225 (Arai et al., 1979) and under these conditions it is not separat ...
... be readily observed in the 'high-activity' crude extracts. Unfortunately, in wild type E. coli there is an abundant protein which co-migrates with EPSP synthase. This has been identified as elongation factor Tu which has an Mr of 43225 (Arai et al., 1979) and under these conditions it is not separat ...
General theory of enzyme action, by Leonor Michaelis and Maud
... Most people have two forms of the acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, a low KM mitochondrial form and a high KM cytosolic form. In susceptible persons, the mitochondrial enzyme is less active due to the substitution of a single amino acid, and acetaldehyde is processed only by the cytosolic enzyme. Because ...
... Most people have two forms of the acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, a low KM mitochondrial form and a high KM cytosolic form. In susceptible persons, the mitochondrial enzyme is less active due to the substitution of a single amino acid, and acetaldehyde is processed only by the cytosolic enzyme. Because ...
Chapter 7 7 The Behavior of Proteins: Enzymes Mechanisms and
... also so se serves es as a positive (stimulatory) modulator, or activator; e.g., the binding g of aspartate p ((its substrate)) to ATCase. ((tends to be positive regulator) • hetero heterotropic tropic p effects: allosteric interactions that occur when different substances are bound to the protein; e ...
... also so se serves es as a positive (stimulatory) modulator, or activator; e.g., the binding g of aspartate p ((its substrate)) to ATCase. ((tends to be positive regulator) • hetero heterotropic tropic p effects: allosteric interactions that occur when different substances are bound to the protein; e ...