Enzyme
... What give the enzyme its shape • How it is folded into its 3-dimensional shape or (tertiary structure) is vital • If this structure is changed or altered then the enzyme is said to have been DENATURED • Denaturation of the enzyme will change the shape of the enzymes active site • This will mean the ...
... What give the enzyme its shape • How it is folded into its 3-dimensional shape or (tertiary structure) is vital • If this structure is changed or altered then the enzyme is said to have been DENATURED • Denaturation of the enzyme will change the shape of the enzymes active site • This will mean the ...
Outline 19.1 Catalysis by Enzymes
... polypeptide enters the active site (b) Hydrogen transfer allows formation of a strained intermediate (c) The peptide bond is broken. ...
... polypeptide enters the active site (b) Hydrogen transfer allows formation of a strained intermediate (c) The peptide bond is broken. ...
Lecture 9 Enzymes: Basic principles
... Holoenzymes Enzyme without its cofactor “apoenzyme” With its cofactor “holoenzyme” Cofactors are essential for activity e.g. many vitamins are cofactors, many diseases associated with vitamin deficiency due to lack of specific enzyme activity ...
... Holoenzymes Enzyme without its cofactor “apoenzyme” With its cofactor “holoenzyme” Cofactors are essential for activity e.g. many vitamins are cofactors, many diseases associated with vitamin deficiency due to lack of specific enzyme activity ...
Practice Exam 1
... Legge Practice Exam I BCHS 3304 Note: This homework will not be collected. However, quizzes and exams will assume that you have completed and understand the homework assignment and could answer related questions. In this homework you are also given a practice exam II, which you may use as a study to ...
... Legge Practice Exam I BCHS 3304 Note: This homework will not be collected. However, quizzes and exams will assume that you have completed and understand the homework assignment and could answer related questions. In this homework you are also given a practice exam II, which you may use as a study to ...
Isolation, cloning and sequence analysis of the lactate
... tropical theileriosis and genomic DNA was extracted following the confirmation of the clinical diagnosis. For the first time, in this study, the lactate dehydrogenase sequence was isolated from from a Theileria species. Following extraction from genomic DNA by PCR the sequence was cloned into the ve ...
... tropical theileriosis and genomic DNA was extracted following the confirmation of the clinical diagnosis. For the first time, in this study, the lactate dehydrogenase sequence was isolated from from a Theileria species. Following extraction from genomic DNA by PCR the sequence was cloned into the ve ...
Name: Date: ______ Block: ______ ENZYMES A CATALYST is a
... An enzyme may not work if its environment is changed. Both models of enzyme action depend on an exact fit between the active site of an enzyme and the substrate to which it binds. If anything were to block the active site or change the shape of the protein (enzyme), it could prevent the enzyme from ...
... An enzyme may not work if its environment is changed. Both models of enzyme action depend on an exact fit between the active site of an enzyme and the substrate to which it binds. If anything were to block the active site or change the shape of the protein (enzyme), it could prevent the enzyme from ...
Novel Specific Halogenating Enzymes from Bacteria
... All isolated bacterial and eukaryotic halo peroxidases only showed very low or no substrate specificity at all (Franssen, 1994). However, as haloperoxidases were the only halogenating enzymes known, with the exception of some Sadenosyl methionine transferases that are involved in the formation of m ...
... All isolated bacterial and eukaryotic halo peroxidases only showed very low or no substrate specificity at all (Franssen, 1994). However, as haloperoxidases were the only halogenating enzymes known, with the exception of some Sadenosyl methionine transferases that are involved in the formation of m ...
Enzymes - HKEdCity
... function and is said to be denatured. Such changed are irreversible. The phenomenon is known as denaturation. 10.The activity of an enzyme is affected by temperature. 11.Enzyme activity is affected by pH of the medium. It worked best at an optimum pH. 12.Some enzymes work efficiently only in the pre ...
... function and is said to be denatured. Such changed are irreversible. The phenomenon is known as denaturation. 10.The activity of an enzyme is affected by temperature. 11.Enzyme activity is affected by pH of the medium. It worked best at an optimum pH. 12.Some enzymes work efficiently only in the pre ...
Enzymes–II
... (one shown in the red and the others in yellow) and eight small subunits (one shown in blue and the others in white). The active sites lie in the large subunits. ...
... (one shown in the red and the others in yellow) and eight small subunits (one shown in blue and the others in white). The active sites lie in the large subunits. ...
CHAPTER 13 DNA manipulation
... isolated from that species, II for the second, and so on. In some cases an additional letter is added, such as in Hin dII, and the letter ‘d’ denotes a particular strain or type (serotype) of the bacterium. ...
... isolated from that species, II for the second, and so on. In some cases an additional letter is added, such as in Hin dII, and the letter ‘d’ denotes a particular strain or type (serotype) of the bacterium. ...
Isolation of a Mycobacterium Virus with the Infectivity Rate Tested at
... the surface receptors on the host cell. The virus can also mimic another cell in the host, this is if the cell is eukaryotic, that interacts with the cell the virus wants to infect. Another way a virus successfully infects the host cell is to enclose itself in a lipid membrane from the host cell tha ...
... the surface receptors on the host cell. The virus can also mimic another cell in the host, this is if the cell is eukaryotic, that interacts with the cell the virus wants to infect. Another way a virus successfully infects the host cell is to enclose itself in a lipid membrane from the host cell tha ...
Putrescine oxidase of Micrococcus rubens : primary
... crude extract was obtained by sonication of cells of M . rubens. Proteins were precipitated with ammonium sulphate (35-70 YO saturation). Putrescine oxidase was further purified by successive chromatography on DEAE-cellulose, aminooctyl-Sepharose and aminododecylSepharose. The final enzyme preparati ...
... crude extract was obtained by sonication of cells of M . rubens. Proteins were precipitated with ammonium sulphate (35-70 YO saturation). Putrescine oxidase was further purified by successive chromatography on DEAE-cellulose, aminooctyl-Sepharose and aminododecylSepharose. The final enzyme preparati ...
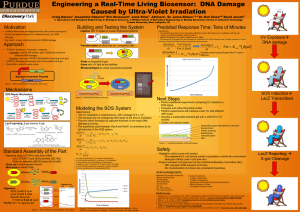
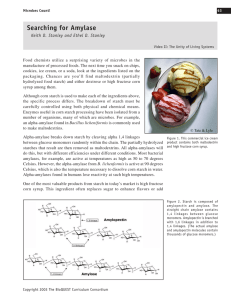
Searching for Amylase - BioQUEST Curriculum Consortium
... the specific process differs. The breakdown of starch must be carefully controlled using both physical and chemical means. Enzymes useful in corn starch processing have been isolated from a number of organisms, many of which are microbes. For example, an alpha-amylase found in Bacillus licheniformis ...
... the specific process differs. The breakdown of starch must be carefully controlled using both physical and chemical means. Enzymes useful in corn starch processing have been isolated from a number of organisms, many of which are microbes. For example, an alpha-amylase found in Bacillus licheniformis ...