CHAPTER 11 Mechanism of Enzyme Action
... is 2-3 pH units greater than that of the protonated form of the acceptor 2. If their pK values of proton donor and acceptor are nearly equal, the distinction breaks down and: the hydrogen atom becomes more or less equally shared between them (D---H---A). 3. Such low-barrier hydrogen bonds (LBHBs) ...
... is 2-3 pH units greater than that of the protonated form of the acceptor 2. If their pK values of proton donor and acceptor are nearly equal, the distinction breaks down and: the hydrogen atom becomes more or less equally shared between them (D---H---A). 3. Such low-barrier hydrogen bonds (LBHBs) ...
DNA extraction from frozen fieldcollected and dehydrated herbarium
... extraction (Rogers, 1994). Furthermore, long-lived basidiomata of many Basidiomycetes species are coriaceous or even woody hard, which poses additional difficulties in DNA extraction. In the studied species, all these problems occur: Hymenochaetaceae are characterized by the extensive production of ...
... extraction (Rogers, 1994). Furthermore, long-lived basidiomata of many Basidiomycetes species are coriaceous or even woody hard, which poses additional difficulties in DNA extraction. In the studied species, all these problems occur: Hymenochaetaceae are characterized by the extensive production of ...
Enzymes
... have of combining and reacting with it. The rate does not continue to rise as you add more and more substrate. There is a limit to the amount of enzyme available A substrate cannot join with the active site of an enzyme until it is free. Therefore, once the number of substrate molecules exce ...
... have of combining and reacting with it. The rate does not continue to rise as you add more and more substrate. There is a limit to the amount of enzyme available A substrate cannot join with the active site of an enzyme until it is free. Therefore, once the number of substrate molecules exce ...
enzyme structure
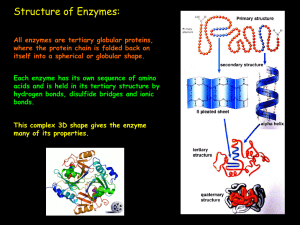
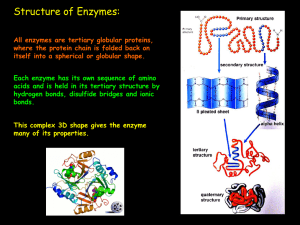
... common being the ribosome; these are referred to as either RNA-enzymes or ribozymes. The activities of enzymes are determined by their three-dimensional structure. However, although structure does determine function, predicting a novel enzyme's activity just from its structure is a very difficult pr ...
... common being the ribosome; these are referred to as either RNA-enzymes or ribozymes. The activities of enzymes are determined by their three-dimensional structure. However, although structure does determine function, predicting a novel enzyme's activity just from its structure is a very difficult pr ...
1.4 Enzymes
... Modern interpretations of the lock and key theory suggest that in the presence of the substrate, the active site may change in order to select the substrate’s shape. ...
... Modern interpretations of the lock and key theory suggest that in the presence of the substrate, the active site may change in order to select the substrate’s shape. ...
Biochemical properties and structural features of the thermostable
... Phylogenetic analyses based on 16S rRNA sequence data indicate that hyperthermophilic microorganisms (i. e. those with an optimal growth temperature of 80 ◦C or higher) represent the deepest and shortest branches in the domains Archaea and Bacteria (STETTER, 1999), suggesting that they could have re ...
... Phylogenetic analyses based on 16S rRNA sequence data indicate that hyperthermophilic microorganisms (i. e. those with an optimal growth temperature of 80 ◦C or higher) represent the deepest and shortest branches in the domains Archaea and Bacteria (STETTER, 1999), suggesting that they could have re ...
Unit: Enzymes I
... monitoring is used most commonly with those enzymes in which changes in NADH or NADPH are measured but can also be used for the determination of other enzyme activities (e.g., alkaline phosphatase) if a colored product is generated from a non-colored substrate. Although a few enzyme tests have been ...
... monitoring is used most commonly with those enzymes in which changes in NADH or NADPH are measured but can also be used for the determination of other enzyme activities (e.g., alkaline phosphatase) if a colored product is generated from a non-colored substrate. Although a few enzyme tests have been ...
Getting a grip on how DNA polymerases function
... multiple DNA polymerases have been identified in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, including the recent discovery of several error-prone DNA polymerases2. Based on primary sequence similarity, these DNA polymerases can be categorized into families (Table 1). The most extensively studied polymerases includ ...
... multiple DNA polymerases have been identified in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, including the recent discovery of several error-prone DNA polymerases2. Based on primary sequence similarity, these DNA polymerases can be categorized into families (Table 1). The most extensively studied polymerases includ ...
Binding of the EcoRII methyltransferase to 5
... FCyt-DNA can be isolated. The enzyme-DNA adduct can be digested with proteases and a DNA-peptide complex isolated by HPLC and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The sequence of the peptide indicates that the reactive portion of the protein contains cysteine-186, an amino acid present in all DNA(cyt ...
... FCyt-DNA can be isolated. The enzyme-DNA adduct can be digested with proteases and a DNA-peptide complex isolated by HPLC and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The sequence of the peptide indicates that the reactive portion of the protein contains cysteine-186, an amino acid present in all DNA(cyt ...
World record enzymes
... One vital class of proteins is enzymes, which are catalysts, i.e. they speed up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. Without them, many reactions essential for life would be far too slow for life to exist. Catalysts do not affect the equilibrium of reactions, only the rate at wh ...
... One vital class of proteins is enzymes, which are catalysts, i.e. they speed up chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. Without them, many reactions essential for life would be far too slow for life to exist. Catalysts do not affect the equilibrium of reactions, only the rate at wh ...
Genomic DNA extraction from small amounts of serum to be used for
... In this study Pi genotyping was compared between DNA extracted from whole blood and DNA extracted from serum. In all cases, the two extraction procedures gave identical Pi genotypes and the results were in accordance with the phenotypic determination by isoelectric focusing. The present authors conf ...
... In this study Pi genotyping was compared between DNA extracted from whole blood and DNA extracted from serum. In all cases, the two extraction procedures gave identical Pi genotypes and the results were in accordance with the phenotypic determination by isoelectric focusing. The present authors conf ...
enzymes
... The allosteric site • The allosteric site is not at the active site or substrate binding site, but is somewhere else on the molecule • The allosteric site is the site where small molecules bind and affect a change in the active site or the substrate binding site • The binding of this specific molecu ...
... The allosteric site • The allosteric site is not at the active site or substrate binding site, but is somewhere else on the molecule • The allosteric site is the site where small molecules bind and affect a change in the active site or the substrate binding site • The binding of this specific molecu ...
Lesson 8. Enzymes
... The global life depends on a series of chemical reactions. Most of the chemical reactions proceed too slowly on their own to sustain life. Hence catalysts are required to greatly accelerate the rates of these chemical reactions. In nature enzymes posses the catalytic power to facilitate life process ...
... The global life depends on a series of chemical reactions. Most of the chemical reactions proceed too slowly on their own to sustain life. Hence catalysts are required to greatly accelerate the rates of these chemical reactions. In nature enzymes posses the catalytic power to facilitate life process ...