Some factors affecting polyphenol oxidase activity
... the enzyme to "mold" itself over the substrate. ...
... the enzyme to "mold" itself over the substrate. ...
Phaeospirillum oryzae sp. nov., a spheroplast
... phylogenetic neighbours and calculation of pairwise 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities were achieved by using the NCBI BLAST search (Altschul et al., 1990) and the EzTaxon server (Chun et al., 2007). The CLUSTAL W algorithm of MEGA 4 was used for sequence alignments and MEGA 4 software (Tamura et a ...
... phylogenetic neighbours and calculation of pairwise 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities were achieved by using the NCBI BLAST search (Altschul et al., 1990) and the EzTaxon server (Chun et al., 2007). The CLUSTAL W algorithm of MEGA 4 was used for sequence alignments and MEGA 4 software (Tamura et a ...
Click here
... Enzyme rates depend on solution conditions and substrate concentration. Conditions that denature the protein abolish enzyme activity, such as high temperatures, extremes of pH or high salt concentrations, while raising substrate concentration tends to increase activity when [S] is low. To find the m ...
... Enzyme rates depend on solution conditions and substrate concentration. Conditions that denature the protein abolish enzyme activity, such as high temperatures, extremes of pH or high salt concentrations, while raising substrate concentration tends to increase activity when [S] is low. To find the m ...
Enzymes - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... Zymogen is inactive enzyme until certain bonds are cleaved. Enzymes accelerate reactions by decreasing activation energy and increasing rate but does NOT change equilibrium Qualities. High Specificity ...
... Zymogen is inactive enzyme until certain bonds are cleaved. Enzymes accelerate reactions by decreasing activation energy and increasing rate but does NOT change equilibrium Qualities. High Specificity ...
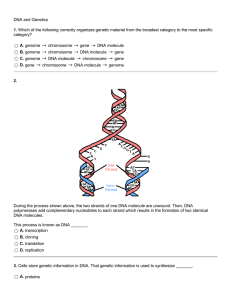
DNA and Genetics 1. Which of the following correctly organizes
... Genetic information is stored in genes on the chromosomes, which, in turn, are located in a cell's nucleus. 23. In DNA replication, first DNA helicases break down the hydrogen bonds that link the complementary nitrogen bases between the old DNA molecules two strands. Proteins hold the two strands of ...
... Genetic information is stored in genes on the chromosomes, which, in turn, are located in a cell's nucleus. 23. In DNA replication, first DNA helicases break down the hydrogen bonds that link the complementary nitrogen bases between the old DNA molecules two strands. Proteins hold the two strands of ...
Proteins and Enzymes
... For every substrate there is one and only one enzyme that causes that substrate to react just like there is only one specific key which fits into a specific type of lock. ...
... For every substrate there is one and only one enzyme that causes that substrate to react just like there is only one specific key which fits into a specific type of lock. ...
Solution
... When the end product of a reaction sequence is produced at sufficient levels for the cell, some product molecules bind to the allosteric enzyme (E1) in the sequence, which shuts down all the reactions that follow and stops the synthesis of intermediate products. ...
... When the end product of a reaction sequence is produced at sufficient levels for the cell, some product molecules bind to the allosteric enzyme (E1) in the sequence, which shuts down all the reactions that follow and stops the synthesis of intermediate products. ...
Chapter 15 The Techniques of Molecular Genetics
... Restriction endonucleases make sitespecific cuts in DNA. The nucleotide sequences are called restriction sites. Restriction endonucleases protect bacteria from foreign DNA. Bacteria protect endogenous restriction sites by methylation. Restriction enzymes commonly recognize palindromic sequences ...
... Restriction endonucleases make sitespecific cuts in DNA. The nucleotide sequences are called restriction sites. Restriction endonucleases protect bacteria from foreign DNA. Bacteria protect endogenous restriction sites by methylation. Restriction enzymes commonly recognize palindromic sequences ...
Mechanism, and Role in Recombination Type-1
... topoisomerase I were displayed by gel electrophoresis (see Fig. 7). The exact position of the break was determined by comparison with the mobility of standards produced by chemical cleavage (Maxam and Gilbert 1980) and by restriction enzyme digestion. Only one cleavage was seen and it was three nucl ...
... topoisomerase I were displayed by gel electrophoresis (see Fig. 7). The exact position of the break was determined by comparison with the mobility of standards produced by chemical cleavage (Maxam and Gilbert 1980) and by restriction enzyme digestion. Only one cleavage was seen and it was three nucl ...
Enzymes How Do Enzymes Work?
... obtains a relationship such as that shown in the plot below. Provide an explanation. Is this the relationship between rate and temperature that is found for reactions that do not involve ...
... obtains a relationship such as that shown in the plot below. Provide an explanation. Is this the relationship between rate and temperature that is found for reactions that do not involve ...
Single-Molecule Experiments in Synthetic Biology: An
... Gene expression in eukaryotes is controlled at the transcriptional level by the specific binding of transcription factors to defined DNA sequences. In this way, cell growth, differentiation, and development are regulated. The possibility to influence and control cell metabolism through modified synt ...
... Gene expression in eukaryotes is controlled at the transcriptional level by the specific binding of transcription factors to defined DNA sequences. In this way, cell growth, differentiation, and development are regulated. The possibility to influence and control cell metabolism through modified synt ...
Enzymes: Regulation 1
... Sketch plots of Vo vs. [S] for an allosteric enzyme that illustrate positive homotropic regulation and positive and negative heterotropic regulation, with ATCase as an example. Specifically, sketch (all on the same axes) for ATCase: Vo vs. [aspartate] curves with no heterotropic regulators present, ...
... Sketch plots of Vo vs. [S] for an allosteric enzyme that illustrate positive homotropic regulation and positive and negative heterotropic regulation, with ATCase as an example. Specifically, sketch (all on the same axes) for ATCase: Vo vs. [aspartate] curves with no heterotropic regulators present, ...
Nucleic Acids Research
... To use the modified translation feature, the parameter SIGNAL should be set equal to a list of amino acids (possibly including an "END") in single quotes. Upon invoking the translation procedure with a line 'NAME' 13 0, only those codons corresponding to the listed amino acids will be translated. Fo ...
... To use the modified translation feature, the parameter SIGNAL should be set equal to a list of amino acids (possibly including an "END") in single quotes. Upon invoking the translation procedure with a line 'NAME' 13 0, only those codons corresponding to the listed amino acids will be translated. Fo ...