Lipid Metabolism - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... Oxidation of fatty acids - regulation Need to regulate so oxidation only occurs when the need for energy requires it 1. Rate-limiting rxn. - fatty acids entering mito. (acyltransferases) 2. Malonyl CoA (important molecule!!) 1st intermediate in biosynthesis of fatty acids increases when lots carbohy ...
... Oxidation of fatty acids - regulation Need to regulate so oxidation only occurs when the need for energy requires it 1. Rate-limiting rxn. - fatty acids entering mito. (acyltransferases) 2. Malonyl CoA (important molecule!!) 1st intermediate in biosynthesis of fatty acids increases when lots carbohy ...
Slides
... of metabolic pathways from genomes Schemas for pathway DBs Exchange formats for pathway data Classification systems for pathway data Pathway diagram layout algorithms ...
... of metabolic pathways from genomes Schemas for pathway DBs Exchange formats for pathway data Classification systems for pathway data Pathway diagram layout algorithms ...
Chapter 5 - Enzymes
... that enhance the probability that the transition state is formed. In some enzymes, these groups can participate in general acid-base catalysis in which amino acid residues provide or accept protons. In other enzymes, catalysis may involve the transient formation of a covalent enzyme-substrate comple ...
... that enhance the probability that the transition state is formed. In some enzymes, these groups can participate in general acid-base catalysis in which amino acid residues provide or accept protons. In other enzymes, catalysis may involve the transient formation of a covalent enzyme-substrate comple ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... Conclusions about large-scale structure In a cell or microorganism, the processes that generate mass, energy, information transfer and cell-fate specification are seamlessly integrated through a complex network of cellular constituents and reactions. A systematic comparative mathematical analysis o ...
... Conclusions about large-scale structure In a cell or microorganism, the processes that generate mass, energy, information transfer and cell-fate specification are seamlessly integrated through a complex network of cellular constituents and reactions. A systematic comparative mathematical analysis o ...
Sugar Metabolism in Yeasts: an Overview of Aerobic and Anaerobic
... polyols, alcohols, organic acids and amino acids) that can support their growth but preferentially they metabolize sugars. The information related to the metabolism of different carbon sources is huge, the most widely studied being sugars such as hexoses (glucose, fructose, galactose or mannose) and ...
... polyols, alcohols, organic acids and amino acids) that can support their growth but preferentially they metabolize sugars. The information related to the metabolism of different carbon sources is huge, the most widely studied being sugars such as hexoses (glucose, fructose, galactose or mannose) and ...
my handy vitamin review
... some closely related primates, it’s a vitamin. Guinea pigs can’t make ascorbic acid, either. Sources of vitamin C are fruit and fresh meat. Vitamin C deficiency causes scurvy, and in human history vitamin C deficiency may have been an impediment to spreading northward. ...
... some closely related primates, it’s a vitamin. Guinea pigs can’t make ascorbic acid, either. Sources of vitamin C are fruit and fresh meat. Vitamin C deficiency causes scurvy, and in human history vitamin C deficiency may have been an impediment to spreading northward. ...
Chapter 9 (Jan 27-29)
... Substrate-level phosphorylation – ATP produced from the transfer of a phosphate group from a substrate to ADP ATP made one at a time Enzyme ...
... Substrate-level phosphorylation – ATP produced from the transfer of a phosphate group from a substrate to ADP ATP made one at a time Enzyme ...
CHAP NUM="9" ID="CH
... respiration, the electron transport chain accepts electrons from the breakdown products of the first two stages (most often via NADH) and passes these electrons from one molecule to another. At the end of the chain, the electrons are combined with molecular oxygen and hydrogen ions (H+), forming wat ...
... respiration, the electron transport chain accepts electrons from the breakdown products of the first two stages (most often via NADH) and passes these electrons from one molecule to another. At the end of the chain, the electrons are combined with molecular oxygen and hydrogen ions (H+), forming wat ...
Enzymes: Basic Concepts and Kinetics
... 1. Michaelis-Menten enzyme kinetics: A simple model to explain the kinetic characteristics of enzymatic reactions was proposed by Leonor Michaelis and Maud Menten in 1913. According to this model, formation of the [ES] complex intermediate is essential for the enzymatic catalysis reaction to take pl ...
... 1. Michaelis-Menten enzyme kinetics: A simple model to explain the kinetic characteristics of enzymatic reactions was proposed by Leonor Michaelis and Maud Menten in 1913. According to this model, formation of the [ES] complex intermediate is essential for the enzymatic catalysis reaction to take pl ...
11-Electrophoretic method for the separation of LDH
... The final reaction of anaerobic (without oxygen) glycolysis is the conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid and this reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). In skeletal muscle, where oxygen deprivation is common during exercise, the reaction is efficient and large amounts of la ...
... The final reaction of anaerobic (without oxygen) glycolysis is the conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid and this reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). In skeletal muscle, where oxygen deprivation is common during exercise, the reaction is efficient and large amounts of la ...
Glycolysis - Rose
... Note that for glycolysis to proceed, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate must be formed, in spite of the fact that the ∆G´° for the formation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is positive. During glycolysis, the formation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate occurs because the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is immediately ...
... Note that for glycolysis to proceed, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate must be formed, in spite of the fact that the ∆G´° for the formation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is positive. During glycolysis, the formation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate occurs because the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is immediately ...
"Nitrogen Metabolism". In: Microbial Physiology (Fourth Edition)
... nitrogenase, nitrogenase 3, is encoded by alternate nitrogen fixation (anfHDK ) genes, which are expressed in A. vinelandii only in the absence of Mo and V. Dinitrogenase reductase 3 contains two identical subunits and dinitrogenase 3 is present in two active configurations, α2 β2 and α1 β2 . The re ...
... nitrogenase, nitrogenase 3, is encoded by alternate nitrogen fixation (anfHDK ) genes, which are expressed in A. vinelandii only in the absence of Mo and V. Dinitrogenase reductase 3 contains two identical subunits and dinitrogenase 3 is present in two active configurations, α2 β2 and α1 β2 . The re ...
Chapter 9
... – ATP synthase – enzyme that makes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate • It uses the energy of an existing gradient to do this. ...
... – ATP synthase – enzyme that makes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate • It uses the energy of an existing gradient to do this. ...
Chem 499 Final Exam Name
... charge would you expect on physostigmine at physiological pH (= 7.4)? If you think charge is present, redraw the structure to show this and explain your reasons. (4 pts) H ...
... charge would you expect on physostigmine at physiological pH (= 7.4)? If you think charge is present, redraw the structure to show this and explain your reasons. (4 pts) H ...
Modification of halogen specificity of a vanadium‐dependent
... activity of the enzyme from A. nodosum (0.49 U/mg) was much less than those of the mutant enzymes. In the case of the Corallina BPO mutants, which utilize chloride as a substrate, other parts of the protein molecule might play an important role in the progress of the enzyme reaction. The lack of act ...
... activity of the enzyme from A. nodosum (0.49 U/mg) was much less than those of the mutant enzymes. In the case of the Corallina BPO mutants, which utilize chloride as a substrate, other parts of the protein molecule might play an important role in the progress of the enzyme reaction. The lack of act ...
video slide - Buena Park High School
... • The electron transport chain – Passes electrons in a series of steps instead of in one explosive reaction – Uses the energy from the electron transfer to form ATP ...
... • The electron transport chain – Passes electrons in a series of steps instead of in one explosive reaction – Uses the energy from the electron transfer to form ATP ...
2.1 Chemistry’s Building Block: The Atom
... that they yield electrons that are carried to the ETC for the final high-yield stage of energy harvesting. ...
... that they yield electrons that are carried to the ETC for the final high-yield stage of energy harvesting. ...
Redox cycling
... only be donated by electron donors, and they can never “disappear” and can thereby only be transferred to electron acceptors Compounds that easily donate electrons have a tendency to reduce other compounds and are therefore often called reductants Compounds that easily take up electrons can ofte ...
... only be donated by electron donors, and they can never “disappear” and can thereby only be transferred to electron acceptors Compounds that easily donate electrons have a tendency to reduce other compounds and are therefore often called reductants Compounds that easily take up electrons can ofte ...
Metabolism & Enzymes
... Enzymes vocabulary substrate reactant which binds to enzyme enzyme-substrate complex: temporary association ...
... Enzymes vocabulary substrate reactant which binds to enzyme enzyme-substrate complex: temporary association ...
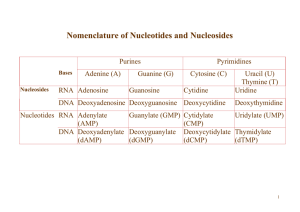
Nomenclature of Nucleotides and Nucleosides
... In glycogen storage disease type I (von Gierke's disease), a deficiency in glucose-6-phosphatase activity leads to an increase in cellular levels of ribose phosphates, which increases the levels of PRPP. The elevated levels of PRPP result in increased de novo synthesis of purines. Lesch-Nyhan syndr ...
... In glycogen storage disease type I (von Gierke's disease), a deficiency in glucose-6-phosphatase activity leads to an increase in cellular levels of ribose phosphates, which increases the levels of PRPP. The elevated levels of PRPP result in increased de novo synthesis of purines. Lesch-Nyhan syndr ...
3D Models Enzyme Student Handout
... each other like a lock and key in order to exert a chemical effect on each other.” Fisher created a mental model of how an enzyme acts and referred to it as the Lock and Key Model of Enzyme Action. This model suggests that the enzyme and the substrate possess specific complementary geometric shapes ...
... each other like a lock and key in order to exert a chemical effect on each other.” Fisher created a mental model of how an enzyme acts and referred to it as the Lock and Key Model of Enzyme Action. This model suggests that the enzyme and the substrate possess specific complementary geometric shapes ...
Essentials of Glycobiology Lecture 13 April 25th. 2000
... phosphotransferase that recognizes lpha1-2 linked Man residues, but it is not specific for lysosomal enzymes. Acanthamoeba produces a phosphotransferase that does show specific recognition of mammalian lysosomal enzymes. ...
... phosphotransferase that recognizes lpha1-2 linked Man residues, but it is not specific for lysosomal enzymes. Acanthamoeba produces a phosphotransferase that does show specific recognition of mammalian lysosomal enzymes. ...
Document
... mitochondrial biogenesis • Affects brain activity and indirectly physicial activity ...
... mitochondrial biogenesis • Affects brain activity and indirectly physicial activity ...
Pentose Phosphate Pathway - Berkeley MCB
... Mechanism. The lactone is opened by hydrolysis, the addition of water to cleave a bond, usually a type of amide or ester. In this case, since the lactone (by definition) is intramolecular, then 6-phosphoglucono-δ-lactone is opened up to the acid form, gluconate. ...
... Mechanism. The lactone is opened by hydrolysis, the addition of water to cleave a bond, usually a type of amide or ester. In this case, since the lactone (by definition) is intramolecular, then 6-phosphoglucono-δ-lactone is opened up to the acid form, gluconate. ...
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms, an oxidized and reduced form abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH respectively.In metabolism, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The coenzyme is, therefore, found in two forms in cells: NAD+ is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced. This reaction forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, the most notable one being a substrate of enzymes that add or remove chemical groups from proteins, in posttranslational modifications. Because of the importance of these functions, the enzymes involved in NAD metabolism are targets for drug discovery.In organisms, NAD can be synthesized from simple building-blocks (de novo) from the amino acids tryptophan or aspartic acid. In an alternative fashion, more complex components of the coenzymes are taken up from food as the vitamin called niacin. Similar compounds are released by reactions that break down the structure of NAD. These preformed components then pass through a salvage pathway that recycles them back into the active form. Some NAD is also converted into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP); the chemistry of this related coenzyme is similar to that of NAD, but it has different roles in metabolism.Although NAD+ is written with a superscript plus sign because of the formal charge on a particular nitrogen atom, at physiological pH for the most part it is actually a singly charged anion (charge of minus 1), while NADH is a doubly charged anion.