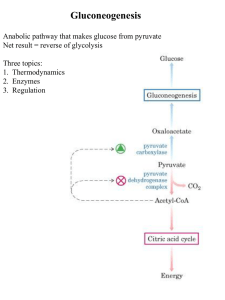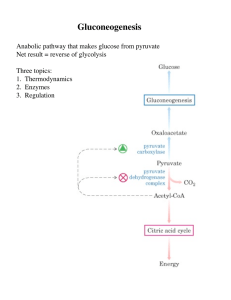
Gluconeogenesis - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... F2,6-BP Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to si ...
... F2,6-BP Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to si ...
No Slide Title
... F2,6-BP Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to si ...
... F2,6-BP Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to si ...
Enzymes - Weber State University
... from binding. It therefore reduces the number of ES complexes that may form, slowing the reaction velocity. Competitive inhibition can be overcome by increasing substrate concentration. Noncompetitive Inhibition: An inhibitor molecule binds to a different site other than the active site, decreasing ...
... from binding. It therefore reduces the number of ES complexes that may form, slowing the reaction velocity. Competitive inhibition can be overcome by increasing substrate concentration. Noncompetitive Inhibition: An inhibitor molecule binds to a different site other than the active site, decreasing ...
Enzymes
... from binding. It therefore reduces the number of ES complexes that may form, slowing the reaction velocity. Competitive inhibition can be overcome by increasing substrate concentration. Noncompetitive Inhibition: An inhibitor molecule binds to a different site other than the active site, decreasing ...
... from binding. It therefore reduces the number of ES complexes that may form, slowing the reaction velocity. Competitive inhibition can be overcome by increasing substrate concentration. Noncompetitive Inhibition: An inhibitor molecule binds to a different site other than the active site, decreasing ...
Flux Balance Analysis of Photoautotrophic
... experiments. This value is consistent with other reported values (22). The carbon balance (in the absence of overflow products) and the growth rate were then used to calculate the maximum CO2 uptake rate as 3.70 mmol CO2/g biomass/h. The maximum glucose uptake rate under heterotrophic conditions was ...
... experiments. This value is consistent with other reported values (22). The carbon balance (in the absence of overflow products) and the growth rate were then used to calculate the maximum CO2 uptake rate as 3.70 mmol CO2/g biomass/h. The maximum glucose uptake rate under heterotrophic conditions was ...
Enzymes - دانشکده پزشکی
... Some important characteristics of enzymes -Potent (high catalytic power) High reaction rates They increase the rate of reaction by a factor of 103-1012 -Efficient (high efficiency) catalytic efficiency is represented by Turnover number: moles of substrate converted to product per second per mole o ...
... Some important characteristics of enzymes -Potent (high catalytic power) High reaction rates They increase the rate of reaction by a factor of 103-1012 -Efficient (high efficiency) catalytic efficiency is represented by Turnover number: moles of substrate converted to product per second per mole o ...
Perspective: emerging evidence for signaling roles of mitochondrial
... glucose-induced insulin secretion, the rate of pyruvate carboxylation is very high and correlates more strongly with the glucose concentration the -cell is exposed to (and thus with insulin release) than does pyruvate decarboxylation, which produces acetyl-CoA for metabolism in the citric acid cycl ...
... glucose-induced insulin secretion, the rate of pyruvate carboxylation is very high and correlates more strongly with the glucose concentration the -cell is exposed to (and thus with insulin release) than does pyruvate decarboxylation, which produces acetyl-CoA for metabolism in the citric acid cycl ...
Gly - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... Generating ribose 5-P from oxidative branch, reverse reaction in Non-oxidative branch Used in muscle , where glucose 6-P dehydrogenase level is low and nucleotides are stored. ...
... Generating ribose 5-P from oxidative branch, reverse reaction in Non-oxidative branch Used in muscle , where glucose 6-P dehydrogenase level is low and nucleotides are stored. ...
REVIEW ARTICLE `New uses for an Old Enzyme
... & Karplus, 1994). Where the side-chains of residues contact the cofactor, these residues are conserved across the family. The residues lying immediately above the plane of the flavin ring, whether involved in catalysis as described above, or forming the hydrophobic substratebinding site, are also hi ...
... & Karplus, 1994). Where the side-chains of residues contact the cofactor, these residues are conserved across the family. The residues lying immediately above the plane of the flavin ring, whether involved in catalysis as described above, or forming the hydrophobic substratebinding site, are also hi ...
Ch. 23 Oxidation of fatty acids, ketones 1. Fatty acids are fuels:
... • FA oxidation gives NADH, FAD(2H) by βoxidation; TCA cycle -> high ATP/ADP, NADH/NAD+ and Acetyl CoA concentrations • AMP-dep PK adjusts [malonyl CoA] so CPT1 and β-oxidation operate as needed ...
... • FA oxidation gives NADH, FAD(2H) by βoxidation; TCA cycle -> high ATP/ADP, NADH/NAD+ and Acetyl CoA concentrations • AMP-dep PK adjusts [malonyl CoA] so CPT1 and β-oxidation operate as needed ...
The Effect of Oxygen on the Growth and Mannitol
... not affected but the cell yield was 0.53 A660 units. When catalase (3000 units m1-I) was added to the growth medium, no change in growth rate was observed, but the cell yield (0.26 A660 units) was slightly increased. The optimum concentration of pyruvate and catalase appeared to alleviate oxygen inh ...
... not affected but the cell yield was 0.53 A660 units. When catalase (3000 units m1-I) was added to the growth medium, no change in growth rate was observed, but the cell yield (0.26 A660 units) was slightly increased. The optimum concentration of pyruvate and catalase appeared to alleviate oxygen inh ...
nucleicacidmetabolism
... dephosphorylations can and do occur ADP and GDP can be reduced to dADP and dGDP AMP can deaminated to IMP (new) IMP can be aminated to AMP IMP can oxidized to XMP XMP can be aminated to GMP Guanine, adenine can be phosphoribosylated to GMP and AMP Nucleic Acid Metabolism ...
... dephosphorylations can and do occur ADP and GDP can be reduced to dADP and dGDP AMP can deaminated to IMP (new) IMP can be aminated to AMP IMP can oxidized to XMP XMP can be aminated to GMP Guanine, adenine can be phosphoribosylated to GMP and AMP Nucleic Acid Metabolism ...
Biochemical properties and structural features of the thermostable
... A and B. Residues of both these domains participate in substrate binding. The three catalyticallyessential acidic residues are located at the Cterminal ends of three β-strands of the (β/α)8 barrel of domain A. In MTase these catalytic residues, which are conserved in the primary structures of all en ...
... A and B. Residues of both these domains participate in substrate binding. The three catalyticallyessential acidic residues are located at the Cterminal ends of three β-strands of the (β/α)8 barrel of domain A. In MTase these catalytic residues, which are conserved in the primary structures of all en ...
Fructose 6-Phosphate
... enzyme lactase, which cleaves lactose into glucose and galactose. Microorganisms in the colon ferment undigested lactose to lactic acid generating methane (CH4) and hydrogen gas (H2). The gas produced creates the uncomfortable feeling of gut distention and the annoying problem of flatulence. The lac ...
... enzyme lactase, which cleaves lactose into glucose and galactose. Microorganisms in the colon ferment undigested lactose to lactic acid generating methane (CH4) and hydrogen gas (H2). The gas produced creates the uncomfortable feeling of gut distention and the annoying problem of flatulence. The lac ...
Teacher Key - 3D Molecular Designs
... You may use the foam pieces to simulate the activation energy needed in a reaction with and without an enzyme. Begin by connecting the green foam pieces. To illustrate the activation energy without the enzyme interaction, pull the apart the two green pieces with your hands. Reconnect the green piece ...
... You may use the foam pieces to simulate the activation energy needed in a reaction with and without an enzyme. Begin by connecting the green foam pieces. To illustrate the activation energy without the enzyme interaction, pull the apart the two green pieces with your hands. Reconnect the green piece ...
ppt
... • Explain how fatty acids are a major fuel source, especially after fasting • Explain how liver makes ketone bodies, fuel for other cells • Describe the basic categories of fatty acids: VLC, LC, med • Explain b-oxidation pathway of fatty acids • Describe the role of the peroxisome for VLCFA ...
... • Explain how fatty acids are a major fuel source, especially after fasting • Explain how liver makes ketone bodies, fuel for other cells • Describe the basic categories of fatty acids: VLC, LC, med • Explain b-oxidation pathway of fatty acids • Describe the role of the peroxisome for VLCFA ...
Anatomy of a Cell :
... Finally, consider the cytoplasm. Once considered merely the aqueous environment in which the “important” molecules or organelles floated, it is now better understood to be filled with important structural and transport elements (fig. 4). The cytoskeleton provides not only an internal physical struct ...
... Finally, consider the cytoplasm. Once considered merely the aqueous environment in which the “important” molecules or organelles floated, it is now better understood to be filled with important structural and transport elements (fig. 4). The cytoskeleton provides not only an internal physical struct ...
LIPID MOBILIZATION
... protein transporters on the cell surface – fatty acid translocase (FAT/CD36), – tissue specific fatty acid transport proteins (FATP), – plasma membrane bound fatty acid binding protein (FABPpm) ...
... protein transporters on the cell surface – fatty acid translocase (FAT/CD36), – tissue specific fatty acid transport proteins (FATP), – plasma membrane bound fatty acid binding protein (FABPpm) ...
Electrone transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation
... electron transport chain (ETC) is used to produce ATP from ADP +Pi. Electron transport is coupled to the phosphorylation of ADP by the transfer "pumping" of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane from matrix to the intermembrane space at complexes I,III, and IV. This process creates an elec ...
... electron transport chain (ETC) is used to produce ATP from ADP +Pi. Electron transport is coupled to the phosphorylation of ADP by the transfer "pumping" of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane from matrix to the intermembrane space at complexes I,III, and IV. This process creates an elec ...
Cell Respiration Review 1
... pathways. In some bacteria and muscle cells, pyruvate is converted into such products as (2) ________. In yeast cells it is converted into (3) ________ and carbon dioxide. Anaerobic pathways do not use oxygen as the final (4) ________ acceptor that ultimately drives the ATPforming machinery. Anaerob ...
... pathways. In some bacteria and muscle cells, pyruvate is converted into such products as (2) ________. In yeast cells it is converted into (3) ________ and carbon dioxide. Anaerobic pathways do not use oxygen as the final (4) ________ acceptor that ultimately drives the ATPforming machinery. Anaerob ...
Science Course Outline Template
... coverage of intermediary metabolism. Major topics covered include: the nature and functions of enzymes; the metabolic working of cells, tissues and organs; the interrelationships between pathways of carbohydrate, lipid and amino acid metabolism; the vital roles of enzymes and hormones in catalysis a ...
... coverage of intermediary metabolism. Major topics covered include: the nature and functions of enzymes; the metabolic working of cells, tissues and organs; the interrelationships between pathways of carbohydrate, lipid and amino acid metabolism; the vital roles of enzymes and hormones in catalysis a ...
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Bacterial class A acid
... essential part in photosynthesis, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, the nitrogen cycle, immune response, host-pathogen interactions, transmembrane signaling, activation of metabolites, cellular control by protein phosphorylation and in numerous other biochemical reactions. Further, phosphorus is pa ...
... essential part in photosynthesis, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, the nitrogen cycle, immune response, host-pathogen interactions, transmembrane signaling, activation of metabolites, cellular control by protein phosphorylation and in numerous other biochemical reactions. Further, phosphorus is pa ...
Pyruvate Oxidation Overview of pyruvate metabolism - Rose
... possible for the pyruvate concentration inside the mitochondria to be higher than outside. The energy for the pump comes from a proton gradient, in which the proton concentration outside the mitochondria is higher than it is inside. Many other molecules are present only on one side of the membrane, ...
... possible for the pyruvate concentration inside the mitochondria to be higher than outside. The energy for the pump comes from a proton gradient, in which the proton concentration outside the mitochondria is higher than it is inside. Many other molecules are present only on one side of the membrane, ...
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme found in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide, because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base and the other nicotinamide. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide exists in two forms, an oxidized and reduced form abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH respectively.In metabolism, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The coenzyme is, therefore, found in two forms in cells: NAD+ is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced. This reaction forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, the most notable one being a substrate of enzymes that add or remove chemical groups from proteins, in posttranslational modifications. Because of the importance of these functions, the enzymes involved in NAD metabolism are targets for drug discovery.In organisms, NAD can be synthesized from simple building-blocks (de novo) from the amino acids tryptophan or aspartic acid. In an alternative fashion, more complex components of the coenzymes are taken up from food as the vitamin called niacin. Similar compounds are released by reactions that break down the structure of NAD. These preformed components then pass through a salvage pathway that recycles them back into the active form. Some NAD is also converted into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP); the chemistry of this related coenzyme is similar to that of NAD, but it has different roles in metabolism.Although NAD+ is written with a superscript plus sign because of the formal charge on a particular nitrogen atom, at physiological pH for the most part it is actually a singly charged anion (charge of minus 1), while NADH is a doubly charged anion.