Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... MODEL OF THE ATOM ESSENTIAL QUESTION: WHAT IS THE CURRENT MODEL OF THE ATOM? ...
... MODEL OF THE ATOM ESSENTIAL QUESTION: WHAT IS THE CURRENT MODEL OF THE ATOM? ...
homework answers - SPHS Devil Physics
... k. What was the purpose of the ‘Electron In A Box’ mind experiment? l. Explain Schrödinger’s quantum model for the behaviour of electrons in atoms. ...
... k. What was the purpose of the ‘Electron In A Box’ mind experiment? l. Explain Schrödinger’s quantum model for the behaviour of electrons in atoms. ...
Document
... X-rays were so named because they came from the element xenon. Rutherford suggested that the atom was mainly empty space. A neutron is a subatomic particle having no charge and a mass about the same as the electron. The Bohr model says that there is a small nucleus containing the positive charge and ...
... X-rays were so named because they came from the element xenon. Rutherford suggested that the atom was mainly empty space. A neutron is a subatomic particle having no charge and a mass about the same as the electron. The Bohr model says that there is a small nucleus containing the positive charge and ...
107 chem Assement Q
... c. fundamental state. d. original state. 5. The hydrogen emission spectrum includes light with a wavelength of 434 nanometers. This is caused by an electron moving from: a. the n = 3 state to the n = 2 state. b. the n = 4 state to the n = 2 state. c. the n = 5 state to the n = 2 state. d. the n = 6 ...
... c. fundamental state. d. original state. 5. The hydrogen emission spectrum includes light with a wavelength of 434 nanometers. This is caused by an electron moving from: a. the n = 3 state to the n = 2 state. b. the n = 4 state to the n = 2 state. c. the n = 5 state to the n = 2 state. d. the n = 6 ...
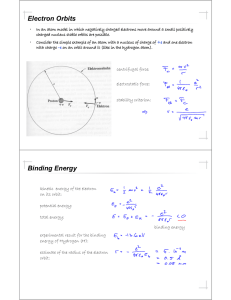
energy levels
... March 22 The nuclear atom 39.2 The nuclear atom and atomic spectra Atomic line spectra: • A discrete line emission spectrum is observed when a low-pressure gas sample is subjected to an electric discharge. • An absorption spectrum is obtained by passing a white light from a continuous source throug ...
... March 22 The nuclear atom 39.2 The nuclear atom and atomic spectra Atomic line spectra: • A discrete line emission spectrum is observed when a low-pressure gas sample is subjected to an electric discharge. • An absorption spectrum is obtained by passing a white light from a continuous source throug ...
Atomic Spectra
... E R 2 2 , where the Rydberg constant R (40 ) 2 h 2 nl nh reduced mass of the electron/nucleus combination, and 4 0 is the permittivity of a vacuum, ( 4 0 )-1 = 8.98755 × 109 J m/C2. The Ritz combination principle states that the wave number of any spectral line (of any atom, no ...
... E R 2 2 , where the Rydberg constant R (40 ) 2 h 2 nl nh reduced mass of the electron/nucleus combination, and 4 0 is the permittivity of a vacuum, ( 4 0 )-1 = 8.98755 × 109 J m/C2. The Ritz combination principle states that the wave number of any spectral line (of any atom, no ...
Page | 1 MATS1101 Chemistry notes semester 2 2012 TOPIC 1
... Using this theory we can explain three fundamental laws of chemical behaviour: 1. Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy: Matter is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Energy is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, but it may be transformed from one form to another. ...
... Using this theory we can explain three fundamental laws of chemical behaviour: 1. Law of Conservation of Mass and Energy: Matter is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Energy is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, but it may be transformed from one form to another. ...
History of Atomic theory
... E. Used wave equations to determine the energy states of matter. His theories led to the development of the secondary quantum number. F. He determined that particles of matter (electrons) also exhibit wave characteristics. G. His uncertainty principle stated that we (the observer) can never exactly ...
... E. Used wave equations to determine the energy states of matter. His theories led to the development of the secondary quantum number. F. He determined that particles of matter (electrons) also exhibit wave characteristics. G. His uncertainty principle stated that we (the observer) can never exactly ...
4.1-Models of the Atom
... Rutherford Model •Around 1911 Rutherford, Marsden and Geiger performed experiments to test the Thomson model •Alpha particles from radioactive sources were directed at ...
... Rutherford Model •Around 1911 Rutherford, Marsden and Geiger performed experiments to test the Thomson model •Alpha particles from radioactive sources were directed at ...
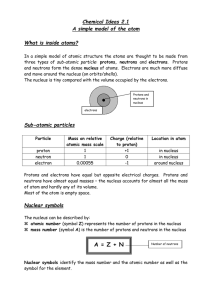
CHAPTER 2 ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS 1 CHAPTER TWO
... a. The smaller parts are electrons and the nucleus. The nucleus is broken down into protons and neutrons which can be broken down into quarks. For our purpose, electrons, neutrons, and protons are the key smaller parts of an atom. b. All atoms of hydrogen have 1 proton in the nucleus. Different isot ...
... a. The smaller parts are electrons and the nucleus. The nucleus is broken down into protons and neutrons which can be broken down into quarks. For our purpose, electrons, neutrons, and protons are the key smaller parts of an atom. b. All atoms of hydrogen have 1 proton in the nucleus. Different isot ...
Chem20u2(5.2) - Mr. Searcy Chemistry 20
... 3. Compare the Bohr and quantum mechanical models of the atom. 4. Explain the impact of de Broglie’s wave-particle duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the modern view of electrons in atoms. 5. Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom’s energy levels, sublevels, and atomic orb ...
... 3. Compare the Bohr and quantum mechanical models of the atom. 4. Explain the impact of de Broglie’s wave-particle duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the modern view of electrons in atoms. 5. Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom’s energy levels, sublevels, and atomic orb ...
Document
... In this reaction two light atomic nuclei, when they are very close to each other, fuse together to form a single heavier nucleus of a new element. The process is exothermic (release of energy). The nuclear fusions occur at only very high temperatures. When 2 hydrogen nuclei fuse together by nuclear ...
... In this reaction two light atomic nuclei, when they are very close to each other, fuse together to form a single heavier nucleus of a new element. The process is exothermic (release of energy). The nuclear fusions occur at only very high temperatures. When 2 hydrogen nuclei fuse together by nuclear ...
Chemistry 1000 Lecture 6: Quantum mechanics and spectroscopy
... Nuclear reactors produce a lot of “thermal” neutrons. These are neutrons which have been equilibrated to a temperature near room temperature. Typically, such neutrons travel at speeds of 2.2 km/s or so. The mass of a neutron is 1.6750 × 10−27 kg. ∴ p = mv = (1.6750 × 10−27 kg)(2.2 × 103 m/s) = 3.7 × ...
... Nuclear reactors produce a lot of “thermal” neutrons. These are neutrons which have been equilibrated to a temperature near room temperature. Typically, such neutrons travel at speeds of 2.2 km/s or so. The mass of a neutron is 1.6750 × 10−27 kg. ∴ p = mv = (1.6750 × 10−27 kg)(2.2 × 103 m/s) = 3.7 × ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.