atoms
... The high voltage source of electricity creates a (-) charge on the electrode at the left (cathode) and a (+) charge on the electrode at the right (anode) Cathode rays pass from the cathode (C) to the anode (A) which is perforated to allow the passage of a narrow beam of the cathode rays They are ...
... The high voltage source of electricity creates a (-) charge on the electrode at the left (cathode) and a (+) charge on the electrode at the right (anode) Cathode rays pass from the cathode (C) to the anode (A) which is perforated to allow the passage of a narrow beam of the cathode rays They are ...
atoms
... The high voltage source of electricity creates a (-) charge on the electrode at the left (cathode) and a (+) charge on the electrode at the right (anode) Cathode rays pass from the cathode (C) to the anode (A) which is perforated to allow the passage of a narrow beam of the cathode rays They are ...
... The high voltage source of electricity creates a (-) charge on the electrode at the left (cathode) and a (+) charge on the electrode at the right (anode) Cathode rays pass from the cathode (C) to the anode (A) which is perforated to allow the passage of a narrow beam of the cathode rays They are ...
vocab chap 6
... packed nucleus and that atoms are mostly empty space; also discovered the proton ...
... packed nucleus and that atoms are mostly empty space; also discovered the proton ...
Chemistry--Chapter 5: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... 9.10939 × 10–28 g); charge and mass of electron determined by Robert Millikan in 1916 B. Protons and Neutrons 1. Protons have a positive charge, cathode ray tube again used in discovery, have a mass about 1840 times that of an electron or 1.67 x 10-24g (more precisely, 1.67262 × 10–24 g) 2. Neutrons ...
... 9.10939 × 10–28 g); charge and mass of electron determined by Robert Millikan in 1916 B. Protons and Neutrons 1. Protons have a positive charge, cathode ray tube again used in discovery, have a mass about 1840 times that of an electron or 1.67 x 10-24g (more precisely, 1.67262 × 10–24 g) 2. Neutrons ...
CHAPTER 1 Practice Exercises 1.1 12.3 g Cd 1.3 26.9814 u 1.5
... definite and unchanging proportion. A reactant is a chemical species which is transformed in a chemical reaction A chemical reaction is a process whereby one or more chemical species is/are transformed into different chemical species. This generally involves the making and/or breaking of chemical bo ...
... definite and unchanging proportion. A reactant is a chemical species which is transformed in a chemical reaction A chemical reaction is a process whereby one or more chemical species is/are transformed into different chemical species. This generally involves the making and/or breaking of chemical bo ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions C Kapler ` , , I 27 O//#W SELF
... - If a new alkaline earth were created, its ato number would most probably be (9) . ...
... - If a new alkaline earth were created, its ato number would most probably be (9) . ...
Preliminary Course Atomic Structure 1 + 2
... elements or compounds that are not bound together, it is called a MIXTURE. ...
... elements or compounds that are not bound together, it is called a MIXTURE. ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 17. This substance is nitrogen. 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny ind ...
... 17. This substance is nitrogen. 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny ind ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 17. This substance is nitrogen. 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny ind ...
... 17. This substance is nitrogen. 18. This substance is carbon. 19. This substance is an ion. 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny ind ...
CH4 PT1 Arrangement of Electrons
... electrons could be particles yet they gave off waves of light. • De Broglie suggested that electrons could be considered waves confined to space around a nucleus only at specific frequencies. • Diffraction experiments proved that electron beams can interfere with each other and produce areas of low ...
... electrons could be particles yet they gave off waves of light. • De Broglie suggested that electrons could be considered waves confined to space around a nucleus only at specific frequencies. • Diffraction experiments proved that electron beams can interfere with each other and produce areas of low ...
Notes on Atomic Structure atoms
... same proportions (by mass and by number) of its elements This means a given compound always has the same composition, regardless of where it came from. ...
... same proportions (by mass and by number) of its elements This means a given compound always has the same composition, regardless of where it came from. ...
File
... b. cannot be broken down further. c. are all composed of carbon. d. have no mass. _____ 2. Using improved chemistry equipment in the late 1700s, chemists observed that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This scientific law is called the law of a. definite proportions. b. g ...
... b. cannot be broken down further. c. are all composed of carbon. d. have no mass. _____ 2. Using improved chemistry equipment in the late 1700s, chemists observed that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This scientific law is called the law of a. definite proportions. b. g ...
Chapter 18 Resource: Matter
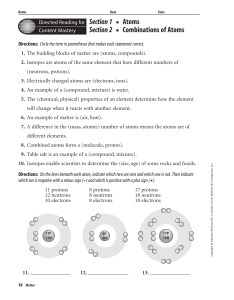
... 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an el ...
... 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an el ...
Lecture 5
... Hartree Approximation (mean field approximation) - electronelectron repulsion is replaced with average mean field potential. Many electron system is described in terms of hydrogen-like single electron states. n : principal quantum number (shell) l, m, s : angular momentum, magnetic momentum (z-compo ...
... Hartree Approximation (mean field approximation) - electronelectron repulsion is replaced with average mean field potential. Many electron system is described in terms of hydrogen-like single electron states. n : principal quantum number (shell) l, m, s : angular momentum, magnetic momentum (z-compo ...
Chapter 31 Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Physics
... no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of values for the four quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms. This principle determines the way in which the electrons in multiple-electron atoms are distributed into shells and subshells. The arrangement of the periodic table of the elements is related t ...
... no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of values for the four quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms. This principle determines the way in which the electrons in multiple-electron atoms are distributed into shells and subshells. The arrangement of the periodic table of the elements is related t ...
Chapter 5 Homework
... 6. Which is a possible explanation for why the neutron was the last of the three fundamental subatomic particles to be discovered? (a) The atoms of very few elements contain neutrons in their nuclei. (b) Its existence was not suspected until Rutherford's gold foil experiment. (c) It was difficult to ...
... 6. Which is a possible explanation for why the neutron was the last of the three fundamental subatomic particles to be discovered? (a) The atoms of very few elements contain neutrons in their nuclei. (b) Its existence was not suspected until Rutherford's gold foil experiment. (c) It was difficult to ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.