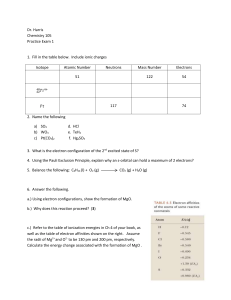
CHAPTER 1 Practice Exercises 1.1 x = 12.3 g Cd 1.3 2.24845 ×12 u
... definite ratios as atoms. This guarantees that elements combine in definite mass ratios, assuming the atoms are indestructible. ...
... definite ratios as atoms. This guarantees that elements combine in definite mass ratios, assuming the atoms are indestructible. ...
Corso di Fisica Moderna
... 1) An electron in an atom moves in a circular orbit about the nucleus under the influence of the Coulomb aNracAon between the electron and the nucleus, obeying the laws of classical mechanics. 2) Inst ...
... 1) An electron in an atom moves in a circular orbit about the nucleus under the influence of the Coulomb aNracAon between the electron and the nucleus, obeying the laws of classical mechanics. 2) Inst ...
physics 30 Matter assignment 4 - ND
... The thyroid gland uses iodine to make hormones that the human body needs. The thyroid gland is the only tissue in the human body that collects iodine. An overactive thyroid gland that causes medical problems can be treated with a high dose of iodine-131, which destroys the thyroid gland only. • A tr ...
... The thyroid gland uses iodine to make hormones that the human body needs. The thyroid gland is the only tissue in the human body that collects iodine. An overactive thyroid gland that causes medical problems can be treated with a high dose of iodine-131, which destroys the thyroid gland only. • A tr ...
The Atom - Effingham County Schools
... » Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form chemical compounds » In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged ...
... » Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form chemical compounds » In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged ...
Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy
... o Review of basic spectroscopy o Hydrogen energy levels o Fine structure o Spin-orbit coupling o Nuclear moments and hyperfine structure ...
... o Review of basic spectroscopy o Hydrogen energy levels o Fine structure o Spin-orbit coupling o Nuclear moments and hyperfine structure ...
The Atom
... Atoms of one element can combine with those of other elements to form compounds, and a given compound always has the same relative numbers (ratios) of types of atoms. • ie, H2O is a 2:1 ratio by mass and that ratio will not change ...
... Atoms of one element can combine with those of other elements to form compounds, and a given compound always has the same relative numbers (ratios) of types of atoms. • ie, H2O is a 2:1 ratio by mass and that ratio will not change ...
Physics 43 Ch 42 HW# Key
... Fz = z(dBz/dz). If a beam of silver atoms travels a horizontal distance of 1.00 m through such a field and each atom has a speed of 100 m/s, how strong must be the field gradient dBz/dz in order to deflect the beam 1.00 mm? ...
... Fz = z(dBz/dz). If a beam of silver atoms travels a horizontal distance of 1.00 m through such a field and each atom has a speed of 100 m/s, how strong must be the field gradient dBz/dz in order to deflect the beam 1.00 mm? ...
Chapter 5 Sec. 2 Bohr`s Model and the Quantum Mechanical Model
... Bohr’s model. He explained that electrons can act like _____________________________. He also showed that electrons on circular orbits can only have _____________________ numbers of wavelengths. o de Broglie predicted that all moving particles have wave characteristics. de Broglie knew that if a ...
... Bohr’s model. He explained that electrons can act like _____________________________. He also showed that electrons on circular orbits can only have _____________________ numbers of wavelengths. o de Broglie predicted that all moving particles have wave characteristics. de Broglie knew that if a ...
Chapter 2 part 1
... • Atom: The smallest part of an element that displays the properties of the element. • Atoms are made up of subatomic particles. ...
... • Atom: The smallest part of an element that displays the properties of the element. • Atoms are made up of subatomic particles. ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... Atoms and Subatomic Particles Atom. Al matter is made up of unique particles called atoms. An atom contains: o Protons- Positively charged; have atomic mass of one; Located in the nucleus of the atom. o Neutrons- Neutral in charge; the same mass as the proton; also located in the nucleus of the at ...
... Atoms and Subatomic Particles Atom. Al matter is made up of unique particles called atoms. An atom contains: o Protons- Positively charged; have atomic mass of one; Located in the nucleus of the atom. o Neutrons- Neutral in charge; the same mass as the proton; also located in the nucleus of the at ...
File
... Its a molecule made of a metal and one or more non-metals. In this type of compounds, there is a transfer of e-→ The metal loses e- and the non-metals gains e- to form an ionic bond. Physical Properties ...
... Its a molecule made of a metal and one or more non-metals. In this type of compounds, there is a transfer of e-→ The metal loses e- and the non-metals gains e- to form an ionic bond. Physical Properties ...
The Atomic Theory
... Law of Multiple Proportions: If two elements combine to form more than one compound the different weights of one which combine with the same weight of the other are in the ration of small whole numbers. Law of Reciprocal Proportions: The weights of two (or more) substances which react separately wit ...
... Law of Multiple Proportions: If two elements combine to form more than one compound the different weights of one which combine with the same weight of the other are in the ration of small whole numbers. Law of Reciprocal Proportions: The weights of two (or more) substances which react separately wit ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.