Atoms, Elements, Compounds File
... An element is a form of matter made up of one type of atom. The atoms of an element are basically alike, though the number of neutrons may vary. The atoms of one element differ from those of another element in the number of protons. Elements can be represented by chemical symbols. ...
... An element is a form of matter made up of one type of atom. The atoms of an element are basically alike, though the number of neutrons may vary. The atoms of one element differ from those of another element in the number of protons. Elements can be represented by chemical symbols. ...
SEMESTER 1 EXAM Prblms/Short Ans
... Eq, S, U, SF – Equations; Show all equations used in all calculations. Steps; show each step leading to each answer. Units; show the appropriate units with each number used in all calculations. SF; Use the correct significant figures when expressing all answers. Use Scientific Notation for all numbe ...
... Eq, S, U, SF – Equations; Show all equations used in all calculations. Steps; show each step leading to each answer. Units; show the appropriate units with each number used in all calculations. SF; Use the correct significant figures when expressing all answers. Use Scientific Notation for all numbe ...
Unit 2: Atom - newshamchemistry
... textbook, pg 865 & 871-873, there are reading and note taking techniques available. What to include in your notes: 1. Democritus Over to ...
... textbook, pg 865 & 871-873, there are reading and note taking techniques available. What to include in your notes: 1. Democritus Over to ...
File
... products are on the right side of the arrow. The mass of the reactants equals 80g and the mass of the products equals 80g (Law of conservation of mass). You should also notice that in CH4 there is one Carbon atom, and four hydrogen atoms (Law of definite proportions). Electrolysis Reactions: Carri ...
... products are on the right side of the arrow. The mass of the reactants equals 80g and the mass of the products equals 80g (Law of conservation of mass). You should also notice that in CH4 there is one Carbon atom, and four hydrogen atoms (Law of definite proportions). Electrolysis Reactions: Carri ...
Atoms and Elements
... putting electrons into orbitals that have the same energy as each other. Put one electron into each orbital before pairing them up. Whichever way the first arrow (electron) points, the others must point the same way until they pair up, then they point in opposite directions. ...
... putting electrons into orbitals that have the same energy as each other. Put one electron into each orbital before pairing them up. Whichever way the first arrow (electron) points, the others must point the same way until they pair up, then they point in opposite directions. ...
Glowing Tubes for Signs, Television Sets, and Computers
... Thomson’s cathode ray tube has many modern applications. For example, “neon” signs consist of small-diameter cathode ray tubes containing different kinds of gases to produce various colors. For example, if the gas in the tube is neon, the tube glows with a red–orange color; if argon is present, a bl ...
... Thomson’s cathode ray tube has many modern applications. For example, “neon” signs consist of small-diameter cathode ray tubes containing different kinds of gases to produce various colors. For example, if the gas in the tube is neon, the tube glows with a red–orange color; if argon is present, a bl ...
Review Chemistry KEY - cms16-17
... 11. Why are valence electrons important? Valence electrons are used for bonding, therefore they determine how elements will react with with other substances. TEKS 5C_Interpret the arrangement of the Periodic Table, including groups and periods to explain how properties are used to classify elements. ...
... 11. Why are valence electrons important? Valence electrons are used for bonding, therefore they determine how elements will react with with other substances. TEKS 5C_Interpret the arrangement of the Periodic Table, including groups and periods to explain how properties are used to classify elements. ...
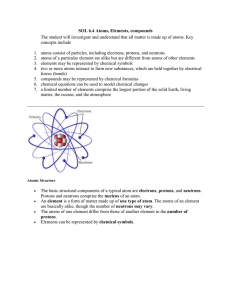
Matter is made of atoms The atom of each element is characterized
... The spectral lines can be resolved with a prism or a diffraction grating. Multi-electron atoms are complicated. Rules to be learned about later limit the number of electrons in any one state. Thus the electrons in an atom are arranged in concentric shells. The shells are labelled K, L, M, N, etc., s ...
... The spectral lines can be resolved with a prism or a diffraction grating. Multi-electron atoms are complicated. Rules to be learned about later limit the number of electrons in any one state. Thus the electrons in an atom are arranged in concentric shells. The shells are labelled K, L, M, N, etc., s ...
Foundations of Atomic Theory
... size, mass, and other properties: atoms of Dalton’s Atomic Theory different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 5. In chemical reacti ...
... size, mass, and other properties: atoms of Dalton’s Atomic Theory different elements differ in size, mass, and other properties 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 5. In chemical reacti ...
Ch. 2-1 Nature of Matter
... Matter is Made of Atoms • Atom—smallest unit of matter that cannot be broken down by chemical means • Made up of subatomic particles – protons – neutrons – electrons ...
... Matter is Made of Atoms • Atom—smallest unit of matter that cannot be broken down by chemical means • Made up of subatomic particles – protons – neutrons – electrons ...
CHAPTER 4: Structure of the Atom
... Various Greek (and Indian) philosophers had only a few elements, concept of an atom that is indivisible smallest unit of any form of matter Various atoms and molecules as depicted in John Dalton's ”A New System of Chemical Philosophy” (1808). Law of constant proportion in chemical reactions, atoms ...
... Various Greek (and Indian) philosophers had only a few elements, concept of an atom that is indivisible smallest unit of any form of matter Various atoms and molecules as depicted in John Dalton's ”A New System of Chemical Philosophy” (1808). Law of constant proportion in chemical reactions, atoms ...
PS7 - Bergen.org
... 7-1Use the details of modern atomic theory to explain each of the following experimental observations. Please note that the "octet rule" is not part of modern atomic theory. (a) The radius of the chlorine atom is smaller than the radius of the chloride ion, Cl-. (Radii: Cl atom = 0.099 nm; Cl- ion = ...
... 7-1Use the details of modern atomic theory to explain each of the following experimental observations. Please note that the "octet rule" is not part of modern atomic theory. (a) The radius of the chlorine atom is smaller than the radius of the chloride ion, Cl-. (Radii: Cl atom = 0.099 nm; Cl- ion = ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. B) Atoms are made of smaller particles of positive, neutral ...
... 20. This substance is an isotope of carbon-12 (12C) 21. The Atomic Theory was first stated in the late 1700s. Which of the following is NOT part of this Atomic Theory? A) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. B) Atoms are made of smaller particles of positive, neutral ...
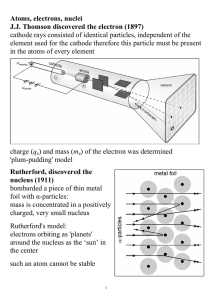
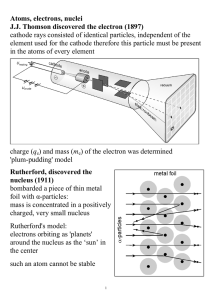
Atoms, electrons, nuclei J.J. Thomson discovered the electron (1897
... Davisson and Germer (1927) used electron beams to induce diffraction through a thin metal foil: interference interference phenomena have been shown with various other particles: duality is a general characteristic of matter Propagation law of free electrons state function ψ(x,t); we can ‘find’ the e ...
... Davisson and Germer (1927) used electron beams to induce diffraction through a thin metal foil: interference interference phenomena have been shown with various other particles: duality is a general characteristic of matter Propagation law of free electrons state function ψ(x,t); we can ‘find’ the e ...
1to7
... That electrons each contain a specific amount of energy as defined by their orbit. The further out the electron orbits, more energy the electron has. Orbits are fixed distances. ...
... That electrons each contain a specific amount of energy as defined by their orbit. The further out the electron orbits, more energy the electron has. Orbits are fixed distances. ...
1-7-
... That electrons each contain a specific amount of energy as defined by their orbit. The further out the electron orbits, more energy the electron has. Orbits are fixed distances. ...
... That electrons each contain a specific amount of energy as defined by their orbit. The further out the electron orbits, more energy the electron has. Orbits are fixed distances. ...
F. The Quantum Atom Theory - River Dell Regional School District
... size, mass, but differ from those of other elements*. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided or destroyed*. ( supports law of conservation of mass) 4.Atoms combine in small whole number ratios to form compounds. (def comp,Mult prop) 5. Atoms combine, separate, or rearrange in chemical reactions. * Modified i ...
... size, mass, but differ from those of other elements*. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided or destroyed*. ( supports law of conservation of mass) 4.Atoms combine in small whole number ratios to form compounds. (def comp,Mult prop) 5. Atoms combine, separate, or rearrange in chemical reactions. * Modified i ...
chapter 3
... … These deductions were later verified by Geiger and Marsden in a series of beautiful experiments. explanation, all the positive charge there is in an atom is concentrated in a tiny core, if α particle heads straight for the core, electric repulsion becomes large and particle is scattered back, all ...
... … These deductions were later verified by Geiger and Marsden in a series of beautiful experiments. explanation, all the positive charge there is in an atom is concentrated in a tiny core, if α particle heads straight for the core, electric repulsion becomes large and particle is scattered back, all ...
Fundamentals Fall Final Review
... mass of 57 amu. Calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom of this isotope. How would you write the isotope symbol for this isotope of iron? 22. When given the isotope symbol for an element be able to give its number of protons, electrons and neutrons. As an example: Give the ...
... mass of 57 amu. Calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom of this isotope. How would you write the isotope symbol for this isotope of iron? 22. When given the isotope symbol for an element be able to give its number of protons, electrons and neutrons. As an example: Give the ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.