chapt02_lecture from text
... between the partially negative O atoms and the partially positive H atoms of two water ...
... between the partially negative O atoms and the partially positive H atoms of two water ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 15
... Planck derived a formula that described the distribution of ...
... Planck derived a formula that described the distribution of ...
Lecture 7 - United International College
... (usually atoms or molecules) in one mole. For example. the number of atoms in exactly 12 grams of carbon-12 is 6.022X10^23. ...
... (usually atoms or molecules) in one mole. For example. the number of atoms in exactly 12 grams of carbon-12 is 6.022X10^23. ...
Name: Date: Chemistry Enriched Per. ______ Midterm Review
... Apply the law of conservation of matter: If 18 grams of water is decomposed and 16 grams of oxygen are produced, how many grams of hydrogen were produced? ...
... Apply the law of conservation of matter: If 18 grams of water is decomposed and 16 grams of oxygen are produced, how many grams of hydrogen were produced? ...
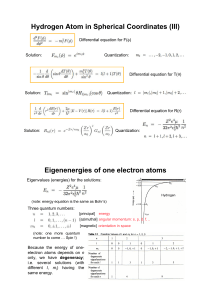
Hydrogen Atom in Spherical Coordinates (III) Eigenenergies of one
... Angular Functions : Spherical Harmonics ...
... Angular Functions : Spherical Harmonics ...
Branches of Chemistry
... According to this law, the total mass of the products of a chemical reaction is equal to the total mass of the substances that react together. Law of constant composition – No matter how a substance is made, it will always contain the same elements in the same proportions. [Joseph Proust, 1779] By P ...
... According to this law, the total mass of the products of a chemical reaction is equal to the total mass of the substances that react together. Law of constant composition – No matter how a substance is made, it will always contain the same elements in the same proportions. [Joseph Proust, 1779] By P ...
Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... a photon knocks the electron off its course. • The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. ...
... a photon knocks the electron off its course. • The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. ...
Chapter 3
... finding an electron at various locations around the nucleus of. An atomic orbitals is represented pictorially as a region of space in which there is a high probably of finding an electron. ...
... finding an electron at various locations around the nucleus of. An atomic orbitals is represented pictorially as a region of space in which there is a high probably of finding an electron. ...
sch3u unit 1 test: matter
... a. lose electrons b. gain electrons c. share electrons d. lose protons 10. Copper (II) hydroxide is composed of a. 2 elements, 2 atoms b. 2 elements, 3 atoms c. 3 elements, 4 atoms d. 3 elements, 5 atoms ...
... a. lose electrons b. gain electrons c. share electrons d. lose protons 10. Copper (II) hydroxide is composed of a. 2 elements, 2 atoms b. 2 elements, 3 atoms c. 3 elements, 4 atoms d. 3 elements, 5 atoms ...
LESSON No. 2 – Structure of atom
... Q.1>Give one word :(1) Any thing that home mass and occupies space:(2) A drug which lower body temperature in high fever:(3) Name of life-saving dugs:(4) A matter which is the combination of two or more elements(5) An element which have both metal and non-metal character(6) SI unit of temperature(7) ...
... Q.1>Give one word :(1) Any thing that home mass and occupies space:(2) A drug which lower body temperature in high fever:(3) Name of life-saving dugs:(4) A matter which is the combination of two or more elements(5) An element which have both metal and non-metal character(6) SI unit of temperature(7) ...
The stability of an atom depends on the ratio and number of protons
... available either for a newly created radiation particle within the nucleus or via internal conversion. During this process, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. Radioactive decay results in the emission of gamma rays and/or subatomic particles such as alpha or beta particles, as sh ...
... available either for a newly created radiation particle within the nucleus or via internal conversion. During this process, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. Radioactive decay results in the emission of gamma rays and/or subatomic particles such as alpha or beta particles, as sh ...
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Models of the Atom The
... Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Models of the Atom The Development of Atomic Models The model for the atom consisted of protons and neutrons making up a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The Bohr Model Bohr proposed that an ______________ is found only in specific circular paths, or orbits, around t ...
... Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Models of the Atom The Development of Atomic Models The model for the atom consisted of protons and neutrons making up a nucleus surrounded by electrons. The Bohr Model Bohr proposed that an ______________ is found only in specific circular paths, or orbits, around t ...
Chapter 30: The Nature of the Atom Very schematic picture of an atom
... Prob. 30.6: There are Z protons in the nucleus of an atom, where Z is the atomic number of the element. An ! particle (nucleus of He atom) carries a charge +2e. In a scattering experiment, an ! particle, heading directly toward a nucleus in a metal foil, will come to a halt when all the particle’s k ...
... Prob. 30.6: There are Z protons in the nucleus of an atom, where Z is the atomic number of the element. An ! particle (nucleus of He atom) carries a charge +2e. In a scattering experiment, an ! particle, heading directly toward a nucleus in a metal foil, will come to a halt when all the particle’s k ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.