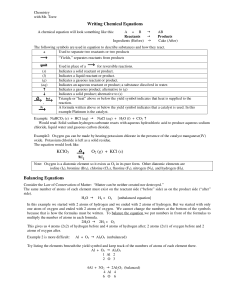
Writing Chemical Equations KClO3 O2 (g) + KCl (s) Balancing
... Indicates an aqueous reactant or product; a substance dissolved in water. Indicates a gaseous product; alternative to (g) Indicates a solid product; alternative to (s) Triangle or “heat” above or below the yield symbol indicates that heat is supplied to the ...
... Indicates an aqueous reactant or product; a substance dissolved in water. Indicates a gaseous product; alternative to (g) Indicates a solid product; alternative to (s) Triangle or “heat” above or below the yield symbol indicates that heat is supplied to the ...
Ch 4 Review
... c. characteristics that can be observed without changing the composition of the substance d. subatomic particle without charge e. positively charged subatomic particle ____ 30. chemical properties ____ 31. neutron ____ 32. proton ____ 33. physical properties ____ 34. electron Match each item with th ...
... c. characteristics that can be observed without changing the composition of the substance d. subatomic particle without charge e. positively charged subatomic particle ____ 30. chemical properties ____ 31. neutron ____ 32. proton ____ 33. physical properties ____ 34. electron Match each item with th ...
Chapter 7: Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
... Nature of Matter & Energy • Louis deBroglie – used work of Planck & Einstein to propose the wave-particle duality concept. • He suggested waves can behave as particles and particles can behave as waves. • For a particle ...
... Nature of Matter & Energy • Louis deBroglie – used work of Planck & Einstein to propose the wave-particle duality concept. • He suggested waves can behave as particles and particles can behave as waves. • For a particle ...
Chemistry Pretest
... Chemistry Pretest This is to tell me how much time we need to spend reviewing in the first unit-- it is only a “For Credit” grade— you will not be marked down for incorrect answers! 1. Define Matter: 2. What is the formula for density? 3. Define “solid,” as in the phase of matter. 4. Define “liquid, ...
... Chemistry Pretest This is to tell me how much time we need to spend reviewing in the first unit-- it is only a “For Credit” grade— you will not be marked down for incorrect answers! 1. Define Matter: 2. What is the formula for density? 3. Define “solid,” as in the phase of matter. 4. Define “liquid, ...
Atoms, Ions, and Molecules File
... • The mass/charge ratio was measured by J.J. Thomson using a cathode ray tube. • The charge of an electron was measured in a famous experiment by Robert Millikan. • The mass of an electron was found to be about 2000 times less than the lightest atom (hydrogen). ...
... • The mass/charge ratio was measured by J.J. Thomson using a cathode ray tube. • The charge of an electron was measured in a famous experiment by Robert Millikan. • The mass of an electron was found to be about 2000 times less than the lightest atom (hydrogen). ...
Advanced Simulation Activity - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... associated with pure elements as you have seen. What models of the atom did it replace? Why? For this, take a look at the models of the atom that have come before: 1. Switch from Experiment to Prediction in the upper left hand corner of the simulation. Highlight the Billiard Ball model (Dalton’s mod ...
... associated with pure elements as you have seen. What models of the atom did it replace? Why? For this, take a look at the models of the atom that have come before: 1. Switch from Experiment to Prediction in the upper left hand corner of the simulation. Highlight the Billiard Ball model (Dalton’s mod ...
2008 Midterm Multiple Choice
... When a metal reacts with a nonmetal, the metal will A) lose electrons and form a positive ion B) gain electrons and form a negative ion C) lose protons and form a positive ion D) gain protons and form a negative ion Which element in Group 17 is the most active ...
... When a metal reacts with a nonmetal, the metal will A) lose electrons and form a positive ion B) gain electrons and form a negative ion C) lose protons and form a positive ion D) gain protons and form a negative ion Which element in Group 17 is the most active ...
Nuclear and Radiation Section - University of Toronto Physics
... targets. Later experiments showed that the nuclei of all atoms are roughly spherical with a radius that depends on the number of nucleons. This radius is given by R = r0 A1/3 where r0 ≈ 1.2 x 10-15 m. (10-15 m is defined as one fermi after the famous Italian physicist; it is also one femtometre. Bot ...
... targets. Later experiments showed that the nuclei of all atoms are roughly spherical with a radius that depends on the number of nucleons. This radius is given by R = r0 A1/3 where r0 ≈ 1.2 x 10-15 m. (10-15 m is defined as one fermi after the famous Italian physicist; it is also one femtometre. Bot ...
Lecture 13
... Impacting electrons cause electrons in core (lowest energy) states to be knocked out. For high Z atoms, these are very tightly bound states (K shells), so require high energies (many keV) to eject them Spectrum shows sharp peaks, due to emission of photons by outer electrons falling to vacated core ...
... Impacting electrons cause electrons in core (lowest energy) states to be knocked out. For high Z atoms, these are very tightly bound states (K shells), so require high energies (many keV) to eject them Spectrum shows sharp peaks, due to emission of photons by outer electrons falling to vacated core ...
453 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics (Winter 2005)
... i) Determine the normalization constant A. ii) Find the expectation value of Sx and Sz . 5. Suppose you had three particles in a one-dimensional harmonic oscillator potential, in thermal equilibrium, with total energy E = (9/2)h̄ω. If they are distinguishable particles (but all with the same mass),( ...
... i) Determine the normalization constant A. ii) Find the expectation value of Sx and Sz . 5. Suppose you had three particles in a one-dimensional harmonic oscillator potential, in thermal equilibrium, with total energy E = (9/2)h̄ω. If they are distinguishable particles (but all with the same mass),( ...
stringtheory1s
... tried to understand them in terms of oldfashioned ideas … But at a certain point the old-fashioned ideas would begin to fail, so a warning was developed that said, in effect, ‘Your old-fashioned ideas are no damn good ...
... tried to understand them in terms of oldfashioned ideas … But at a certain point the old-fashioned ideas would begin to fail, so a warning was developed that said, in effect, ‘Your old-fashioned ideas are no damn good ...
Quantum Mechanics
... Electrons in an atom • Electrons can form standing waves going around a nucleus • Only some wavelengths fit only certain energy levels ...
... Electrons in an atom • Electrons can form standing waves going around a nucleus • Only some wavelengths fit only certain energy levels ...
Honors Chemistry Semester 1 Exam Review
... _________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the overall charge of an atom? Why? _________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Isotope ...
... _________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the overall charge of an atom? Why? _________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Isotope ...
Honors Chemistry Exam Review Questions
... 7. Identify the false statement: A A scientific law fully explains a natural phenomenon. B The scientific method is a logical, systematic approach to the solution of a problem. C For the results of an experiment to be accepted, the experiment must produce the same results no matter how many times it ...
... 7. Identify the false statement: A A scientific law fully explains a natural phenomenon. B The scientific method is a logical, systematic approach to the solution of a problem. C For the results of an experiment to be accepted, the experiment must produce the same results no matter how many times it ...
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
... Experimenting with cathode rays in 1897, J.J. Thomson had discovered negatively charged 'corpuscles', as he called them, with a charge to mass ratio 1840 times that of a hydrogen ion. In 1913, Robert A. Millikan measured the charge of an electron, one of the fundamental physical constants. His exper ...
... Experimenting with cathode rays in 1897, J.J. Thomson had discovered negatively charged 'corpuscles', as he called them, with a charge to mass ratio 1840 times that of a hydrogen ion. In 1913, Robert A. Millikan measured the charge of an electron, one of the fundamental physical constants. His exper ...
states of Matter
... newly formed nuclei is less than the mass of the reacting particles; this mass has been converted into energy according Einstein’s famous formula: E = ∆mc2. Remember, this relationship was not invented by Einstein. Nature already knew about it and followed it without fail. Einstein and others discov ...
... newly formed nuclei is less than the mass of the reacting particles; this mass has been converted into energy according Einstein’s famous formula: E = ∆mc2. Remember, this relationship was not invented by Einstein. Nature already knew about it and followed it without fail. Einstein and others discov ...
Einstein
... Listen to Albert Einstein explain his famous formula: http://www.aip.org/history/einstein/sound/voice1.mp3 ...
... Listen to Albert Einstein explain his famous formula: http://www.aip.org/history/einstein/sound/voice1.mp3 ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.