Models of the Atom
... – Only specific frequencies are allowed – And, hence, only certain energy levels ...
... – Only specific frequencies are allowed – And, hence, only certain energy levels ...
Bohr Model and Principal Quantum Number
... Bohr’s model requires the use of the principal Quantum Number (n) It predicts the line spectra of hydrogen through the energy levels of electron orbitals Unfortunately, Bohr’s model works well for hydrogen but does not completely predict other atoms ...
... Bohr’s model requires the use of the principal Quantum Number (n) It predicts the line spectra of hydrogen through the energy levels of electron orbitals Unfortunately, Bohr’s model works well for hydrogen but does not completely predict other atoms ...
Lecture 5 (2.1-2.3)
... • Postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory (1808) 1. Matter consist of small, indivisible and indestructible atoms. 2. All atoms of an element are identical in mass and different from the atoms of other elements. 3. Compounds result from chemical combinations of different elements in specific atomic rat ...
... • Postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory (1808) 1. Matter consist of small, indivisible and indestructible atoms. 2. All atoms of an element are identical in mass and different from the atoms of other elements. 3. Compounds result from chemical combinations of different elements in specific atomic rat ...
6.1.1
... • They conceptualized the building blocks of matter – which they called the ‘atom’ -- literally means ‘cannot be cut’. ...
... • They conceptualized the building blocks of matter – which they called the ‘atom’ -- literally means ‘cannot be cut’. ...
Midterm Review
... Define the law of multiple proportions and provide examples of two compounds that illustrate the concept. ...
... Define the law of multiple proportions and provide examples of two compounds that illustrate the concept. ...
3. atomic structure
... In this class we will be performing an experiment called the “Flame Test”. We will be heating up metal powders in order to excite the electrons to jump from a lower energy level to a higher energy level. When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific ...
... In this class we will be performing an experiment called the “Flame Test”. We will be heating up metal powders in order to excite the electrons to jump from a lower energy level to a higher energy level. When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific ...
Exam #: Printed Name: Signature: PHYSICS
... d) Discuss qualitatively whether or not the entropy would remain approximately the same after removing the barrier if, initially, there were twice as many atoms on one side of the barrier as the other. ...
... d) Discuss qualitatively whether or not the entropy would remain approximately the same after removing the barrier if, initially, there were twice as many atoms on one side of the barrier as the other. ...
Chemistry Name______________________________________
... While there are many different orbits they can only occupy one at a time. They will gain energy to jump to higher orbit and lose energy to fall to lower lowest energy for atom (all electrons in orbits closest to nucleus) couldnot explain other atom’s spectra couldnot account for chemical behavior of ...
... While there are many different orbits they can only occupy one at a time. They will gain energy to jump to higher orbit and lose energy to fall to lower lowest energy for atom (all electrons in orbits closest to nucleus) couldnot explain other atom’s spectra couldnot account for chemical behavior of ...
Atomic Structure
... energy emitted by atoms or molecules is always in whole number multiples of energy of certain well-defined quantities. The word Quanta or Quantum refers to the smallest quantity of energy that can be emitted or absorbed in the form of electromagnetic radiation. E=h, where h is Planck’s constant = 6 ...
... energy emitted by atoms or molecules is always in whole number multiples of energy of certain well-defined quantities. The word Quanta or Quantum refers to the smallest quantity of energy that can be emitted or absorbed in the form of electromagnetic radiation. E=h, where h is Planck’s constant = 6 ...
Physics 102, Class 11 “The Atomic Nature of Matter” Physics 102
... CPS Question • J. J. Thomson: – A: found that negative electricity was transported by tiny particles – B: found the first particles smaller than the hydrogen atom – C: found that negative electricity particles were always exactly the same, regardless of the materials used to make the electrodes or ...
... CPS Question • J. J. Thomson: – A: found that negative electricity was transported by tiny particles – B: found the first particles smaller than the hydrogen atom – C: found that negative electricity particles were always exactly the same, regardless of the materials used to make the electrodes or ...
Physics Notes for Class 12 Chapter 12 Atoms
... (i) About the Stability of Atom According to Maxwell’s electromagnetic wave theory electron should emit energy in the form of electromagnetic wave during its orbital motion. Therefore. radius of orbit of electron will decrease gradually and ultimately it will fall in the nucleus. (ii) About the Line ...
... (i) About the Stability of Atom According to Maxwell’s electromagnetic wave theory electron should emit energy in the form of electromagnetic wave during its orbital motion. Therefore. radius of orbit of electron will decrease gradually and ultimately it will fall in the nucleus. (ii) About the Line ...
Phy. Sci Mid-term review
... 12. The law of conservation of mass states that matter cannot be made or destroyed by ordinary chemical means. Explain what is meant by this statement. 13. Who is Democritus and what did he believe? How about the early Greeks? 14. John Dalton created an atomic theory in the early 1800’s. It has been ...
... 12. The law of conservation of mass states that matter cannot be made or destroyed by ordinary chemical means. Explain what is meant by this statement. 13. Who is Democritus and what did he believe? How about the early Greeks? 14. John Dalton created an atomic theory in the early 1800’s. It has been ...
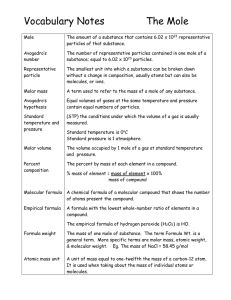
Vocabulary Notes
... The mass of one mole of substance. The term Formula Wt. is a general term. More specific terms are molar mass, atomic weight, & molecular weight. Eg. The mass of NaCl = 58.45 g/mol ...
... The mass of one mole of substance. The term Formula Wt. is a general term. More specific terms are molar mass, atomic weight, & molecular weight. Eg. The mass of NaCl = 58.45 g/mol ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.