chapter 7: atomic structure and periodicity
... 2) Photoelectric effect – the emission of electrons from metal surfaces when light strikes it. Max Planck theorized that energy can either be released or absorbed by atoms in discrete “packets” of some minimum size (a quantum) Equation: ...
... 2) Photoelectric effect – the emission of electrons from metal surfaces when light strikes it. Max Planck theorized that energy can either be released or absorbed by atoms in discrete “packets” of some minimum size (a quantum) Equation: ...
CHM 101 - Academic Computer Center
... Oxygen can form either covalent or ionic bonds. Explain the nature of each bond, the conditions under which each forms and the type of substances in each bond. ...
... Oxygen can form either covalent or ionic bonds. Explain the nature of each bond, the conditions under which each forms and the type of substances in each bond. ...
Review Questions
... 5. Find the percent composition of Oxygen in Na2S2O3 __________________________ ...
... 5. Find the percent composition of Oxygen in Na2S2O3 __________________________ ...
Section 5-1
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
CHM 50- Class activity
... The retina of a human eye can detect light when radiant energy incident on it is at least 4.0 x 10-17 J. For light of 5.85 nm wavelength , how many photons does this energy correspond to? ...
... The retina of a human eye can detect light when radiant energy incident on it is at least 4.0 x 10-17 J. For light of 5.85 nm wavelength , how many photons does this energy correspond to? ...
Sample Papers - SA2 (Science Class 9 )
... (b) A1 (c) Valency , Valence Electrons = 3 Ion formed by x = Cat ion as it needs to lose 3 electrons to acquire an octate ...
... (b) A1 (c) Valency , Valence Electrons = 3 Ion formed by x = Cat ion as it needs to lose 3 electrons to acquire an octate ...
Chapter 1: Atomic Structure
... his high regard among scholars, that was the idea that flourished. However, there was no effort made by the Greeks to prove or disprove this idea. During the dark ages, alchemists started experimenting and keeping records of their results, sending science on a pathway of experimentation and discover ...
... his high regard among scholars, that was the idea that flourished. However, there was no effort made by the Greeks to prove or disprove this idea. During the dark ages, alchemists started experimenting and keeping records of their results, sending science on a pathway of experimentation and discover ...
PowerPoint
... Bohr’s theory correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum The theory failed for all other elements with more than 1 electron Bohr’s theory attempted to use classical mechanics to solve a problem that could not be solved by classical mechanics ...
... Bohr’s theory correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum The theory failed for all other elements with more than 1 electron Bohr’s theory attempted to use classical mechanics to solve a problem that could not be solved by classical mechanics ...
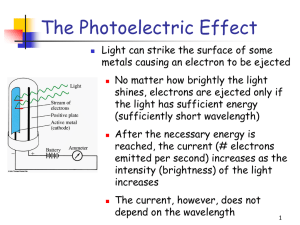
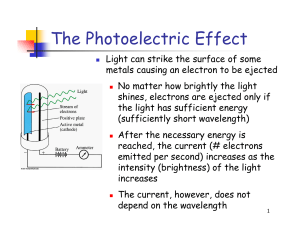
The Photoelectric Effect
... Bohr’s theory correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum The theory failed for all other elements with more than 1 electron Bohr’s theory attempted to use classical mechanics to solve a problem that could not be solved by classical mechanics ...
... Bohr’s theory correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum The theory failed for all other elements with more than 1 electron Bohr’s theory attempted to use classical mechanics to solve a problem that could not be solved by classical mechanics ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and Childhood
... 3. ______ _____________ unit of an ___________ and maintain the ______________ of that element 4. ____________ ___________ unit of a ___________; maintaining _____________ of the compound 5. ______________ matter that is composed of one kind of ________ (e.g. sulfur [__]; carbon [__]) a. each ...
... 3. ______ _____________ unit of an ___________ and maintain the ______________ of that element 4. ____________ ___________ unit of a ___________; maintaining _____________ of the compound 5. ______________ matter that is composed of one kind of ________ (e.g. sulfur [__]; carbon [__]) a. each ...
Ch-1-PPT
... If electrons existed inside the nucleus, then it should be bound inside with a force stronger than coulomb force. ii) If electrons existed inside the nucleus, due to uncertainty principle electrons should have an energy of 20 MeV but the electrons emitted during -decay have energies less than 1 MeV ...
... If electrons existed inside the nucleus, then it should be bound inside with a force stronger than coulomb force. ii) If electrons existed inside the nucleus, due to uncertainty principle electrons should have an energy of 20 MeV but the electrons emitted during -decay have energies less than 1 MeV ...
Name: Midterm Review (Part II) Fill in the blanks (Chapter 6.1 – 6.3
... Describe the trends in the atomic size of elements within groups? (Increase/Decrease down a group?) Describe the trends in the atomic size of elements across periods in the periodic table? (Increase/Decrease across the period?) Which element has the largest radius? Lithium, Sodium, Rubidium, Cesium ...
... Describe the trends in the atomic size of elements within groups? (Increase/Decrease down a group?) Describe the trends in the atomic size of elements across periods in the periodic table? (Increase/Decrease across the period?) Which element has the largest radius? Lithium, Sodium, Rubidium, Cesium ...
Section 1 Notes
... A. Whatever the frequency of the incident light, electrons will be emitted from the metal surface as long as the light carries enough energy - i.e. if it is sufficiently intense (bright). B. If the intensity of the light is increased the maximum energy of the electrons should also increase. C. There ...
... A. Whatever the frequency of the incident light, electrons will be emitted from the metal surface as long as the light carries enough energy - i.e. if it is sufficiently intense (bright). B. If the intensity of the light is increased the maximum energy of the electrons should also increase. C. There ...
KEY Midterm Exam 1 Sept.14, 1999 Chemistry 211 PAGE 1 0f 5
... (a) atoms with different numbers of protons and neutrons. (b) atoms with the same number of neutrons and electrons. (c) atoms with the same atomic number and different mass numbers. (d) atoms with the same mass number but different atomic numbers. ...
... (a) atoms with different numbers of protons and neutrons. (b) atoms with the same number of neutrons and electrons. (c) atoms with the same atomic number and different mass numbers. (d) atoms with the same mass number but different atomic numbers. ...
CHEMISTRY 1 FINAL EXAM REVIEW
... A. a reaction in which a single compound is broken down into simpler substances B. a reaction in which oxygen reacts with another substance, often producing heat or light C. a reaction in which the atoms of one element replace the atoms of a cation in a compound D. a reaction in which two or more su ...
... A. a reaction in which a single compound is broken down into simpler substances B. a reaction in which oxygen reacts with another substance, often producing heat or light C. a reaction in which the atoms of one element replace the atoms of a cation in a compound D. a reaction in which two or more su ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.