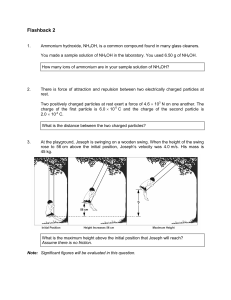
Chapter 5 Practice Section 5-1 Discuss the placement (if any) of
... If a quantum of energy is added to an atom, an electron ________________________________ ________________________________________. An ________________ is where you will most probably find an electron. How many orbitals are in the following sublevels? a. 4 p sublevel b. 3d sublevel How do the px, py, ...
... If a quantum of energy is added to an atom, an electron ________________________________ ________________________________________. An ________________ is where you will most probably find an electron. How many orbitals are in the following sublevels? a. 4 p sublevel b. 3d sublevel How do the px, py, ...
Physics 11 Laboratory
... According to Bohr, an electron in an atom can only orbit the nucleus in a circular manner with certain values of angular momentum. These values correspond to integer multiples of Planck’s constant divided by 2 . L=nh/2 , n=1,2,3,... ...
... According to Bohr, an electron in an atom can only orbit the nucleus in a circular manner with certain values of angular momentum. These values correspond to integer multiples of Planck’s constant divided by 2 . L=nh/2 , n=1,2,3,... ...
Chapter 5: The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom I. The
... Analyzing the light given off by H2 gas in a discharge tube. ...
... Analyzing the light given off by H2 gas in a discharge tube. ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... have the same number of protons, but have different numbers of neutrons. Radioisotopes – radioactive decay The time it takes for half of a radioactive substance to decay is called its half-life. ...
... have the same number of protons, but have different numbers of neutrons. Radioisotopes – radioactive decay The time it takes for half of a radioactive substance to decay is called its half-life. ...
particles - Prof.Dr.Ümit Demir
... incident x-rays, and hence the energies of the scattered rays were lower. The amount of energy reduction depended on the angle at which the x-rays were scattered. The change in wavelength between a scattered x-ray and an incident x-ray is called the Compton shift. In order to explain this effect, Co ...
... incident x-rays, and hence the energies of the scattered rays were lower. The amount of energy reduction depended on the angle at which the x-rays were scattered. The change in wavelength between a scattered x-ray and an incident x-ray is called the Compton shift. In order to explain this effect, Co ...
Unit 2 Notes Name - Mr. Walsh`s AP Chemistry
... proton: a subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom. It has a charge of +1, and a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (amu). neutron: a subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom. It has no charge (is neutral), and has a mass of 1 amu. electron: a subatomic particle found outside the nucleu ...
... proton: a subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom. It has a charge of +1, and a mass of 1 atomic mass unit (amu). neutron: a subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom. It has no charge (is neutral), and has a mass of 1 amu. electron: a subatomic particle found outside the nucleu ...
Atomic and Molecular Structure
... material is much larger in nuclear fusion or fission reactions than in chemical reactions. The change in mass (calculated by E = mc2 ) is small but significant in nuclear reactions. Fusion = atoms come together (H+H=He) Fission = atoms split ...
... material is much larger in nuclear fusion or fission reactions than in chemical reactions. The change in mass (calculated by E = mc2 ) is small but significant in nuclear reactions. Fusion = atoms come together (H+H=He) Fission = atoms split ...
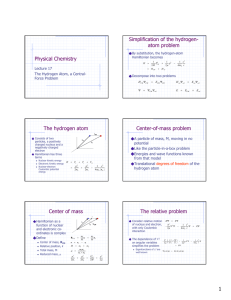
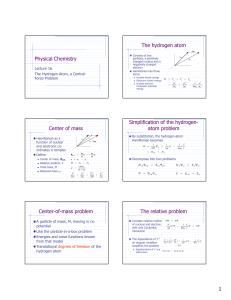
Physical Chemistry The hydrogen atom Center of mass
... Eigenstates of the spin angular momentum operators ...
... Eigenstates of the spin angular momentum operators ...
Physical Chemistry The hydrogen atom Center of mass
... A Rnl (r / a0 )Ylm ( , ) spin , S ,ms ...
... A Rnl (r / a0 )Ylm ( , ) spin , S ,ms ...
Exam #: Printed Name: Signature: PHYSICS
... atoms, each of which has a net spin of 1/2 and a magnetic moment of m. The solution is placed in a an external magnetic field pointing in the z direction which ~ = B(z)ẑ. Assume specifically that B has the value B1 at the varies in the z direction as B bottom of the solution where z = z1 and a larg ...
... atoms, each of which has a net spin of 1/2 and a magnetic moment of m. The solution is placed in a an external magnetic field pointing in the z direction which ~ = B(z)ẑ. Assume specifically that B has the value B1 at the varies in the z direction as B bottom of the solution where z = z1 and a larg ...
Carbon-12 Stable
... -electrons roughly move in patterns called orbitals which coincide with their energy level, but their exact position cannot be determined. ...
... -electrons roughly move in patterns called orbitals which coincide with their energy level, but their exact position cannot be determined. ...
QUANTUM THEORY OF ATOMS AND MOLECULES
... given a C-H vibrational stretching frequency of 2900 cm. Hence explain why C-H bonds react more rapidly than C-D bonds in many organic reactions. 4. Compare the classical and quantum mechanical probability distributions for a simple harmonic oscillator at (a) low quantum numbers; (b) at high quant ...
... given a C-H vibrational stretching frequency of 2900 cm. Hence explain why C-H bonds react more rapidly than C-D bonds in many organic reactions. 4. Compare the classical and quantum mechanical probability distributions for a simple harmonic oscillator at (a) low quantum numbers; (b) at high quant ...
Some Quantum Considerations II
... n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +½. n = 3, l = 1, ml = 0, ms = +½. n = 3, l = 2, ml = -2, ms = -½. n = 2, l = 1, ml = 0, ms = +½. n = 1, l = 1, ml = 1, ms = +½. ...
... n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +½. n = 3, l = 1, ml = 0, ms = +½. n = 3, l = 2, ml = -2, ms = -½. n = 2, l = 1, ml = 0, ms = +½. n = 1, l = 1, ml = 1, ms = +½. ...
PowerPoint Lecture Chapter 17-20
... 1. chemical formula– tells proportions of each kind of atom in compound 2. A compound may or may not be made of molecules Alpha Lipoic Acid C8H14O2S2 Chemical formula ...
... 1. chemical formula– tells proportions of each kind of atom in compound 2. A compound may or may not be made of molecules Alpha Lipoic Acid C8H14O2S2 Chemical formula ...
Physics 120 Homework Set #1 (due Sunday
... b) Does the principle describe a property of a quantum object (e.g. electron) or the limitations of an action (i.e. observation or measurement)? Explain. The limit posed by the Uncertainty Principle is not a consequence of some deficiency in the experimental techniques. Rather, it signifies that an ...
... b) Does the principle describe a property of a quantum object (e.g. electron) or the limitations of an action (i.e. observation or measurement)? Explain. The limit posed by the Uncertainty Principle is not a consequence of some deficiency in the experimental techniques. Rather, it signifies that an ...
The Atom Board - ETC Montessori
... Many middle and high school teachers today, continue to teach chemistry using the Bohr’s model, with the caveat that it is not the current model. It is a terrific opportunity to talk about how science evolves and models change. The Bohr model makes things more concrete and definite for kids. Moving ...
... Many middle and high school teachers today, continue to teach chemistry using the Bohr’s model, with the caveat that it is not the current model. It is a terrific opportunity to talk about how science evolves and models change. The Bohr model makes things more concrete and definite for kids. Moving ...
Vocabulary Terms Defined
... specific energy difference. These collections of different transitions, leading to different radiated wavelengths, make up an emission spectrum. Each element's emission spectrum is unique. Therefore, spectroscopy can be used to identify the elements in matter of unknown composition. Similarly, the e ...
... specific energy difference. These collections of different transitions, leading to different radiated wavelengths, make up an emission spectrum. Each element's emission spectrum is unique. Therefore, spectroscopy can be used to identify the elements in matter of unknown composition. Similarly, the e ...
- Jersey College For Girls
... (ii) Isotopes are atoms with the same number of .................................................................... but different numbers of .................................................................... in the nucleus. ...
... (ii) Isotopes are atoms with the same number of .................................................................... but different numbers of .................................................................... in the nucleus. ...
Louie de Broglie
... Erwin Schrodinger However, the equation does not define the exact path the electron takes around the nucleus. It only estimates the probability of finding an electron in a certain position, unlike Bohr’s circular orbits. ...
... Erwin Schrodinger However, the equation does not define the exact path the electron takes around the nucleus. It only estimates the probability of finding an electron in a certain position, unlike Bohr’s circular orbits. ...
Sir Joseph John “J
... that the rays could be deflected by an electric field (in addition to magnetic fields, which was already known). He concluded that these rays, rather than being waves, were composed of very light negatively charged particles which he called "corpuscles". (Later scientists preferred the name electron ...
... that the rays could be deflected by an electric field (in addition to magnetic fields, which was already known). He concluded that these rays, rather than being waves, were composed of very light negatively charged particles which he called "corpuscles". (Later scientists preferred the name electron ...
Name: Period
... 1. Another name for the representative elements is ________________. Where are these elements located on the periodic table? 2. Who was the first scientist to arrange the elements according to similar chemical and physical properties in order of increasing atomic mass? 3. What is characteristic of t ...
... 1. Another name for the representative elements is ________________. Where are these elements located on the periodic table? 2. Who was the first scientist to arrange the elements according to similar chemical and physical properties in order of increasing atomic mass? 3. What is characteristic of t ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.