AP Physics Daily Problem #107
... How much work was done on the electron while it was between the plates? ...
... How much work was done on the electron while it was between the plates? ...
Page 1 of 3 FOSS California Matter and Energy Module Glossary
... 2007 Edition Absorb: To take in or soak up. Accurate: Correct and precise. Atom: The smallest particle of an element. Atoms are the building blocks of matter. Battery: A source of stored electric energy. Chemical energy: Energy in the connections between atoms in a substance. Convert: To change. Ele ...
... 2007 Edition Absorb: To take in or soak up. Accurate: Correct and precise. Atom: The smallest particle of an element. Atoms are the building blocks of matter. Battery: A source of stored electric energy. Chemical energy: Energy in the connections between atoms in a substance. Convert: To change. Ele ...
ACS Practice Test 1
... They lower the vapor pressure of water when dissolved in it. (E) They raise the boiling point of water when dissolved in it. 42. The addition of a catalyst in a chemical reaction (A) increases the concentration of products at equilibrium. (B) increases the fraction of reactant molecules with a given ...
... They lower the vapor pressure of water when dissolved in it. (E) They raise the boiling point of water when dissolved in it. 42. The addition of a catalyst in a chemical reaction (A) increases the concentration of products at equilibrium. (B) increases the fraction of reactant molecules with a given ...
Unit 1 PowerPoint Complete Notes
... Predict the products of chemical reactions, given the reactants and type of reaction. Determine the average atomic mass using isotopes and their relative abundance. Research the importance and application of isotopes. Describe the concept of the mole and its importance to measurement in chemistr ...
... Predict the products of chemical reactions, given the reactants and type of reaction. Determine the average atomic mass using isotopes and their relative abundance. Research the importance and application of isotopes. Describe the concept of the mole and its importance to measurement in chemistr ...
Study Guide Summative Exam The following represent the
... The following represent the performance indicators around which I will create your test questions. You should expect to demonstrate your knowledge through free response questions. Chapter 3 spi 3221 1.1 Compare and contrast the major models of the atom (eg. Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, and the ...
... The following represent the performance indicators around which I will create your test questions. You should expect to demonstrate your knowledge through free response questions. Chapter 3 spi 3221 1.1 Compare and contrast the major models of the atom (eg. Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, Bohr, and the ...
Electron
... pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass • Matter is made up of elements ...
... pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass • Matter is made up of elements ...
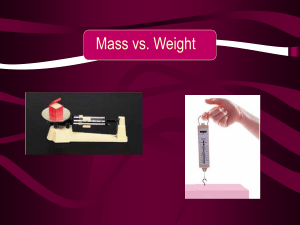
Mass vs. Weight
... Newton on Earth equals about ________grams A _______ of mass. So, if you know an objects mass, you could calculate it’s weight on Earth. ...
... Newton on Earth equals about ________grams A _______ of mass. So, if you know an objects mass, you could calculate it’s weight on Earth. ...
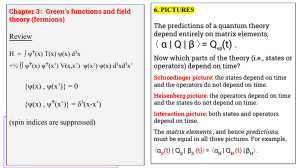
α | Q | β 〉= Q (t) . 〈 Review
... interactions, possibly having small effects. {Usually H0 is a single particle operator; and H1 is a two-particle operator describing the interactions between particles.} ...
... interactions, possibly having small effects. {Usually H0 is a single particle operator; and H1 is a two-particle operator describing the interactions between particles.} ...
File - Romona Olton
... within a molecule (intramolecular bonding) are relatively strong BUT the attractive forces between molecules (intermolecular forces) are relatively weak. Hence covalent compounds have lower mp and bp than ionic compounds ...
... within a molecule (intramolecular bonding) are relatively strong BUT the attractive forces between molecules (intermolecular forces) are relatively weak. Hence covalent compounds have lower mp and bp than ionic compounds ...
Chapter 2
... pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass • Matter is made up of elements ...
... pure form and in combinations called compounds • Organisms are composed of matter • Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass • Matter is made up of elements ...
quanta-and-waves-student-booklet-i-ror
... The solar wind, and its accompanying magnet field, is strong enough to interact with planets and their magnetic fields to shape magnetospheres. A magnetosphere is the region surrounding a planet where the planet's magnetic field has dominant control over the motions of gas and fast charged particles ...
... The solar wind, and its accompanying magnet field, is strong enough to interact with planets and their magnetic fields to shape magnetospheres. A magnetosphere is the region surrounding a planet where the planet's magnetic field has dominant control over the motions of gas and fast charged particles ...
5.1 Revising the Atomic Model - Somerset Academy Silver Palms
... • Previous models of the atom were physical models based on the motion of large objects. • Theoretical calculations and experimental results showed that these models did not always correctly describe electron motion. • Schrödinger devised a mathematical equation describing the behavior of the electr ...
... • Previous models of the atom were physical models based on the motion of large objects. • Theoretical calculations and experimental results showed that these models did not always correctly describe electron motion. • Schrödinger devised a mathematical equation describing the behavior of the electr ...
Critical Thinking Questions 4
... How many C, H and O atoms are on the left of the arrow and how many C, H and O atoms are on the right of the arrow? ...
... How many C, H and O atoms are on the left of the arrow and how many C, H and O atoms are on the right of the arrow? ...
detailed syllabus for online entrance test, click
... characteristics. Coordination Chemistry: Coordination compounds, nomenclature: terminology - Werner’s coordination theory. Applications of coordination compounds. 4: Atomic Structure Discovery of sub-atomic particles (electron, proton and neutron); Thomson and Rutherford atomic models and their limi ...
... characteristics. Coordination Chemistry: Coordination compounds, nomenclature: terminology - Werner’s coordination theory. Applications of coordination compounds. 4: Atomic Structure Discovery of sub-atomic particles (electron, proton and neutron); Thomson and Rutherford atomic models and their limi ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.