Document
... radial and angular eigenfunctions. Neither one of these are trivial derivations, but they are both analytical. ...
... radial and angular eigenfunctions. Neither one of these are trivial derivations, but they are both analytical. ...
Physical and Chemical Tests
... The pulse may be applied multiple times and the results accumulated and averaged, which provides for very high sensitivity. The signal measured is actually the decay, with time, of the absorption event. This signal is then mathematically transformed using a Fourier transform, producing the more fami ...
... The pulse may be applied multiple times and the results accumulated and averaged, which provides for very high sensitivity. The signal measured is actually the decay, with time, of the absorption event. This signal is then mathematically transformed using a Fourier transform, producing the more fami ...
PHY 410 Final Examination, Spring 2008 April 30, 2008 (5:45-7:45 p.m.)
... 3. 1 mole of water at 50oC is added to 1 mole of water at 10oC. The heat capacity of water CP is 75.29 J/Kmole and assume it to be a constant.(10 points) a) What is the final temperature? b) What is the net change in entropy in this mixing process? Is it positive, negative or zero? ...
... 3. 1 mole of water at 50oC is added to 1 mole of water at 10oC. The heat capacity of water CP is 75.29 J/Kmole and assume it to be a constant.(10 points) a) What is the final temperature? b) What is the net change in entropy in this mixing process? Is it positive, negative or zero? ...
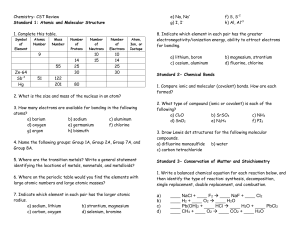
Chemistry- CST Review
... 6. How does changing the amount of gas, volume of gas, and temperature affect the gas pressure? For Q’s #9-14, name the gas law and show all your work. 7. The pressure on 2.00 L of anesthetic gas changes from 100 kPa to 40 kPa. What will be the new volume if the temperature remains constant? 8. If a ...
... 6. How does changing the amount of gas, volume of gas, and temperature affect the gas pressure? For Q’s #9-14, name the gas law and show all your work. 7. The pressure on 2.00 L of anesthetic gas changes from 100 kPa to 40 kPa. What will be the new volume if the temperature remains constant? 8. If a ...
Multielectron Atoms * The Independent Particle Approximation
... The difference between classical and Einstein models comes from zero point energy. ...
... The difference between classical and Einstein models comes from zero point energy. ...
ICP Background - Center for Applied Isotope Studies
... in an ICP-MS consists of two (or more) metal cone-shaped disks with a single hole in the center of each. The small diameter of the hole allows for sampling of ions concentrated at the center of the plasma—herein lies one of the limitations of ICPMS as the small diameter of the cones inherently req ...
... in an ICP-MS consists of two (or more) metal cone-shaped disks with a single hole in the center of each. The small diameter of the hole allows for sampling of ions concentrated at the center of the plasma—herein lies one of the limitations of ICPMS as the small diameter of the cones inherently req ...
Chemistry Academic v. 2016
... Explain why compounds are composed of integer ratios of elements. Interpret and apply the law of conservation of energy, law of conservation of mass, constant composition (definite proportions), and multiple proportions. Recognize the contributions of Robert Millikan to the early atomic model. Calcu ...
... Explain why compounds are composed of integer ratios of elements. Interpret and apply the law of conservation of energy, law of conservation of mass, constant composition (definite proportions), and multiple proportions. Recognize the contributions of Robert Millikan to the early atomic model. Calcu ...
Lecture Outline Chapter 31 Physics, 4th Edition James S. Walker
... 31-3 Bohr’s Model of the Hydrogen Atom Assumptions of the Bohr model: • The electron in a hydrogen atom moves in a circular orbit around the nucleus. • Only certain orbits are allowed, where the angular momentum in the nth allowed orbit is • Electrons in allowed orbits do not radiate. Radiation is ...
... 31-3 Bohr’s Model of the Hydrogen Atom Assumptions of the Bohr model: • The electron in a hydrogen atom moves in a circular orbit around the nucleus. • Only certain orbits are allowed, where the angular momentum in the nth allowed orbit is • Electrons in allowed orbits do not radiate. Radiation is ...
31_LectureOutline
... 31-3 Bohr’s Model of the Hydrogen Atom Assumptions of the Bohr model: • The electron in a hydrogen atom moves in a circular orbit around the nucleus. • Only certain orbits are allowed, where the angular momentum in the nth allowed orbit is • Electrons in allowed orbits do not radiate. Radiation is ...
... 31-3 Bohr’s Model of the Hydrogen Atom Assumptions of the Bohr model: • The electron in a hydrogen atom moves in a circular orbit around the nucleus. • Only certain orbits are allowed, where the angular momentum in the nth allowed orbit is • Electrons in allowed orbits do not radiate. Radiation is ...
Chapter 8
... – Noble gas e- configurations (full outer shell) are very stable – Valence electrons do not feel the complete charge of the nucleus because of shielding – The n quantum number of the valence electrons increases as go down a group in the periodic table ...
... – Noble gas e- configurations (full outer shell) are very stable – Valence electrons do not feel the complete charge of the nucleus because of shielding – The n quantum number of the valence electrons increases as go down a group in the periodic table ...
Balancing Equations
... so that the left side has the same number of atoms as the right side for EACH element in order to balance the equation. Check your answer to see if: The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ratios. (reduced) ...
... so that the left side has the same number of atoms as the right side for EACH element in order to balance the equation. Check your answer to see if: The numbers of atoms on both sides of the equation are now balanced. The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ratios. (reduced) ...
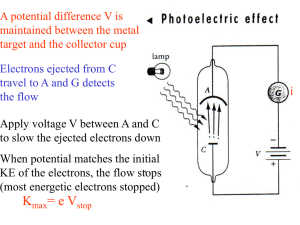
Notes - Photons, the Photoelectric Effect and the Compton Effect (ppt)
... • Again, experimental data shows this is not the case; increasing the intensity of the light only increases the number of electrons emitted, not their kinetic energy. • THUS the photoelectric effect is strong evidence for the photon model of light. ...
... • Again, experimental data shows this is not the case; increasing the intensity of the light only increases the number of electrons emitted, not their kinetic energy. • THUS the photoelectric effect is strong evidence for the photon model of light. ...
Atomic physics: Atomic Spectra: Thomson`s plum
... Drawbacks of Rutherford’s model is that the atom as a whole cannot be stable. because, according to Rutherford that the electrons are in circular motion, the centripetal force would provided by electrostatic attraction. But uniform rotation is an accelerated motion and according to the classical el ...
... Drawbacks of Rutherford’s model is that the atom as a whole cannot be stable. because, according to Rutherford that the electrons are in circular motion, the centripetal force would provided by electrostatic attraction. But uniform rotation is an accelerated motion and according to the classical el ...
1,0-,1,2 + ½
... Bohr used work of others… • Balmer—made an equation (math) to connect the lines of the hydrogen spectrum to each other. • Planck—Energy is directly proportional to the frequency of light. ...
... Bohr used work of others… • Balmer—made an equation (math) to connect the lines of the hydrogen spectrum to each other. • Planck—Energy is directly proportional to the frequency of light. ...
lectures-week1
... Synchrotrons accelerate electrons around a circular path (relativistic) Directional, continuous, intense (one is operating in Melbourne now!) ...
... Synchrotrons accelerate electrons around a circular path (relativistic) Directional, continuous, intense (one is operating in Melbourne now!) ...
Take notes on this document while you are watching the recorded
... A. Minerals: Are defined depending on the context. Any natural, inorganic molecule might be defined as a mineral (therefore, some include water and phosphate). However, most often, when we discuss minerals in nutrition, we are talking about those inorganic substances in pure, or elemental, form (Cal ...
... A. Minerals: Are defined depending on the context. Any natural, inorganic molecule might be defined as a mineral (therefore, some include water and phosphate). However, most often, when we discuss minerals in nutrition, we are talking about those inorganic substances in pure, or elemental, form (Cal ...
Chapter 2: Atomic Structure and Inter-atomic Bonding
... protons – Positively charged particles of 0.16 x 10-18 C and a mass of 1.66 x 10-24g. neutrons – Neutral particles having approximately the same mass as protons. electrons – Negatively charged particles with a mass of 0.911 x 10-27 g. The charge is the same magnitude as that on the proton. The elect ...
... protons – Positively charged particles of 0.16 x 10-18 C and a mass of 1.66 x 10-24g. neutrons – Neutral particles having approximately the same mass as protons. electrons – Negatively charged particles with a mass of 0.911 x 10-27 g. The charge is the same magnitude as that on the proton. The elect ...
June 2010 Regents Exam Part C Questions
... Q14 The molarity of an aqueous solution of NaCl is defined as the (1) grams of NaCl per liter of water (2) grams of NaCl per liter of solution (3) moles of NaCl per liter of water (4) moles of NaCl per liter of solution Q 15 A real gas behaves least like an ideal gas under the conditions of (1) ...
... Q14 The molarity of an aqueous solution of NaCl is defined as the (1) grams of NaCl per liter of water (2) grams of NaCl per liter of solution (3) moles of NaCl per liter of water (4) moles of NaCl per liter of solution Q 15 A real gas behaves least like an ideal gas under the conditions of (1) ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.