Notes & Ideas on Static Electricity
... the oppositely charged atomic nucleus. The outermost electrons of many atoms are bound very loosely and can be easily dislodged. How much energy is required to tear an electron away from an atom varies for different substances. ...
... the oppositely charged atomic nucleus. The outermost electrons of many atoms are bound very loosely and can be easily dislodged. How much energy is required to tear an electron away from an atom varies for different substances. ...
Question - Bellingham High School
... from chemical formulas, we are able to reverse the process and determine formulas from percent composition. However, when we use this process, we are able to determine only the empirical formula. ...
... from chemical formulas, we are able to reverse the process and determine formulas from percent composition. However, when we use this process, we are able to determine only the empirical formula. ...
LIQUIDS
... Definition: An atom is the smallest particle of an element that can exist or take part in a chemical change. MOLECULES All elements are made up of atoms. In some gaseous elements (e.g. argon) single atoms move around freely. But in other gaseous elements, single atoms cannot exist on their own at or ...
... Definition: An atom is the smallest particle of an element that can exist or take part in a chemical change. MOLECULES All elements are made up of atoms. In some gaseous elements (e.g. argon) single atoms move around freely. But in other gaseous elements, single atoms cannot exist on their own at or ...
New Approaches in Deep Laser Cooling of Magnesium Atoms for
... course, one have three pairs of σ+ and σ– waves). In this section we neglect the influence of a static magnetic field on the kinetics of atoms assuming the field to be sufficiently small at the scale of a cloud in the trap. This influence will be considered in the next section. Also, we do not limit ...
... course, one have three pairs of σ+ and σ– waves). In this section we neglect the influence of a static magnetic field on the kinetics of atoms assuming the field to be sufficiently small at the scale of a cloud in the trap. This influence will be considered in the next section. Also, we do not limit ...
Theory & Implementation of the Scanning Tunneling Microscope
... We can look at the above probability as the chance of an electron on one metal being found on the other, but likewise this works the opposite way as well. This brings rise to another problem with the above equation, even if an electron could tunnel the gap it has to have a home on the other metal. F ...
... We can look at the above probability as the chance of an electron on one metal being found on the other, but likewise this works the opposite way as well. This brings rise to another problem with the above equation, even if an electron could tunnel the gap it has to have a home on the other metal. F ...
How many grams of oxygen are made if 3.75 moles of KClO 3
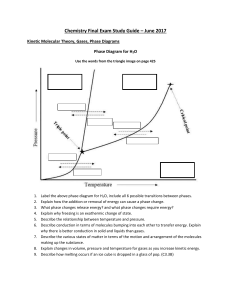
... Label the above phase diagram for H2O, include all 6 possible transitions between phases. Explain how the addition or removal of energy can cause a phase change. What phase changes release energy? and what phase changes require energy? Explain why freezing is an exothermic change of state. Describe ...
... Label the above phase diagram for H2O, include all 6 possible transitions between phases. Explain how the addition or removal of energy can cause a phase change. What phase changes release energy? and what phase changes require energy? Explain why freezing is an exothermic change of state. Describe ...
orbital - Waterford Public Schools
... quantum effects like the wave-particle duality make a difference only in the 34th decimal place when predicting the behavior of a moving baseball • Bottom line is large objects obey Newton’s laws and subatomic particles defy classical physics and obey quantum ...
... quantum effects like the wave-particle duality make a difference only in the 34th decimal place when predicting the behavior of a moving baseball • Bottom line is large objects obey Newton’s laws and subatomic particles defy classical physics and obey quantum ...
The Chemical Context of Life
... Potential energy is the energy that matter has because of its location or structure The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of ...
... Potential energy is the energy that matter has because of its location or structure The electrons of an atom differ in their amounts of ...
The two states of matter they didn`t teach you about in school… Until
... Universe is in the plasma state. ...
... Universe is in the plasma state. ...
The Two Body Problem
... earth’s moon is considered. The force on the moon due to the sun has a greater magnitude than that on the moon due to the earth. The moon basically orbits the sun while the earth perturbs its motion to speed up and slow down and to weave inside of and outside of the earth’s orbit. None-the-less, the ...
... earth’s moon is considered. The force on the moon due to the sun has a greater magnitude than that on the moon due to the earth. The moon basically orbits the sun while the earth perturbs its motion to speed up and slow down and to weave inside of and outside of the earth’s orbit. None-the-less, the ...
ECE692_3_1008
... Electrons get energy from the field, hotter than the lattice – hot electrons When the energy of hot electrons becomes comparable to that of optical phonons, energy is transferred to the lattice via optical phonons. ...
... Electrons get energy from the field, hotter than the lattice – hot electrons When the energy of hot electrons becomes comparable to that of optical phonons, energy is transferred to the lattice via optical phonons. ...
2016
... foundation in chemistry and insure all students are on a relatively even plane. It will be important for everyone to come to class the first day prepared. While I review, extensive remediation is not an option as we work towards our goal of being 100% prepared for the AP Exam in early May 2017. Ther ...
... foundation in chemistry and insure all students are on a relatively even plane. It will be important for everyone to come to class the first day prepared. While I review, extensive remediation is not an option as we work towards our goal of being 100% prepared for the AP Exam in early May 2017. Ther ...
DÆ Upgrade - FSU High Energy Physics
... charge from the cathode and are repelled by it. 1874 George Johnstone Stoney estimates the charge of the then unknown electron to be about 10-20 coulomb, close to the modern value of 1.6021892 x 10-19 coulomb. (He used the Faraday constant (total electric charge per mole of univalent atoms) divided ...
... charge from the cathode and are repelled by it. 1874 George Johnstone Stoney estimates the charge of the then unknown electron to be about 10-20 coulomb, close to the modern value of 1.6021892 x 10-19 coulomb. (He used the Faraday constant (total electric charge per mole of univalent atoms) divided ...
9182747 Chemistry Ja02
... 62 The diagram below represents radioactive emanations passing through an electric field. ...
... 62 The diagram below represents radioactive emanations passing through an electric field. ...
Chemistry -- Oxidation
... reduced? How many electrons? 2. C atom goes from -2 to -4. Oxidized or reduced? How many electrons? 3. An atom goes from +5 to +3. Oxidized or reduced? How many electrons? 4. An atom goes from -6 to -1. Oxidized or reduced? How many electrons? ...
... reduced? How many electrons? 2. C atom goes from -2 to -4. Oxidized or reduced? How many electrons? 3. An atom goes from +5 to +3. Oxidized or reduced? How many electrons? 4. An atom goes from -6 to -1. Oxidized or reduced? How many electrons? ...
Step Potential
... If the particles interact, the potential energy U contains terms with both x1 and x2 that can not be separated. For example, the electrostatic repulsion of two electrons in one dimension is represented by potential energy ke2/(x2-x1). However if the particles do not interact, as we assuming here, we ...
... If the particles interact, the potential energy U contains terms with both x1 and x2 that can not be separated. For example, the electrostatic repulsion of two electrons in one dimension is represented by potential energy ke2/(x2-x1). However if the particles do not interact, as we assuming here, we ...
ASFG High School Summer Assignment Summer 2016
... lab reports will also be assigned and evaluated. Do not expect any grade curves or ‘fluff’ assignments this year! Assessments are administered and graded as if they are AP exams. Be aggressive in pursuit of knowledge not just the grades. Prioritize your learn ...
... lab reports will also be assigned and evaluated. Do not expect any grade curves or ‘fluff’ assignments this year! Assessments are administered and graded as if they are AP exams. Be aggressive in pursuit of knowledge not just the grades. Prioritize your learn ...
Karim Khaidarov - Aethereal Atom
... electrostatic density (elecrostrictional, potential energy) of electrons, expressing in growing of a dielectrical permeability of ether in material. Let's try to understand, what it is. Domain Model of the Ether In works [1-6] the working model of ether reducing to the following thesises is develope ...
... electrostatic density (elecrostrictional, potential energy) of electrons, expressing in growing of a dielectrical permeability of ether in material. Let's try to understand, what it is. Domain Model of the Ether In works [1-6] the working model of ether reducing to the following thesises is develope ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.