Unit A Review Questions
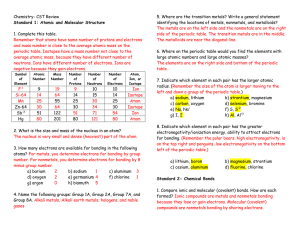
... b. The compounds used to give colour to a glaze include iron oxide, chromium oxide, magnesium dioxide, and copper carbonate. c. All of the compounds listed in 27.b. are classified as ionic compounds because they consist of both a metal and a non-metal. d. The compounds used to make glazes are mixed ...
... b. The compounds used to give colour to a glaze include iron oxide, chromium oxide, magnesium dioxide, and copper carbonate. c. All of the compounds listed in 27.b. are classified as ionic compounds because they consist of both a metal and a non-metal. d. The compounds used to make glazes are mixed ...
Module 11 - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... The flip side of pair annihilation is pair production where a gamma ray, when interacting with a matter particle, is converted into a matter-antimatter pair. This is predicted by theory and observed in nature. An extreme case of pair production is the postulated “vacuum fluctuation” that is common i ...
... The flip side of pair annihilation is pair production where a gamma ray, when interacting with a matter particle, is converted into a matter-antimatter pair. This is predicted by theory and observed in nature. An extreme case of pair production is the postulated “vacuum fluctuation” that is common i ...
Chemistry- CST Review
... 2. Amino acids are building blocks for ___proteins___. 3. How many bonds does the carbon atom form? Carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds. ...
... 2. Amino acids are building blocks for ___proteins___. 3. How many bonds does the carbon atom form? Carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds. ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... Figure 4. Shows the distributions of the electron states (1s, 2s, 3s, 2p, 3p, 3d) in case of Schrödinger’s wave functions.The corresponding distributions for muonic hydrogen are shown in figure 5 for the same states.In these distributions, we take the reduced mass of muon in place of its mass.Lookin ...
... Figure 4. Shows the distributions of the electron states (1s, 2s, 3s, 2p, 3p, 3d) in case of Schrödinger’s wave functions.The corresponding distributions for muonic hydrogen are shown in figure 5 for the same states.In these distributions, we take the reduced mass of muon in place of its mass.Lookin ...
Module 11
... The flip side of pair annihilation is pair production where a gamma ray, when interacting with a matter particle, is converted into a matter-antimatter pair. This is predicted by theory and observed in nature. An extreme case of pair production is the postulated “vacuum fluctuation” that is common i ...
... The flip side of pair annihilation is pair production where a gamma ray, when interacting with a matter particle, is converted into a matter-antimatter pair. This is predicted by theory and observed in nature. An extreme case of pair production is the postulated “vacuum fluctuation” that is common i ...
Term 1 and 2 Powerpoints
... Well when fossil fuels are burned, or maybe even things like wood or who knows, scientists most likely calculate the molecules given off so they can come up with these statistics. Well maybe they deal with moles or liters of gas at STP, who knows, but I’m sure somewhere in there scientists will have ...
... Well when fossil fuels are burned, or maybe even things like wood or who knows, scientists most likely calculate the molecules given off so they can come up with these statistics. Well maybe they deal with moles or liters of gas at STP, who knows, but I’m sure somewhere in there scientists will have ...
End-semester Examination 2013 Mechanics (PHY102A/N
... (b) Einstein’s theory of relativity is valid for high speeds, but not for small speeds.! (c) √ According to Einstein’s theory of relativity, no particle can have velocity greater than speed of light.! (d) √ Time interval between two events remains invariant under Galilean transformation.! 3. Which ...
... (b) Einstein’s theory of relativity is valid for high speeds, but not for small speeds.! (c) √ According to Einstein’s theory of relativity, no particle can have velocity greater than speed of light.! (d) √ Time interval between two events remains invariant under Galilean transformation.! 3. Which ...
QuantumDots
... – The proximity effect: Electrons scatter because they are relatively low in mass, reducing the resolution. • Heavy ion lithography has been proposed, but still is in development stages ...
... – The proximity effect: Electrons scatter because they are relatively low in mass, reducing the resolution. • Heavy ion lithography has been proposed, but still is in development stages ...
Photoelectric Effect
... Using the an investigation into special relativity, we see that E = mc2. Knowing that “waves” can act like “particles” might mean that “particles” can act like “waves”. This is the de Broglie wavelengths. This leads to the conclusion of wave-particle duality. ...
... Using the an investigation into special relativity, we see that E = mc2. Knowing that “waves” can act like “particles” might mean that “particles” can act like “waves”. This is the de Broglie wavelengths. This leads to the conclusion of wave-particle duality. ...
Anyons in the fractional quantum Hall effect
... is related to a reverse sign of the Hall voltage when the measurements are performed in a ptype semiconductor. The Hall voltage is the transverse voltage that develops from sideways acceleration of a moving particle by a magnetic field. It is classically proportional to the current of particles. The ...
... is related to a reverse sign of the Hall voltage when the measurements are performed in a ptype semiconductor. The Hall voltage is the transverse voltage that develops from sideways acceleration of a moving particle by a magnetic field. It is classically proportional to the current of particles. The ...
The uncertainty principle, virtual particles and real forces
... wave–particle duality. Two of the simplest are the following: (1) The photoelectric effect. When light of frequency f is shone onto a metal surface, electrons can be knocked out. Increasing the intensity of the light does not affect the energy with which individual electrons emerge, a fact that cann ...
... wave–particle duality. Two of the simplest are the following: (1) The photoelectric effect. When light of frequency f is shone onto a metal surface, electrons can be knocked out. Increasing the intensity of the light does not affect the energy with which individual electrons emerge, a fact that cann ...
Quantum mechanics is the theory that we use to describe the
... Quantum mechanics is the theory that we use to describe the microscopic world. The microscopic world is the realm of atoms, photons, nuclei, electrons, neutrons, and a whole host of other subatomic particles. These particles are the “building blocks” of our universe, in the sense that everything tha ...
... Quantum mechanics is the theory that we use to describe the microscopic world. The microscopic world is the realm of atoms, photons, nuclei, electrons, neutrons, and a whole host of other subatomic particles. These particles are the “building blocks” of our universe, in the sense that everything tha ...
Science 10 - SharpSchool
... atoms have a nucleus which is positive and has most of the mass most of the atom is empty space occupied by the moving negatively charged electrons proposed the existence of protons 4. Neils Bohr: 1913 electrons move in circular orbits around the nucleus cannot exist between orbits 5. Jame ...
... atoms have a nucleus which is positive and has most of the mass most of the atom is empty space occupied by the moving negatively charged electrons proposed the existence of protons 4. Neils Bohr: 1913 electrons move in circular orbits around the nucleus cannot exist between orbits 5. Jame ...
Document
... direction. If the atoms passing through have angular momentum of 1 so L 2 but the z-component Lz m is unknown, how many possibilities are there for deflection? A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. 3 E. Infinite ...
... direction. If the atoms passing through have angular momentum of 1 so L 2 but the z-component Lz m is unknown, how many possibilities are there for deflection? A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. 3 E. Infinite ...
AP CHEMISTRY SYLLABUS STUDENT VERSION
... answered in a format where the question asked is understood. All mathematical manipulations must be shown and significant figures must always be kept correctly. Non mathematical questions must be answered in depth to show understanding of underlying principles. Homework may or may not be graded; how ...
... answered in a format where the question asked is understood. All mathematical manipulations must be shown and significant figures must always be kept correctly. Non mathematical questions must be answered in depth to show understanding of underlying principles. Homework may or may not be graded; how ...
Atomic Orbitals
... Valence electrons – electrons in the outermost (highest) principal energy level of an atom Core electrons – inner electrons Elements with the same valence electron arrangement show very similar chemical behavior. ...
... Valence electrons – electrons in the outermost (highest) principal energy level of an atom Core electrons – inner electrons Elements with the same valence electron arrangement show very similar chemical behavior. ...
110 REVIEW MATERIALTro 2011
... Diatomic Elementsare those elements that exists as two atoms bonded together Representative elementsare "A" group elements Metals are those elements which have the characteristic properities of: high luster, good conductors of heat and electricity, and are malleable Nonmetals are those elements, unl ...
... Diatomic Elementsare those elements that exists as two atoms bonded together Representative elementsare "A" group elements Metals are those elements which have the characteristic properities of: high luster, good conductors of heat and electricity, and are malleable Nonmetals are those elements, unl ...
CHEM-UA 127: Advanced General Chemistry
... That is, we know that this guess is not correct, however, we can try to optimize the form of the functions ψ1 (r) and ψ2 (r) so as to make Eg as small as possible, thereby making it approach E0 . If we do this, we find that ψ1 (r) and ψ2 (r) satisfy a set of 2 coupled Schrödinger-like equations and ...
... That is, we know that this guess is not correct, however, we can try to optimize the form of the functions ψ1 (r) and ψ2 (r) so as to make Eg as small as possible, thereby making it approach E0 . If we do this, we find that ψ1 (r) and ψ2 (r) satisfy a set of 2 coupled Schrödinger-like equations and ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.