Electronic Structure of Sr2RuO4
... ABAABABA Ã ABAAB Ã ABA Ã AB Ã A • 2D Quasicrystal: Penrose tilings ...
... ABAABABA Ã ABAAB Ã ABA Ã AB Ã A • 2D Quasicrystal: Penrose tilings ...
Chemical Equations and Stoichiometry
... • Mass: depends on the amount of matter in a substance. Unlike weight it does not depend on gravity. In chemistry we most commonly measure mass in grams. • Mole: a package of 6.02 X 1023 items, usually molecules. Technically, it is the number of atoms found in 12.000 grams of 12C. (One way of gettin ...
... • Mass: depends on the amount of matter in a substance. Unlike weight it does not depend on gravity. In chemistry we most commonly measure mass in grams. • Mole: a package of 6.02 X 1023 items, usually molecules. Technically, it is the number of atoms found in 12.000 grams of 12C. (One way of gettin ...
Molecular Modeling Activity for Carbohydrates
... disaccharide. One carbon on each participating monosaccharide is chemically bound together by oxygen. Two forms of this C–O–C bond exists in nature, called alpha () bonds and beta () bonds. The beta bond makes lactose difficult to digest for individuals who show a low activity of the enzyme lactas ...
... disaccharide. One carbon on each participating monosaccharide is chemically bound together by oxygen. Two forms of this C–O–C bond exists in nature, called alpha () bonds and beta () bonds. The beta bond makes lactose difficult to digest for individuals who show a low activity of the enzyme lactas ...
particle in a box the uncertainty principle
... principle are fundamental to nature, and are due to the wave properties of matter. This follows cleanly and logically from the mathematics of waves. As humans, we are left with nagging doubts about the uncertainty principle. How dare nature tell us there are things we cannot know! Surely this is jus ...
... principle are fundamental to nature, and are due to the wave properties of matter. This follows cleanly and logically from the mathematics of waves. As humans, we are left with nagging doubts about the uncertainty principle. How dare nature tell us there are things we cannot know! Surely this is jus ...
Holt Chemistry – Guided Notes, Chapter 1
... Liquid – particles moving, sliding past each other Gas – constant, random, straight-line motion 6. Give three examples each of physical and chemical changes. Physical – change of state, same substance remains before and after Chemical – one or more new substances forms, chemical reaction ...
... Liquid – particles moving, sliding past each other Gas – constant, random, straight-line motion 6. Give three examples each of physical and chemical changes. Physical – change of state, same substance remains before and after Chemical – one or more new substances forms, chemical reaction ...
Notes for Unit
... Conductors – materials in which valence electrons are loosely bound to the atom. -Therefore charge can flow freely through conductors. Electrons in the outer valence shell are loosely bound. An electron from each atom can easily escape the atom. These electrons freely float in the substance and go f ...
... Conductors – materials in which valence electrons are loosely bound to the atom. -Therefore charge can flow freely through conductors. Electrons in the outer valence shell are loosely bound. An electron from each atom can easily escape the atom. These electrons freely float in the substance and go f ...
3. Born-Oppenheimer approximation
... mass of lattice ions (104 times larger) electronic system is much faster and can almost instantaneously adapt to the new ion positions (adiabatic approximation) Procedure: 1) describe electron motion in static ion lattice 2) describe ion motion in a homogenous electron sea 3) perturbative descriptio ...
... mass of lattice ions (104 times larger) electronic system is much faster and can almost instantaneously adapt to the new ion positions (adiabatic approximation) Procedure: 1) describe electron motion in static ion lattice 2) describe ion motion in a homogenous electron sea 3) perturbative descriptio ...
Unit 9 - Chemical Quantities: The Mole
... 3. Divide each by the smallest answer from step 2. 4. If whole numbers are not obtained in step 3, multiply everything by a factor to make the ratios whole #s. – If .5, multiply everything by 2. If .33, multiply everything by 3. ...
... 3. Divide each by the smallest answer from step 2. 4. If whole numbers are not obtained in step 3, multiply everything by a factor to make the ratios whole #s. – If .5, multiply everything by 2. If .33, multiply everything by 3. ...
Electronic Structure and Chemical Periodicity Periodic - Ars
... table, this means that all of the elements in a given column have similar chemical properties. For example, all of the group IA elements react with water to produce a metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas. The chemical reactions are very similar, there are different amou ...
... table, this means that all of the elements in a given column have similar chemical properties. For example, all of the group IA elements react with water to produce a metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas. The chemical reactions are very similar, there are different amou ...
Rational Quantum Physics R. N. Boyd, Ph. D., USA “There is good
... theoretical atomic weight 100,000,000 times lighter than hydrogen. The kinetic velocity of this gas was calculated by Mendeleev to be 2,500,000 meters per second. Nearly massless, these gases were assumed by Mendeleev to permeate all matter, rarely interacting chemically. The high mobility and very ...
... theoretical atomic weight 100,000,000 times lighter than hydrogen. The kinetic velocity of this gas was calculated by Mendeleev to be 2,500,000 meters per second. Nearly massless, these gases were assumed by Mendeleev to permeate all matter, rarely interacting chemically. The high mobility and very ...
South Pasadena · Chemistry
... 13. The quantum numbers listed below are for four different electrons in the same atom. Arrange them in order of increasing energy. Indicate whether any two have the same energy. (a) n = 4, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = ½ (b) n = 3, l = 2, ml = 1, ms = ½ (c) n = 3, l = 2, ml = -2, ms = -½ (d) n = 3, l = 1, ml ...
... 13. The quantum numbers listed below are for four different electrons in the same atom. Arrange them in order of increasing energy. Indicate whether any two have the same energy. (a) n = 4, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = ½ (b) n = 3, l = 2, ml = 1, ms = ½ (c) n = 3, l = 2, ml = -2, ms = -½ (d) n = 3, l = 1, ml ...
Free Fall of Elementary Particles
... Mathematically, the dielectric force produced by a single atom acting on another dielectric atom can be found by integrating one revolution of the moving electron (ignoring the y and z components, for now) by using Eq. (5.0): ...
... Mathematically, the dielectric force produced by a single atom acting on another dielectric atom can be found by integrating one revolution of the moving electron (ignoring the y and z components, for now) by using Eq. (5.0): ...
Wave packets Uncertainty - cranson
... Such events are known as “QUANTUM FLUCTUATIONS” and they form the basis for our understanding of particle interactions. ...
... Such events are known as “QUANTUM FLUCTUATIONS” and they form the basis for our understanding of particle interactions. ...
Highligh in Physics 2005
... One of the most intriguing problems in modern physics is to explain the emergence of the classical appearance of the macroscopic world from the quantum mechanical laws that rule the behavior of matter at the microscopic level. The fundamental features of quantum mechanics, such as linearity and enta ...
... One of the most intriguing problems in modern physics is to explain the emergence of the classical appearance of the macroscopic world from the quantum mechanical laws that rule the behavior of matter at the microscopic level. The fundamental features of quantum mechanics, such as linearity and enta ...
Lecture 5 Molecular Orbital Theory Part 1 Molecular Orbital Theory
... that matters is whether the two AOs are in-phase (c’s both positive or both negative) or out-of-phase (one c’s positive & the other negative). ...
... that matters is whether the two AOs are in-phase (c’s both positive or both negative) or out-of-phase (one c’s positive & the other negative). ...
Nuclear Physics I (PHY 551) Lecture 24:
... Protons and neutrons are moving in opposite directions (the opposite phase keeps the center of mass of the nucleus stationary) or “out of phase” with respect to each other g isovector mode of excitation. Note: if protons and neutrons are moving in phase, it is an isoscalar dipole vibration (entire ...
... Protons and neutrons are moving in opposite directions (the opposite phase keeps the center of mass of the nucleus stationary) or “out of phase” with respect to each other g isovector mode of excitation. Note: if protons and neutrons are moving in phase, it is an isoscalar dipole vibration (entire ...
Electric Field - Uplift Meridian
... • Objects can be charged – there can be net charge on an object. How? The only type of charge that can move around is the negative charge, or electrons. The positive charge stays in the nuclei. So, we can put a NET CHARGE on different objects in two ways ◊ Add electrons and make the object negativel ...
... • Objects can be charged – there can be net charge on an object. How? The only type of charge that can move around is the negative charge, or electrons. The positive charge stays in the nuclei. So, we can put a NET CHARGE on different objects in two ways ◊ Add electrons and make the object negativel ...
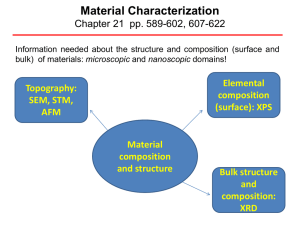
Material Characterization
... X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its "as received" state, or after some treatment XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot detect hyd ...
... X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) XPS is a surface chemical analysis technique that can be used to analyze the surface chemistry of a material in its "as received" state, or after some treatment XPS detects all elements with an atomic number (Z) of 3 (lithium) and above. It cannot detect hyd ...
Atomic Structure
... Stern-Gerlach Experiment The magnetic moment of a free electron is difficult to observe because the electric and magnetic forces due to the electronic charge are large. Evidence appeared in experiments with neutral atoms. ...
... Stern-Gerlach Experiment The magnetic moment of a free electron is difficult to observe because the electric and magnetic forces due to the electronic charge are large. Evidence appeared in experiments with neutral atoms. ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.