Introduction to gas discharges - University of San Diego Home Pages
... Similar concepts apply to charged particle populations. In the following some more useful rabbits are pulled out of the hat of kinetic theory. Use will be made of the following data: ...
... Similar concepts apply to charged particle populations. In the following some more useful rabbits are pulled out of the hat of kinetic theory. Use will be made of the following data: ...
1 - Academics
... In essence, what this means is: a) No particle can travel faster than Planck’s Constant; b) The velocity and the position of an electron can be measured to greater than h/4 significant figures; c) Electrons exhibit wave-particle duality but nothing else does; d) The momentum and the position of a p ...
... In essence, what this means is: a) No particle can travel faster than Planck’s Constant; b) The velocity and the position of an electron can be measured to greater than h/4 significant figures; c) Electrons exhibit wave-particle duality but nothing else does; d) The momentum and the position of a p ...
Decoherence - Center for Ultracold Atoms
... momentum transfer caused by a diffraction grating. In this case, loss of contrast still occurs, but less abruptly as a function of separation, and this de-phasing arises from a qualitatively different reason. The atom’s own longitudinal momentum plays the role of the environment. This mechanism may ...
... momentum transfer caused by a diffraction grating. In this case, loss of contrast still occurs, but less abruptly as a function of separation, and this de-phasing arises from a qualitatively different reason. The atom’s own longitudinal momentum plays the role of the environment. This mechanism may ...
Electron Transport Through Thiolized Gold Nanoparticles in Single
... conducting island seems very promising for the future of electronics. The size of the conducting island is the main factor that determines the maximum possible operating temperature of the SET. Because of their chemical-mechanical stability and only small deviations in their size and shape, gold nan ...
... conducting island seems very promising for the future of electronics. The size of the conducting island is the main factor that determines the maximum possible operating temperature of the SET. Because of their chemical-mechanical stability and only small deviations in their size and shape, gold nan ...
Chapter Outline Measuring Polarity Examples Permanent Dipole
... around the central C atom is tetrahedral. ...
... around the central C atom is tetrahedral. ...
Monday, February 8, 2010
... • 1895 Roentgen found that when fast moving electrons strike matter a highly penetrating unknown radiation (X-Ray) is produced. He found certain characteristics of X-Rays: they 1) travel in straight lines 2) are unaffected by E+B fields (what does this imply?) 3) can pass through opaque materials 4) ...
... • 1895 Roentgen found that when fast moving electrons strike matter a highly penetrating unknown radiation (X-Ray) is produced. He found certain characteristics of X-Rays: they 1) travel in straight lines 2) are unaffected by E+B fields (what does this imply?) 3) can pass through opaque materials 4) ...
Jon Abbatt - Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Physics
... Although sulfate aerosols all contain the SO42- ion, they are a highly heterogeneous mix of aerosol types. Formed from the oxidation of more chemically reduced sulfur compounds. Present in the nucleation and accumulation modes. Over the continents, the major sulfur source is SO2, formed from ...
... Although sulfate aerosols all contain the SO42- ion, they are a highly heterogeneous mix of aerosol types. Formed from the oxidation of more chemically reduced sulfur compounds. Present in the nucleation and accumulation modes. Over the continents, the major sulfur source is SO2, formed from ...
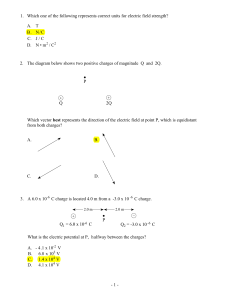
1. Which one of the following represents correct units for electric field
... 14. A particle with a charge of 2.4 × 10 −5 C is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 6.2 × 10 4 V . If the final speed of this particle is 9.3 × 103 m/s, what is the mass of the particle? A. 7. 7 × 10 −10 kg B. 5. 2 × 10 −9 kg C. 3. 4 × 10 −8 kg D. 1. 5 × 10 −1 kg 15. Two positi ...
... 14. A particle with a charge of 2.4 × 10 −5 C is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 6.2 × 10 4 V . If the final speed of this particle is 9.3 × 103 m/s, what is the mass of the particle? A. 7. 7 × 10 −10 kg B. 5. 2 × 10 −9 kg C. 3. 4 × 10 −8 kg D. 1. 5 × 10 −1 kg 15. Two positi ...
homework assignment - Global Change Program
... This mass balance equation can be used to ask several questions. For example, if you were interested in the effect of photosynthesis on the net change of oxygen in the atmosphere, then the equation would be written as follows: Net change = Photosynthesis (the INPUT of O2 to the atm) + Outputs (in th ...
... This mass balance equation can be used to ask several questions. For example, if you were interested in the effect of photosynthesis on the net change of oxygen in the atmosphere, then the equation would be written as follows: Net change = Photosynthesis (the INPUT of O2 to the atm) + Outputs (in th ...
artificial atoms - Quantum Device Lab
... One way to learn about natural atoms is to measure the energy required to add or remove electrons. This is usually done by photoelectron spectroscopy. For example, the minimum photon energy needed to remove an electron is the ionization potential, and the maximum energy of photons emitted when an at ...
... One way to learn about natural atoms is to measure the energy required to add or remove electrons. This is usually done by photoelectron spectroscopy. For example, the minimum photon energy needed to remove an electron is the ionization potential, and the maximum energy of photons emitted when an at ...
CHAP4
... sort of pattern do you think you will observed? It’s the interference pattern that are in fact observed in experiments At the source the electron is being emitted as particle and is experimentally detected as a electron which is absorbed by an individual atom in the fluorescent plate In between, we ...
... sort of pattern do you think you will observed? It’s the interference pattern that are in fact observed in experiments At the source the electron is being emitted as particle and is experimentally detected as a electron which is absorbed by an individual atom in the fluorescent plate In between, we ...
1 STOICHIOMETRY (I) Molecular Mass: The sum of the masses of
... and 27.55 % O. Determine its empirical formula. 2. Molecular formula (the actual formula): i) Calculate the empirical formula. ii) Calculate the formula mass for the empirical formula. iii) Divide the empirical formula mass by the molecular mass giving the integral factor. iv) Multiply all subscript ...
... and 27.55 % O. Determine its empirical formula. 2. Molecular formula (the actual formula): i) Calculate the empirical formula. ii) Calculate the formula mass for the empirical formula. iii) Divide the empirical formula mass by the molecular mass giving the integral factor. iv) Multiply all subscript ...
Does Quantum Mechanics Make Sense?
... A free particle, a photon, an electron, a rock, is the simplest system. A free particle is a particle moving without any forces acting on it, no electric or magnetic fields, no gravity, etc. Photon with perfectly defined momentum p, (momentum eigenstate) has a wavelength of its probability amplitude ...
... A free particle, a photon, an electron, a rock, is the simplest system. A free particle is a particle moving without any forces acting on it, no electric or magnetic fields, no gravity, etc. Photon with perfectly defined momentum p, (momentum eigenstate) has a wavelength of its probability amplitude ...
Electronic Structure of Sr2RuO4
... ABAABABA Ã ABAAB Ã ABA Ã AB Ã A • 2D Quasicrystal: Penrose tilings ...
... ABAABABA Ã ABAAB Ã ABA Ã AB Ã A • 2D Quasicrystal: Penrose tilings ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.