Heisenberg microscope and which-way experiments
... experiment. It is one of the most important experiments of wave theory and a clear example of the diffraction of light conducted with essentially basic scientific equipment. The double-slit experiment consists of letting light diffract through two slits producing fringes on a screen. These fringes o ...
... experiment. It is one of the most important experiments of wave theory and a clear example of the diffraction of light conducted with essentially basic scientific equipment. The double-slit experiment consists of letting light diffract through two slits producing fringes on a screen. These fringes o ...
Chapter 7_honors
... as an anion. Likewise the less electronegative element is assigned the positive charge as the cation. ...
... as an anion. Likewise the less electronegative element is assigned the positive charge as the cation. ...
Quantum Mechanics
... Photoelectric Fact #3 Work function, f, is defined as the least energy that must be supplied to remove a free electron from the surface of the metal, against the attractive forces of surrounding positive ions. Shown here is a PHOTOCELL. When incident light of appropriate frequency strikes the metal ...
... Photoelectric Fact #3 Work function, f, is defined as the least energy that must be supplied to remove a free electron from the surface of the metal, against the attractive forces of surrounding positive ions. Shown here is a PHOTOCELL. When incident light of appropriate frequency strikes the metal ...
CHEMISTRY 120A FALL 2006
... Week 6: Chapter 6 — The Hydrogen Atom. Spherical solution to the Schrödinger equation, spherical harmonics, hydrogen atom wavefunctions and energy levels, Rotational spectroscopy, angular momentum. (WHM/HY) Week 7: Chapter 7 — Approximation Methods. Variational theory, non-degenerate perturbation th ...
... Week 6: Chapter 6 — The Hydrogen Atom. Spherical solution to the Schrödinger equation, spherical harmonics, hydrogen atom wavefunctions and energy levels, Rotational spectroscopy, angular momentum. (WHM/HY) Week 7: Chapter 7 — Approximation Methods. Variational theory, non-degenerate perturbation th ...
AP® Physics B 2011 Free-Response Questions - AP Central
... fall under the influence of gravity between two parallel metal plates separated by a fixed distance L . A variable potential difference may be applied between the two plates. The experiment is conducted inside a vacuum chamber. (a) A potential difference of magnitude V is applied between the top and ...
... fall under the influence of gravity between two parallel metal plates separated by a fixed distance L . A variable potential difference may be applied between the two plates. The experiment is conducted inside a vacuum chamber. (a) A potential difference of magnitude V is applied between the top and ...
Particle Notes
... Note that in order for energy and momentum to remain finite, velocity has an upper bound at c, because γ diverges as v → c in equations (1.26) and (1.28). The only way around the prohibition against light speed is for a particle to have zero mass. Conversely, any massless particle must move at speed ...
... Note that in order for energy and momentum to remain finite, velocity has an upper bound at c, because γ diverges as v → c in equations (1.26) and (1.28). The only way around the prohibition against light speed is for a particle to have zero mass. Conversely, any massless particle must move at speed ...
Core_Class_Science_Chemistry_for_the_web 838.3 KB
... Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes that give off radiation are called radioactive isotopes. A compound is a pure substance formed when two or more different elements combine. Compounds are always formed from a specific combination of elem ...
... Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes that give off radiation are called radioactive isotopes. A compound is a pure substance formed when two or more different elements combine. Compounds are always formed from a specific combination of elem ...
CHEMISTRY 120A FALL 2006 Lectures: MWF 10
... Week 6: Chapter 6 — The Hydrogen Atom. Spherical solution to the Schrödinger equation, spherical harmonics, hydrogen atom wavefunctions and energy levels, Rotational spectroscopy, angular momentum. (WHM/HY) Week 7: Chapter 7 — Approximation Methods. Variational theory, non-degenerate perturbation th ...
... Week 6: Chapter 6 — The Hydrogen Atom. Spherical solution to the Schrödinger equation, spherical harmonics, hydrogen atom wavefunctions and energy levels, Rotational spectroscopy, angular momentum. (WHM/HY) Week 7: Chapter 7 — Approximation Methods. Variational theory, non-degenerate perturbation th ...
Sub Unit Plan 1 Chem Periodic Table
... or a period for Groups 1, 2, 13-18 on the Periodic Table xv determine the group of an element, given the chemical formula of a compound, e.g., XCl or XCl2 xvi explain the placement of an unknown element on the Periodic Table based on its properties Explain the properties of materials in terms of the ...
... or a period for Groups 1, 2, 13-18 on the Periodic Table xv determine the group of an element, given the chemical formula of a compound, e.g., XCl or XCl2 xvi explain the placement of an unknown element on the Periodic Table based on its properties Explain the properties of materials in terms of the ...
Document
... Product of annihilation and creation operators , we defined the normal ordered product by Moving all annihilation operators to the right Of all creation operators as if commutators ...
... Product of annihilation and creation operators , we defined the normal ordered product by Moving all annihilation operators to the right Of all creation operators as if commutators ...
Chapter 7 The Quantum- Mechanical Model of the Atom
... particle was inversely proportional to its mass. – x = position, x = uncertainty in position – v = velocity, v = uncertainty in velocity – m = mass • This means that the more accurately you know the position of a small particle, such as an electron, the less you know about its speed, and vice vers ...
... particle was inversely proportional to its mass. – x = position, x = uncertainty in position – v = velocity, v = uncertainty in velocity – m = mass • This means that the more accurately you know the position of a small particle, such as an electron, the less you know about its speed, and vice vers ...
Energy and angular distributions of electrons resulting from barrier
... atom after approximately one orbit around the atomic core (i.e., after a time of order one Kepler period t,=2rn3): ...
... atom after approximately one orbit around the atomic core (i.e., after a time of order one Kepler period t,=2rn3): ...
Chapter 8
... surrounding the oxygen tend to arrange themselves as far from each other as possible in order to minimize repulsive forces. This results in a tetrahedral geometry in which the H-O-H bond angle would be 109.5°. However, the two lone pairs around the oxygen atom, have a greater space requirement, effe ...
... surrounding the oxygen tend to arrange themselves as far from each other as possible in order to minimize repulsive forces. This results in a tetrahedral geometry in which the H-O-H bond angle would be 109.5°. However, the two lone pairs around the oxygen atom, have a greater space requirement, effe ...
Section 7.5 Quantum Mechanics and the Atom
... physics to explain the behavior of the atom. • This process had already begun with the breaking down of the barrier between light as a wave and matter as a particle. • Einstein showed that light behaves as a particle • The Bohr model is the beginning to the process of treating matter (electrons) as ...
... physics to explain the behavior of the atom. • This process had already begun with the breaking down of the barrier between light as a wave and matter as a particle. • Einstein showed that light behaves as a particle • The Bohr model is the beginning to the process of treating matter (electrons) as ...
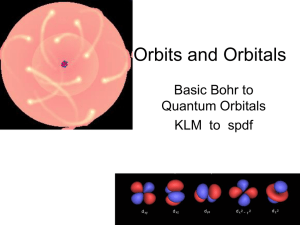
Orbits and Orbitals
... • Orbitals are half filled (with spins in the same direction) before they are doubly filled. • Orbitals are filled from lowest energy to highest energy. ...
... • Orbitals are half filled (with spins in the same direction) before they are doubly filled. • Orbitals are filled from lowest energy to highest energy. ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.