The Preparation of an Explosive: Nitrogen
... One mole of N2 is created at 944 kJ mol-1 and 3 I-I at 151 kJ mol-1 producing 1397 KJ mol-1. The change in energy is equal to the enthalphy of the reactants deducting the enthalphy of the products, giving the highly exothermic reaction (Fig. 3) and overall energy change of -437 kJ mol-1. 5 Results a ...
... One mole of N2 is created at 944 kJ mol-1 and 3 I-I at 151 kJ mol-1 producing 1397 KJ mol-1. The change in energy is equal to the enthalphy of the reactants deducting the enthalphy of the products, giving the highly exothermic reaction (Fig. 3) and overall energy change of -437 kJ mol-1. 5 Results a ...
Section 1.6 - 1 1.6 Term Symbols A brief general review of atomic
... Leads to the Pauli-Principle: No two Fermions in any spatially/energetically confined system can have the same four quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms). SEE SUPP. INFO ON HUND’S RULE ...
... Leads to the Pauli-Principle: No two Fermions in any spatially/energetically confined system can have the same four quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms). SEE SUPP. INFO ON HUND’S RULE ...
laser-assisted electron-atom collisions
... with Feshbach projection operators, Francken and Joanchain 24 have analyzed the electron impact excitation of the 2S and 21p states of helium in the presence of a laser field which resonantly couples the two excited final states. To conclude, we shall now briefly describe a completely non-perturbati ...
... with Feshbach projection operators, Francken and Joanchain 24 have analyzed the electron impact excitation of the 2S and 21p states of helium in the presence of a laser field which resonantly couples the two excited final states. To conclude, we shall now briefly describe a completely non-perturbati ...
2.5 THE NAMES AND FORMULAS OF COMPOUNDS
... explain many of the properties of ionic compounds, but they aren’t sufficient to explain the physical state of molecular compounds. If covalent bonds were the only forces at work, molecular compounds would all be gases, as there would be no attraction between the molecules strong enough to order the ...
... explain many of the properties of ionic compounds, but they aren’t sufficient to explain the physical state of molecular compounds. If covalent bonds were the only forces at work, molecular compounds would all be gases, as there would be no attraction between the molecules strong enough to order the ...
Chapter 10 - Chemical Quantities
... 21. Find the empirical formula of a compound, given that the compound is found to be 47.9% zinc (Zn) and 52.1% chlorine (Cl) by mass. (Zn = 65.4 g/mol; Cl = 35.5 g/mol) Ans: ZnCl2 22. Find the empirical formula of a compound, given that a 48.5-g sample of the compound is found to contain 1.75 g of c ...
... 21. Find the empirical formula of a compound, given that the compound is found to be 47.9% zinc (Zn) and 52.1% chlorine (Cl) by mass. (Zn = 65.4 g/mol; Cl = 35.5 g/mol) Ans: ZnCl2 22. Find the empirical formula of a compound, given that a 48.5-g sample of the compound is found to contain 1.75 g of c ...
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc
... The uncertainty ("x) is given as ±1% (0.01) of 6x106 m/s. Once we calculate this, plug it into the uncertainty equation. ...
... The uncertainty ("x) is given as ±1% (0.01) of 6x106 m/s. Once we calculate this, plug it into the uncertainty equation. ...
Additional background material on the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1998
... be possible to minimize the energy of the system with respect to variations in the geometrical parameters. In order to do that, one needs not only the energy itself for a given geometry, but also the energy derivatives, at least the gradient, but preferably also the second derivatives, the Hessian. ...
... be possible to minimize the energy of the system with respect to variations in the geometrical parameters. In order to do that, one needs not only the energy itself for a given geometry, but also the energy derivatives, at least the gradient, but preferably also the second derivatives, the Hessian. ...
F - Purdue Physics
... accelerating to the right. It will eventually match velocity with the belt, at which point Fk will VANISH ...
... accelerating to the right. It will eventually match velocity with the belt, at which point Fk will VANISH ...
Quantum Mechanics Unit Review Answers AP Physics
... It turns out that electrons shot through two tiny slits will produce an interference pattern on the screen behind the slits, exactly like light with the same wavelength. Realistically, you can’t construct slits small enough to diffract electrons, but you can use the regular spacing between atoms in ...
... It turns out that electrons shot through two tiny slits will produce an interference pattern on the screen behind the slits, exactly like light with the same wavelength. Realistically, you can’t construct slits small enough to diffract electrons, but you can use the regular spacing between atoms in ...
Molecular Geometry and Polarity1
... A key to understanding the wide range of physical and chemical properties of substances is recognizing that atoms combine with other atoms to form molecules or compounds and that the shape or geometry of a collection of atoms strongly affects the properties of that substance. One reason this occurs ...
... A key to understanding the wide range of physical and chemical properties of substances is recognizing that atoms combine with other atoms to form molecules or compounds and that the shape or geometry of a collection of atoms strongly affects the properties of that substance. One reason this occurs ...
Phase Transitions of Dirac Electrons Observed in Bismuth
... electronic phase transitions into states in which the repulsion energy can be lowered. (A familiar example of a phase transition is the melting of ice to water. In metals, electronic transitions occur to the superconducting state or the ferromagnetic state as the temperature is lowered.) Theorists h ...
... electronic phase transitions into states in which the repulsion energy can be lowered. (A familiar example of a phase transition is the melting of ice to water. In metals, electronic transitions occur to the superconducting state or the ferromagnetic state as the temperature is lowered.) Theorists h ...
superposition - University of Illinois at Urbana
... “macroscopically distinct” than those of dust particles! ...
... “macroscopically distinct” than those of dust particles! ...
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding
... formation of a covalent bond.) Continue doing this until each atom has an octet (exceptions are H, Be, B, Al, elements on rows 3, 4, 5, and 6.) No electrons should be left unpaired (only in rare cases will a species contain an unpaired electron.) For those atoms that can have more than an octet, if ...
... formation of a covalent bond.) Continue doing this until each atom has an octet (exceptions are H, Be, B, Al, elements on rows 3, 4, 5, and 6.) No electrons should be left unpaired (only in rare cases will a species contain an unpaired electron.) For those atoms that can have more than an octet, if ...
mole concept and stoichiometry
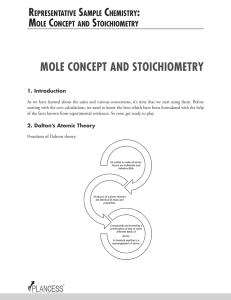
... Jeremiasa Richter German scientist in 1972 proposed a law known as “Law of Reciprocal Proportions “ The Law States that , “The ratio of the weights of two elements, A and B which combine separately with a fixed weight of the third element C is either the same or some simple multiple of the ratio of ...
... Jeremiasa Richter German scientist in 1972 proposed a law known as “Law of Reciprocal Proportions “ The Law States that , “The ratio of the weights of two elements, A and B which combine separately with a fixed weight of the third element C is either the same or some simple multiple of the ratio of ...
Notes-C12-121
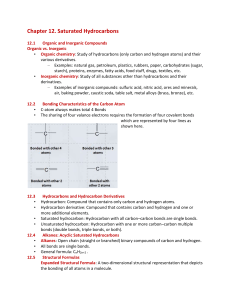
... • Rule 2: Number the carbon atoms in the parent chain in such a way so that to give the lowest possible number for a substituent (alkyl group). • Rule 3: If only one substituent present, name and locate it by number; then, prefix the number and name to that of the parent carbon chain. • Rule 4: If t ...
... • Rule 2: Number the carbon atoms in the parent chain in such a way so that to give the lowest possible number for a substituent (alkyl group). • Rule 3: If only one substituent present, name and locate it by number; then, prefix the number and name to that of the parent carbon chain. • Rule 4: If t ...
Quantum Mechanics Bohr`s model: - one of the first ones to use idea
... - a vast number of experiments in physics and chemistry is successfully explained using this new theory - up to now the theory of quantum mechanics has been proven to be correct by many experiments - quantum mechanics is a very successful theory ...
... - a vast number of experiments in physics and chemistry is successfully explained using this new theory - up to now the theory of quantum mechanics has been proven to be correct by many experiments - quantum mechanics is a very successful theory ...
Chapter 4 The structure of diatomic molecules
... of our own imagination.” --C.A. Coulson (1910-1974) ...
... of our own imagination.” --C.A. Coulson (1910-1974) ...
Chemical Reactions
... 1. Write the word equation for the reaction. water hydrogen + oxygen 2. Write the formula equation. H2O(l) H2(g) + O2(g) 3. Balance the formula equation according to the law of conservation of mass. 4. Double check the number of atoms on each side. ...
... 1. Write the word equation for the reaction. water hydrogen + oxygen 2. Write the formula equation. H2O(l) H2(g) + O2(g) 3. Balance the formula equation according to the law of conservation of mass. 4. Double check the number of atoms on each side. ...
Class 23_270_11
... will produce an interference pattern, like a wave. • However, each electron makes a single impact on a phosphorescent screen‐like a particle. • Electrons have indivisible (as far as we know) mass and electric charge, so if you suddenly closed one of the slits, you couldn’t chop the electron in ...
... will produce an interference pattern, like a wave. • However, each electron makes a single impact on a phosphorescent screen‐like a particle. • Electrons have indivisible (as far as we know) mass and electric charge, so if you suddenly closed one of the slits, you couldn’t chop the electron in ...
Quantum Statistics - Ole Witt
... 4. An ideal gas consisting of non identical particles.................................................................. 8 5. The linear harmonic oscillator. Solid crystal materials........................................................ 10 6. Planck’s law for black body radiation.................... ...
... 4. An ideal gas consisting of non identical particles.................................................................. 8 5. The linear harmonic oscillator. Solid crystal materials........................................................ 10 6. Planck’s law for black body radiation.................... ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.