CHAP6a
... (x) inside the well. Note that in a fixed quantum state n, B is a constant because E is conserved. However, if the particle jumps to a state n’ ≠ n, E takes on other values. In this case, E is not conserved because there is an net change in the total energy of the system due to interactions with e ...
... (x) inside the well. Note that in a fixed quantum state n, B is a constant because E is conserved. However, if the particle jumps to a state n’ ≠ n, E takes on other values. In this case, E is not conserved because there is an net change in the total energy of the system due to interactions with e ...
CHEM 322 - Queen`s Chemistry
... experimental research on electronically excited states. Each spectroscopic technique will be first introduced using fundamental QM principles, and then expanded by introducing practical applications. Evaluation: The course involves 4-6 assignments. A midterm and a final exam are going to contribute ...
... experimental research on electronically excited states. Each spectroscopic technique will be first introduced using fundamental QM principles, and then expanded by introducing practical applications. Evaluation: The course involves 4-6 assignments. A midterm and a final exam are going to contribute ...
Cavity QED
... and the single ion/atom trapping. This is not just doubly-veryhard, but may well be (very-hard)2 • Assuming “hard” > 1, we have “very hard” >> 1, and (“very hard”)2 >> “very hard” • However, the benefits of cavity QED, namely, the connection of static qubits to flying qubits, are very exciting and a ...
... and the single ion/atom trapping. This is not just doubly-veryhard, but may well be (very-hard)2 • Assuming “hard” > 1, we have “very hard” >> 1, and (“very hard”)2 >> “very hard” • However, the benefits of cavity QED, namely, the connection of static qubits to flying qubits, are very exciting and a ...
Impulse, Momentum and Conservation of Momentum
... By rewriting his own 2nd law, Newton defined impulse F= m . a =m . v t F . t = m . Δv J = F . t= mΔv = Δp =change in momentum ...
... By rewriting his own 2nd law, Newton defined impulse F= m . a =m . v t F . t = m . Δv J = F . t= mΔv = Δp =change in momentum ...
PPT
... can't function) so there could be no minds whatever. • The low-entropy property of the past is needed to allow some information about it to be conveyed with a relatively small number of bits. I.e. a photograph of some place tells you a lot about it, but a photograph of some equilibrated mush conveys ...
... can't function) so there could be no minds whatever. • The low-entropy property of the past is needed to allow some information about it to be conveyed with a relatively small number of bits. I.e. a photograph of some place tells you a lot about it, but a photograph of some equilibrated mush conveys ...
Quantum Mechanics: Concepts and Applications, 2nd Edition
... with the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, except as permitted by the UK Copyright, Desi ...
... with the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, except as permitted by the UK Copyright, Desi ...
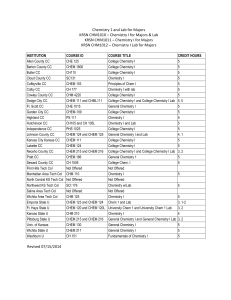
Chemistry 1 and Lab for Majors KRSN CHM1010 – Chemistry I for
... Explain the processes involved in the scientific method, and be able to apply it to investigate natural phenomena and solve problems. II. Explain the design and significance of experiments that led to the adoption of modern atomic theory. III. Recognize and interpret isotopic notation; understanding ...
... Explain the processes involved in the scientific method, and be able to apply it to investigate natural phenomena and solve problems. II. Explain the design and significance of experiments that led to the adoption of modern atomic theory. III. Recognize and interpret isotopic notation; understanding ...
Superfluid Helium
... zero entropy system has Ω=1. In other words any system must collapse to a unique ground state as temperature goes to absolute zero. But what is this state? For simplicity we will start by considering only the case of 4He. 4He is what is known as a boson. In brief bosons are all particles with intege ...
... zero entropy system has Ω=1. In other words any system must collapse to a unique ground state as temperature goes to absolute zero. But what is this state? For simplicity we will start by considering only the case of 4He. 4He is what is known as a boson. In brief bosons are all particles with intege ...
George Facer`s A level Chemistry
... We are working with Edexcel to get these resources endorsed: Edexcel A level Biology Year 1 Student Book 9781471807343 Mar 2015 £24.99 Edexcel A level Biology Year 2 Student Book 9781471807374 May 2015 £24.99 Edexcel A level Chemistry Year 1 Student Book 9781471807466 Mar 2015 £24.99 Edexcel A level ...
... We are working with Edexcel to get these resources endorsed: Edexcel A level Biology Year 1 Student Book 9781471807343 Mar 2015 £24.99 Edexcel A level Biology Year 2 Student Book 9781471807374 May 2015 £24.99 Edexcel A level Chemistry Year 1 Student Book 9781471807466 Mar 2015 £24.99 Edexcel A level ...
84 MULTI-SCALE SIMULATIONS OF DYE SENSITIZED SOLAR
... rate: KL and K0 correspond to saturation current and photocurrent. Such equivalent circuit models of DSSC are useful in association with experimental approach for finding empirical values in electron kinetic describing [4], [5]. Since DSSC enabled entities at different dimensional scale, the constru ...
... rate: KL and K0 correspond to saturation current and photocurrent. Such equivalent circuit models of DSSC are useful in association with experimental approach for finding empirical values in electron kinetic describing [4], [5]. Since DSSC enabled entities at different dimensional scale, the constru ...
Gr. 11 Chemistry Student Workbook (Spring 2016)
... One of the most important educational skills you can develop is how to monitor and track your own learning. Either at the end of class or at home, you will complete a daily entry in your learning log. Written Work: Use our marking scheme for daily class work (out of 5) to assess your written work. W ...
... One of the most important educational skills you can develop is how to monitor and track your own learning. Either at the end of class or at home, you will complete a daily entry in your learning log. Written Work: Use our marking scheme for daily class work (out of 5) to assess your written work. W ...
THE CHEMICAL FORMULA CnH2n+2 AND ITS MATHEMATICAL
... the zillion possible alkanes possesses more than 2n + 2 or less than 2n + 2 hydrogen atoms? If someone wants to embarrass his chemistry teacher, he may ask him this question. It is unlikely that the teacher will be able of offer a satisfactory answer. In the best case (typical for chemists) he will ...
... the zillion possible alkanes possesses more than 2n + 2 or less than 2n + 2 hydrogen atoms? If someone wants to embarrass his chemistry teacher, he may ask him this question. It is unlikely that the teacher will be able of offer a satisfactory answer. In the best case (typical for chemists) he will ...
Technical Tricks of Coarse-Grained MD Visualization
... Put a lattice on central image (“cells”) Cell size ~ cutoff Store a list of particles per cell Interaction partners must all be in neighboring 27 cells When a particle moves, move it to new cell Reduces complexity to O(N) (at constant density) Requires at least 3 cells per ...
... Put a lattice on central image (“cells”) Cell size ~ cutoff Store a list of particles per cell Interaction partners must all be in neighboring 27 cells When a particle moves, move it to new cell Reduces complexity to O(N) (at constant density) Requires at least 3 cells per ...
How physics could explain the mind
... understood and included in the accepted theories that are used to model the world. Many theoretical physicists are feeling pressured to come up with new theories that can explain these measurements. This is what is called the imminent crisis of theoretical physics. The best known phenomena that cann ...
... understood and included in the accepted theories that are used to model the world. Many theoretical physicists are feeling pressured to come up with new theories that can explain these measurements. This is what is called the imminent crisis of theoretical physics. The best known phenomena that cann ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.