Tunneling spectroscopy of disordered two
... is still observable (red). Considering, in addition, the influence of the heated charge distribution in the tunneling electrode renders this ...
... is still observable (red). Considering, in addition, the influence of the heated charge distribution in the tunneling electrode renders this ...
Redox Balancing Worksheet
... Fortunately, the film of Ag2S that collects on the metal surface forms a protective coating that slows down further oxidation of the silver metal. For many years, chemists thought of oxidation and reduction as involving the element oxygen in some way or another. That's where the name oxidation came ...
... Fortunately, the film of Ag2S that collects on the metal surface forms a protective coating that slows down further oxidation of the silver metal. For many years, chemists thought of oxidation and reduction as involving the element oxygen in some way or another. That's where the name oxidation came ...
Problem Set 3: Solutions
... With the given photon frequency of 1 MHz, we find P ∼ 10−21 W, a negligible amount of power. For photons of visible light, in the 1015 Hz range, the power is ∼ 10−12 W, which is close to the limit of human vision. With dark-adapted scotopic vision, we detect about 8 × 10−11 W/m2 of green light (550 ...
... With the given photon frequency of 1 MHz, we find P ∼ 10−21 W, a negligible amount of power. For photons of visible light, in the 1015 Hz range, the power is ∼ 10−12 W, which is close to the limit of human vision. With dark-adapted scotopic vision, we detect about 8 × 10−11 W/m2 of green light (550 ...
Balancing Equations
... 1. Word Equations—Show the names of reactants and products. Example: Sodium + Chlorine Sodium chloride 2. Chemical equations—Show the formulas of reactants and products. Example: Na + Cl2 NaCl (Not Balanced Yet!) 3. Skeleton equations—Equations that are not yet balanced to represent what actuall ...
... 1. Word Equations—Show the names of reactants and products. Example: Sodium + Chlorine Sodium chloride 2. Chemical equations—Show the formulas of reactants and products. Example: Na + Cl2 NaCl (Not Balanced Yet!) 3. Skeleton equations—Equations that are not yet balanced to represent what actuall ...
1 - Intro to Electrochemistry
... A redox reaction is one where one substance is _______________ while another substance is simultaneously _______________ ...
... A redox reaction is one where one substance is _______________ while another substance is simultaneously _______________ ...
293) Physics
... 26) Theory : a hypothesis that has been tested many times and is supported by evidence. 27) Vein – A bundle of vascular tissue that carries materials to and from a leaf. 28) Regeneration: is the regrowth of body parts that have been lost or damaged 29) Palisade – The layer of columnlike cells below ...
... 26) Theory : a hypothesis that has been tested many times and is supported by evidence. 27) Vein – A bundle of vascular tissue that carries materials to and from a leaf. 28) Regeneration: is the regrowth of body parts that have been lost or damaged 29) Palisade – The layer of columnlike cells below ...
Quantum Computing Using Electrons Floating on
... Vs eE ?z, which Stark-shifts the energy levels. The transitions were observed at frequencies from 130 to 220 GHz by measuring the microwave absorption derivative at a fixed frequency as the splitting between the states was tuned past resonance by modulating the field E ?, see Fig. 2. The calculate ...
... Vs eE ?z, which Stark-shifts the energy levels. The transitions were observed at frequencies from 130 to 220 GHz by measuring the microwave absorption derivative at a fixed frequency as the splitting between the states was tuned past resonance by modulating the field E ?, see Fig. 2. The calculate ...
Laser Selective Chemistry: A New Challenge for
... given a relatively low energy, the bond vibrates in a harmonic way (like a harmonic oscillator o r regular pendulum motion). As the energy increases, the vibration becomes anharmonic, o r irregular. The motion in the low- and high-energy limits can be visualized in terms of a potential energy surfa ...
... given a relatively low energy, the bond vibrates in a harmonic way (like a harmonic oscillator o r regular pendulum motion). As the energy increases, the vibration becomes anharmonic, o r irregular. The motion in the low- and high-energy limits can be visualized in terms of a potential energy surfa ...
Valence Bond theory
... predictions concerning bond order, unpaired electron spins. Difficulties in use for some molecules (requiring resonance structures). VSEPR- Based on Lewis theory, and allows predictions of molecular geometries. However, some of the same weaknesses of Lewis theory. Valence Bond theory (with hybridiza ...
... predictions concerning bond order, unpaired electron spins. Difficulties in use for some molecules (requiring resonance structures). VSEPR- Based on Lewis theory, and allows predictions of molecular geometries. However, some of the same weaknesses of Lewis theory. Valence Bond theory (with hybridiza ...
Physics 2170
... • Next weeks homework should be available by 5pm today and is due next week, 4/22. • The last homework set will be out on 4/22 and will be due on 4/30 (one day later than normal). It is a normal assignment, not an extra credit assignment. ...
... • Next weeks homework should be available by 5pm today and is due next week, 4/22. • The last homework set will be out on 4/22 and will be due on 4/30 (one day later than normal). It is a normal assignment, not an extra credit assignment. ...
PH1130LAB_SK - WPI - Worcester Polytechnic Institute
... absorbed by a system results from a change in state whereby the quantum number, n, of the system changes by one. In 1905 Albert Einstein (1879-1955) published a paper in which he used Planck's quantization of energy principle to explain the photoelectric effect. The photoelectric effect involves the ...
... absorbed by a system results from a change in state whereby the quantum number, n, of the system changes by one. In 1905 Albert Einstein (1879-1955) published a paper in which he used Planck's quantization of energy principle to explain the photoelectric effect. The photoelectric effect involves the ...
Adobe Photoshop PDF - Perimeter Institute
... the rod sags. Ask students to explain why the rod is sagging–typically students will say “force of gravity!” 2. Place the rod on a table. Have two students apply horizontal forces on the ends while you hold the middle in place by applying an opposing horizontal force. The class observes the same s ...
... the rod sags. Ask students to explain why the rod is sagging–typically students will say “force of gravity!” 2. Place the rod on a table. Have two students apply horizontal forces on the ends while you hold the middle in place by applying an opposing horizontal force. The class observes the same s ...
Chemistry - Edexcel
... (iii) Suggest a connection between the atomic number and the reactivity of the elements in Group 2. ...
... (iii) Suggest a connection between the atomic number and the reactivity of the elements in Group 2. ...
Title: Understanding of Molecular Orbital
... We also came to know about their symmetry such as gerade (g) and ungerade (u) depending on electronic distribution about the center of inversion. This arises only for the symmetric molecules that have inversion symmetry. We have also understood how to distribute electrons into the molecular orbitals ...
... We also came to know about their symmetry such as gerade (g) and ungerade (u) depending on electronic distribution about the center of inversion. This arises only for the symmetric molecules that have inversion symmetry. We have also understood how to distribute electrons into the molecular orbitals ...
LECTURE 13 QUARKS PHY492 Nuclear and Elementary Particle Physics
... Hadron Spectroscopy The study of the static properties of hadrons: their masses, lifetimes, and decay modes, and their quantum numbers (spin, electric charge etc) lead to the inference of quarks by Gell-Mann and Zweig in 1964. Example: ...
... Hadron Spectroscopy The study of the static properties of hadrons: their masses, lifetimes, and decay modes, and their quantum numbers (spin, electric charge etc) lead to the inference of quarks by Gell-Mann and Zweig in 1964. Example: ...
Part I - American Chemical Society
... DIRECTIONS TO THE EXAMINER–PART I Part I of this test is designed to be taken with a Scantron® answer sheet on which the student records his or her responses. Only this Scantron sheet is graded for a score on Part I. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the Scantron sheet should be made available t ...
... DIRECTIONS TO THE EXAMINER–PART I Part I of this test is designed to be taken with a Scantron® answer sheet on which the student records his or her responses. Only this Scantron sheet is graded for a score on Part I. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the Scantron sheet should be made available t ...
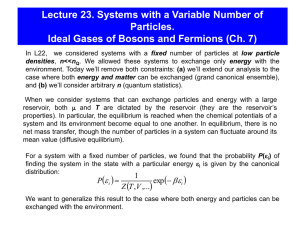
Lecture 23. Statistics of Ideal Quantum Systems
... Bosons: particles with zero or integer spin (in units of ħ). Examples: photons, all nuclei with even mass numbers. The wavefunction of a system of bosons is symmetric under the exchange of any pair of particles: (...,Qj,...Qi,..)= (...,Qi,...Qj,..). The number of bosons in a given state is unlimit ...
... Bosons: particles with zero or integer spin (in units of ħ). Examples: photons, all nuclei with even mass numbers. The wavefunction of a system of bosons is symmetric under the exchange of any pair of particles: (...,Qj,...Qi,..)= (...,Qi,...Qj,..). The number of bosons in a given state is unlimit ...
h h mv p =
... Wave-particle duality, a strange dichotomous co-dependency, was first recognized as a permanent feature of modern nanoscience when Niels Bohr proclaimed the complementarity principle as the corner stone of the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum theory. This scientific dogma states, among other thi ...
... Wave-particle duality, a strange dichotomous co-dependency, was first recognized as a permanent feature of modern nanoscience when Niels Bohr proclaimed the complementarity principle as the corner stone of the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum theory. This scientific dogma states, among other thi ...
A Molecular--Structure Hypothesis
... classical reasoning is most frequently used for dealing with conformational analysis [and] reaction mechanisms [...]. [I]t will not be very easy to rebuild some connection [...] from quantum theory toward classical theory [...] and this is a somewhat ridiculous situation since [...] classical models ...
... classical reasoning is most frequently used for dealing with conformational analysis [and] reaction mechanisms [...]. [I]t will not be very easy to rebuild some connection [...] from quantum theory toward classical theory [...] and this is a somewhat ridiculous situation since [...] classical models ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.