L1 – CHEMISTRY FINAL REVIEW
... 32. Describe the Van Der Waals forces between water molecules called dipole interactions or Hydrogen bonds. H-bond is a strong intermolecular bond between the slightly positive Hydrogen end of one water molecule and the slightly neg. oxygen end of an adjacent water molecule. 33. Name 4 unique proper ...
... 32. Describe the Van Der Waals forces between water molecules called dipole interactions or Hydrogen bonds. H-bond is a strong intermolecular bond between the slightly positive Hydrogen end of one water molecule and the slightly neg. oxygen end of an adjacent water molecule. 33. Name 4 unique proper ...
Technical Tricks of Coarse-Grained MD Visualization
... Put a lattice on central image (“cells”) Cell size ~ cutoff Store a list of particles per cell Interaction partners must all be in neighboring 27 cells When a particle moves, move it to new cell Reduces complexity to O(N) (at constant density) Requires at least 3 cells per ...
... Put a lattice on central image (“cells”) Cell size ~ cutoff Store a list of particles per cell Interaction partners must all be in neighboring 27 cells When a particle moves, move it to new cell Reduces complexity to O(N) (at constant density) Requires at least 3 cells per ...
Slides
... How does the GRW equation link up with the distribution of matter in space-time? GRWm (Ghirardi): matter density field described by Y GRWf (Bell): collapse of Y (spontaneous localization in configu-ration space) describes single events (flashes) in physical space In any case, no radical change from ...
... How does the GRW equation link up with the distribution of matter in space-time? GRWm (Ghirardi): matter density field described by Y GRWf (Bell): collapse of Y (spontaneous localization in configu-ration space) describes single events (flashes) in physical space In any case, no radical change from ...
How physics could explain the mind
... understood and included in the accepted theories that are used to model the world. Many theoretical physicists are feeling pressured to come up with new theories that can explain these measurements. This is what is called the imminent crisis of theoretical physics. The best known phenomena that cann ...
... understood and included in the accepted theories that are used to model the world. Many theoretical physicists are feeling pressured to come up with new theories that can explain these measurements. This is what is called the imminent crisis of theoretical physics. The best known phenomena that cann ...
AP Chemistry Syllabus
... AP Chemistry is designed to provide the student with the equivalent of an introductory first year course sequence in COLLEGE CHEMISTRY. The course is designed for college-bound students who either would like to earn college credit (by AP examination) or would like to prepare for college chemistry wh ...
... AP Chemistry is designed to provide the student with the equivalent of an introductory first year course sequence in COLLEGE CHEMISTRY. The course is designed for college-bound students who either would like to earn college credit (by AP examination) or would like to prepare for college chemistry wh ...
East Meck Chemistry
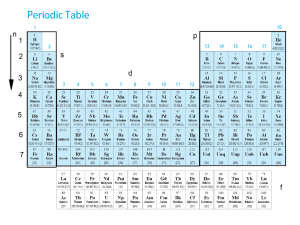
... any chemical change involves only a rearrangement of the atoms. Atoms do not just appear. Atoms do not just disappear. This is an example of the law of conservation of mass (or matter), which says that in a chemical change, matter is neither ________________ nor destroyed. All chemical changes also ...
... any chemical change involves only a rearrangement of the atoms. Atoms do not just appear. Atoms do not just disappear. This is an example of the law of conservation of mass (or matter), which says that in a chemical change, matter is neither ________________ nor destroyed. All chemical changes also ...
Slide 1
... • S is “real” in that it has classical analogs in mechanics (intrinsic angular momentum) and electrodynamics (magnetic moment) = gsS N • T has no classical analog; it is a quantum mechanical vector, literally “like spin” (iso = ‘like’), so it follows the same addition rules as S, L, J, etc... ...
... • S is “real” in that it has classical analogs in mechanics (intrinsic angular momentum) and electrodynamics (magnetic moment) = gsS N • T has no classical analog; it is a quantum mechanical vector, literally “like spin” (iso = ‘like’), so it follows the same addition rules as S, L, J, etc... ...
Discussion Questions
... a. The limiting reactant is the one with the higher molar mass. b. A is the limiting reactant because you need 6 moles of A and have 4 moles. c. B is the limiting reactant because you have fewer moles of B than A. d. B is the limiting reactant because three A molecules react with each B mole ...
... a. The limiting reactant is the one with the higher molar mass. b. A is the limiting reactant because you need 6 moles of A and have 4 moles. c. B is the limiting reactant because you have fewer moles of B than A. d. B is the limiting reactant because three A molecules react with each B mole ...
Real-World Quantum Measurements
... Problem: D C Consider a collection of bombs so sensitive that a collision with any single particle (photon, electron, etc.) Bomb absent: is guarranteed to trigger it. Only detector C fires BS2 that certain of Suppose the bombs are defective, but differ in their behaviour in no way other than that Bo ...
... Problem: D C Consider a collection of bombs so sensitive that a collision with any single particle (photon, electron, etc.) Bomb absent: is guarranteed to trigger it. Only detector C fires BS2 that certain of Suppose the bombs are defective, but differ in their behaviour in no way other than that Bo ...
Alkali D Line Data
... f is the partial pressure of water vapor in the air, in Pa (which can be computed from the relative humidity via the Goff-Gratch equation [15]). This formula is appropriate for laboratory conditions and has an estimated (3σ) uncertainty of 3 × 10−8 from 350-650 nm. The lifetimes are weighted average ...
... f is the partial pressure of water vapor in the air, in Pa (which can be computed from the relative humidity via the Goff-Gratch equation [15]). This formula is appropriate for laboratory conditions and has an estimated (3σ) uncertainty of 3 × 10−8 from 350-650 nm. The lifetimes are weighted average ...
DO NOW - PBworks
... Answer the DO NOW in your INB. Sometime tectonic plates do not move easily past one another, and the plates become stuck. Forces build up, and when the plates finally move, tension is released, as shown below. The sudden movement of the plates is caused by – A. The mass of the plates B. The weight o ...
... Answer the DO NOW in your INB. Sometime tectonic plates do not move easily past one another, and the plates become stuck. Forces build up, and when the plates finally move, tension is released, as shown below. The sudden movement of the plates is caused by – A. The mass of the plates B. The weight o ...
Some Basic Aspects of Fractional Quantum Numbers
... Quantization of charge is a very basic feature of our picture of the physical world. The explanation of how matter can be built up from a few types of indivisible buildingblocks, each occurring in vast numbers of identical copies, is a major triumph of local quantum field theory. In many ways, it fo ...
... Quantization of charge is a very basic feature of our picture of the physical world. The explanation of how matter can be built up from a few types of indivisible buildingblocks, each occurring in vast numbers of identical copies, is a major triumph of local quantum field theory. In many ways, it fo ...
Advanced Physical Chemistry
... position is measured first, and then the momentum, or if the momentum is measure before the position. Thus if x is the position operator and px is the momentum operator in the x direction, in one dimension if the Heisenberg Uncertainty principle is valid: (x px - px x)g 0 g where g is the function ...
... position is measured first, and then the momentum, or if the momentum is measure before the position. Thus if x is the position operator and px is the momentum operator in the x direction, in one dimension if the Heisenberg Uncertainty principle is valid: (x px - px x)g 0 g where g is the function ...
Atomic theory
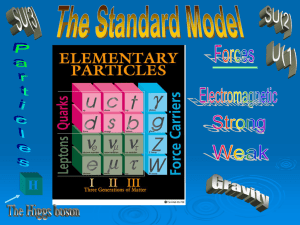
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.