3 - LPS
... certain results (E) Scientific law A logical approach to the solution of (F) Scientific theory scientific problems A concise statement that summarizes the results of many observation and experiments ...
... certain results (E) Scientific law A logical approach to the solution of (F) Scientific theory scientific problems A concise statement that summarizes the results of many observation and experiments ...
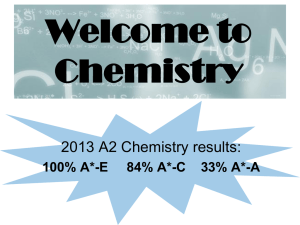
Welcome to Chemistry
... A numerate subject such as CHEMISTRY is useful for… • Accountancy/Business • Architecture • Law ...
... A numerate subject such as CHEMISTRY is useful for… • Accountancy/Business • Architecture • Law ...
chemistry writing team
... SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY Law of conservation of mass : ‘Mass can neither be created nor destroyed.’ In all physical and chemical changes, the total mass of reactants is equal to that of products. Law of constant composition : A chemical compound is always found to be made of same elements co ...
... SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY Law of conservation of mass : ‘Mass can neither be created nor destroyed.’ In all physical and chemical changes, the total mass of reactants is equal to that of products. Law of constant composition : A chemical compound is always found to be made of same elements co ...
Mathematical physics - Institute of Physics
... not clearly defined. Despite his misgivings, Einstein himself could be counted as a mathematical physicist. His general theory of relativity was not a result of extensive experimentation, but of theoretical and mathematical considerations. Because it differs from Newton’s classical theory of gravity ...
... not clearly defined. Despite his misgivings, Einstein himself could be counted as a mathematical physicist. His general theory of relativity was not a result of extensive experimentation, but of theoretical and mathematical considerations. Because it differs from Newton’s classical theory of gravity ...
On Water, Steam and String Theory
... about the structure of water molecules, hydrogen bridges, and so on, in order to explain why β is about 0.33. But surprisingly, if one measures β for other substances with water-like phase diagrams like Xenon or carbon dioxide, one always finds roughly 0.33.2 This value seems to be a universal prope ...
... about the structure of water molecules, hydrogen bridges, and so on, in order to explain why β is about 0.33. But surprisingly, if one measures β for other substances with water-like phase diagrams like Xenon or carbon dioxide, one always finds roughly 0.33.2 This value seems to be a universal prope ...
Empirical and Molecular Formulas.studentsdoc
... Then look at the three numbers of moles and determine the lowest number they can be multiplied by to get all whole numbers. In this case the number is 2. 3.390/3.390 = 1 mol of C X 2 =2 mol of C 5.04/3.390 = 1.5 mol of H X 2=3 mol of H 3.390/3.390 = 1 mol of O X 2 =2 mol of O Step 3: Create Empirica ...
... Then look at the three numbers of moles and determine the lowest number they can be multiplied by to get all whole numbers. In this case the number is 2. 3.390/3.390 = 1 mol of C X 2 =2 mol of C 5.04/3.390 = 1.5 mol of H X 2=3 mol of H 3.390/3.390 = 1 mol of O X 2 =2 mol of O Step 3: Create Empirica ...
Week 8
... Final notes: Using conservation of energy to solve simple physical problems In addition to being a a fundamental principle of classical mechanics, conservation of energy can often be an effective tool to analyze physical systems. In many cases, it is simpler, perhaps much simpler, to use conservatio ...
... Final notes: Using conservation of energy to solve simple physical problems In addition to being a a fundamental principle of classical mechanics, conservation of energy can often be an effective tool to analyze physical systems. In many cases, it is simpler, perhaps much simpler, to use conservatio ...
Multiscale Modeling of Biological Functions: From Enzymes to Molecular Machines
... developed CFF method (with the spring-like description of bonds with localized electrons) and a valence bond (VB) quantum model [15]. This QM (VB) + MM model helped to describe the extremely large isotope effect in a chemical reaction between oxygen and a medium sized organic molecule, and indicated ...
... developed CFF method (with the spring-like description of bonds with localized electrons) and a valence bond (VB) quantum model [15]. This QM (VB) + MM model helped to describe the extremely large isotope effect in a chemical reaction between oxygen and a medium sized organic molecule, and indicated ...
11-Apr-16 15 - Fulton Schools of Engineering Tutoring Centers
... Example: Body 1 of mass M has an original velocity of 6.00 m/s in the +xdirection toward a stationary body 2 of the same mass. After the collision, body 1 has vx=+1.00 m/s and vy=+2.00 m/s. What is the magnitude of body 2’s velocity after the collision? ...
... Example: Body 1 of mass M has an original velocity of 6.00 m/s in the +xdirection toward a stationary body 2 of the same mass. After the collision, body 1 has vx=+1.00 m/s and vy=+2.00 m/s. What is the magnitude of body 2’s velocity after the collision? ...
Why were two theories (Matrix Mechanics and Wave Mechanics
... (h/2πi)ψ, a differential operator F[(h/2πi)(∂/∂q), q] can be associated with the function of momentum and position F = F (p, q). • If the phase velocity functions, uk = uk (q), in the configuration space of the position q form a complete orthonormal set, then an equation ...
... (h/2πi)ψ, a differential operator F[(h/2πi)(∂/∂q), q] can be associated with the function of momentum and position F = F (p, q). • If the phase velocity functions, uk = uk (q), in the configuration space of the position q form a complete orthonormal set, then an equation ...
Physics of Smell - Department of Theoretical Physics
... fully valid but some aspects of “lock and key” model are also taken into account. Obviously, the shape of the molecule matters to some extent, because molecules can be smelt only if they are small enough to fit into the olfactory receptor. There is also at least one documented case of mirror molecul ...
... fully valid but some aspects of “lock and key” model are also taken into account. Obviously, the shape of the molecule matters to some extent, because molecules can be smelt only if they are small enough to fit into the olfactory receptor. There is also at least one documented case of mirror molecul ...
equilibrium theory of the kaolinite
... finally hydrate on kaolinite at relative pressures near one (Martin, 1959; Jurinak, 1963) is no contradiction of the theory, because the exchangeable cations on a wet clay interact directly with the mineral surface hydration water rather than with water vapor. For such an interaction, equation (2) m ...
... finally hydrate on kaolinite at relative pressures near one (Martin, 1959; Jurinak, 1963) is no contradiction of the theory, because the exchangeable cations on a wet clay interact directly with the mineral surface hydration water rather than with water vapor. For such an interaction, equation (2) m ...
The Concept of Limiting Reactant
... The atomic mass of any substance express in grams is the molar mass of that substance. The atomic mass of iron is 55.85amu. Therefore, the molar mass of iron is 55.85g/mol. Since oxygen occurs naturally as a diatomic, O2 the molar mass is 2 times 16.00g = 32.00g/mol. ...
... The atomic mass of any substance express in grams is the molar mass of that substance. The atomic mass of iron is 55.85amu. Therefore, the molar mass of iron is 55.85g/mol. Since oxygen occurs naturally as a diatomic, O2 the molar mass is 2 times 16.00g = 32.00g/mol. ...
Quantum Superposition, Quantum Entanglement, and Quantum
... • Is there any classical analog? • Application/Technologies ...
... • Is there any classical analog? • Application/Technologies ...
Feynman Diagrams for Beginners
... theory of such fields — quantum field theory. This theory can be described at various levels of rigor but in any case is complicated enough to be beyond the scope of these notes. However, predictions of quantum field theory pertaining to the elementary particle interactions can often be calculated u ...
... theory of such fields — quantum field theory. This theory can be described at various levels of rigor but in any case is complicated enough to be beyond the scope of these notes. However, predictions of quantum field theory pertaining to the elementary particle interactions can often be calculated u ...
1D PIC code with Monte
... Here the charge density ρk in the greed cell k is defined by the equation N qN s p k ( xk ) W ( xi xk ) 0 h i 1 where W(x) is a so-called charge assignment (or weighting) function. The different kinds of this function will be discussed later. The force on the particle interpolated from ...
... Here the charge density ρk in the greed cell k is defined by the equation N qN s p k ( xk ) W ( xi xk ) 0 h i 1 where W(x) is a so-called charge assignment (or weighting) function. The different kinds of this function will be discussed later. The force on the particle interpolated from ...
Slide 1
... They see the Čerenkov rings produced by the charged leptons as they emerge inside the detector from the neutrino charged current interaction. In the atmosphere, two νμ are produced for each νe. This 2:1 ratio was observed for neutrinos coming from directly above the detector where the upper atmosphe ...
... They see the Čerenkov rings produced by the charged leptons as they emerge inside the detector from the neutrino charged current interaction. In the atmosphere, two νμ are produced for each νe. This 2:1 ratio was observed for neutrinos coming from directly above the detector where the upper atmosphe ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.