Chapter 1: The Nature of Analytical Chemistry
... • Four general areas of analysis – 3. Electrochemical methods measure electrical properties (potential, current, resistance) to find composition of samples. – 4. Spectroscopic methods based on interaction of electromagnetic radiation with analyte atoms & molecules, or on the production of radiation ...
... • Four general areas of analysis – 3. Electrochemical methods measure electrical properties (potential, current, resistance) to find composition of samples. – 4. Spectroscopic methods based on interaction of electromagnetic radiation with analyte atoms & molecules, or on the production of radiation ...
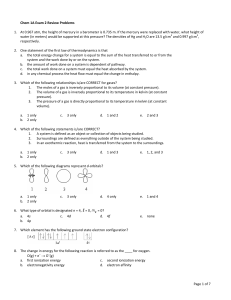
Page 1 of 7 Chem 1A Exam 2 Review Problems 1. At 0.967 atm, the
... a. Electrons have both wave and particle properties. b. It is not possible to know the exact location of an electron and its exact energy simultaneously. c. The behavior of an atom's electrons can be described by circular orbits around a nucleus. d. Quantum numbers define the energy states and t ...
... a. Electrons have both wave and particle properties. b. It is not possible to know the exact location of an electron and its exact energy simultaneously. c. The behavior of an atom's electrons can be described by circular orbits around a nucleus. d. Quantum numbers define the energy states and t ...
Lecture II Simple One-Dimensional Vibrating Systems
... Lecture II Simple One-Dimensional Vibrating Systems One method of producing a sound relies on a physical object (e.g. various types of musical instruments – stringed and wind instruments in particular) to be made to vibrate, by whatever means possible. This vibration is (clearly) mechanical in natur ...
... Lecture II Simple One-Dimensional Vibrating Systems One method of producing a sound relies on a physical object (e.g. various types of musical instruments – stringed and wind instruments in particular) to be made to vibrate, by whatever means possible. This vibration is (clearly) mechanical in natur ...
Chapter 9
... • How many moles of LiOH are required to react with 20 mol of CO2, the average amount exhaled by a person each day? ...
... • How many moles of LiOH are required to react with 20 mol of CO2, the average amount exhaled by a person each day? ...
Chapter 11 - Rolling, Torque and Angular Momentum
... To find the directions of the torques, we use the right hand rule and rotate r into F through the smaller of the two angles between their directions. ...
... To find the directions of the torques, we use the right hand rule and rotate r into F through the smaller of the two angles between their directions. ...
Chapter 9 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Collisions – Characteristics The term collision represents an event during which two particles come close to each other and interact by means of forces. May involve physical contact, but must be generalized to include cases with interaction without physical contact The interaction forces are assu ...
... Collisions – Characteristics The term collision represents an event during which two particles come close to each other and interact by means of forces. May involve physical contact, but must be generalized to include cases with interaction without physical contact The interaction forces are assu ...
Electron Orbital Angular Momentum - FSU Chemistry
... When an external magnetic field interacts with a conductor it changes the motion of the conducting elections unless the electrons are traveling precisely along the polar axis of the magnetic field. In the most general case, where the magnetic field axis crosses the crystal axis of the conductor at ...
... When an external magnetic field interacts with a conductor it changes the motion of the conducting elections unless the electrons are traveling precisely along the polar axis of the magnetic field. In the most general case, where the magnetic field axis crosses the crystal axis of the conductor at ...
Many-Body effects in Semiconductor Nanostructures Stockholm University Licentiat Thesis
... The effects of an applied magnetic field to a QD are of great importance when manufacturing spintronic devices, and are also discussed in the thesis. In paper II, experimental results by Meunier on an elliptical QD with a tilted magnetic field, [5], are compared to theoretical results. These atom-li ...
... The effects of an applied magnetic field to a QD are of great importance when manufacturing spintronic devices, and are also discussed in the thesis. In paper II, experimental results by Meunier on an elliptical QD with a tilted magnetic field, [5], are compared to theoretical results. These atom-li ...
Subject Area Standard Area Organizing Category Grade Level
... CHEM.B.2.2.1: Utilize mathematical relationships to predict changes in the number of particles, the temperature, the pressure, and the volume in a gaseous system (i.e., Boyle’s law, Charles’s law, Dalton’s law of partial pressures, the combined gas law, and the ideal gas law). ...
... CHEM.B.2.2.1: Utilize mathematical relationships to predict changes in the number of particles, the temperature, the pressure, and the volume in a gaseous system (i.e., Boyle’s law, Charles’s law, Dalton’s law of partial pressures, the combined gas law, and the ideal gas law). ...
Monday, April 7, 2008 - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... • Describe in detail what happens to the final velocities if m1=m2. – 5 point extra credit ...
... • Describe in detail what happens to the final velocities if m1=m2. – 5 point extra credit ...
From Classical to Wave-Mechanical Dynamics
... and of the Wave Potential were computed, with initial momentum components px (t = 0) = 0 ; pz (t = 0) = p0 = 2π~/λ0 , by means of a symplectic numerical integration method. We limit ourselves to present in Fig.1, on the (x, z)−plane, the case of the diffraction of a Gaussian particle beam traveling ...
... and of the Wave Potential were computed, with initial momentum components px (t = 0) = 0 ; pz (t = 0) = p0 = 2π~/λ0 , by means of a symplectic numerical integration method. We limit ourselves to present in Fig.1, on the (x, z)−plane, the case of the diffraction of a Gaussian particle beam traveling ...
Lattice QCD in Mainland China: Status and Perspectives
... This figure and table on next page illustrate the results from the finest lattice. The continuum extrapolation will be taken later ...
... This figure and table on next page illustrate the results from the finest lattice. The continuum extrapolation will be taken later ...
orange review book_2014_key
... 19. One similarity between all mixtures and compounds is that both (1) are heterogeneous (2) consist of two or more substances (3) are homogeneous (4) are heterogeneous 20. A dilute, aqueous potassium nitrate solution is best classified as a (1) homogeneous compound (2) homogeneous mixture ...
... 19. One similarity between all mixtures and compounds is that both (1) are heterogeneous (2) consist of two or more substances (3) are homogeneous (4) are heterogeneous 20. A dilute, aqueous potassium nitrate solution is best classified as a (1) homogeneous compound (2) homogeneous mixture ...
2.6 M - Thierry Karsenti
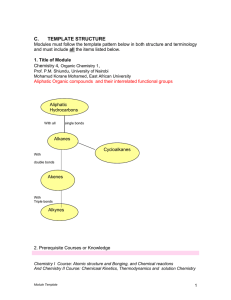
... atoms in the cyclic structure is other than carbon. Heterocyclic componds may be aliphatic or aromatic 15. Isomers: These are different compounds that have the same molecular formula. Isomers are further subdivided into: (a) structural isomers, (b) geometrical isomers and (c) stereoisomers(optical i ...
... atoms in the cyclic structure is other than carbon. Heterocyclic componds may be aliphatic or aromatic 15. Isomers: These are different compounds that have the same molecular formula. Isomers are further subdivided into: (a) structural isomers, (b) geometrical isomers and (c) stereoisomers(optical i ...
Principles of Statistical Mechanics and the
... microstate, specified by the energy of each particle, will remain in that microstate. A system in which the particles interact is much more interesting: if the particles can exchange energy, then the system can achieve an equilibrium in which the microstate is essentially independent of the initial ...
... microstate, specified by the energy of each particle, will remain in that microstate. A system in which the particles interact is much more interesting: if the particles can exchange energy, then the system can achieve an equilibrium in which the microstate is essentially independent of the initial ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.