mole concept type 1 - teko classes bhopal
... [Useful when only two reactant are there] By calculating amount of any one product obtained taking each reactant one by one irrespective of other reactants. The one giving least product is limiting reagent. Divide given moles of each reactant by their stoichiometric coefficient, the one with least r ...
... [Useful when only two reactant are there] By calculating amount of any one product obtained taking each reactant one by one irrespective of other reactants. The one giving least product is limiting reagent. Divide given moles of each reactant by their stoichiometric coefficient, the one with least r ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... Atomic Mass Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams. • Use atomic mass units or amus – 1 amu is 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. ...
... Atomic Mass Atoms are so small, it is difficult to discuss how much they weigh in grams. • Use atomic mass units or amus – 1 amu is 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. ...
Electric Potential Energy versus Electric Potential
... Imagine a third particle, which we will call a cyberon. It has three times the mass of an electron ( ). It has a positive charge that is three times the magnitude ( ) of the charge on an electron. What is the ratio of the speed that the cyberon would have when it reaches the upper plate after being ...
... Imagine a third particle, which we will call a cyberon. It has three times the mass of an electron ( ). It has a positive charge that is three times the magnitude ( ) of the charge on an electron. What is the ratio of the speed that the cyberon would have when it reaches the upper plate after being ...
Physics 30 Student Review Package V6
... 0.224 8 lb (pounds) = 1.000 0 N (newtons) The orbital radius of Earth around the sun is 1.50 × 1011 m. The orbital radius of Mars around the sun is 2.28 × 1011 m. ...
... 0.224 8 lb (pounds) = 1.000 0 N (newtons) The orbital radius of Earth around the sun is 1.50 × 1011 m. The orbital radius of Mars around the sun is 2.28 × 1011 m. ...
100, 027001 (2008)
... well, it will enter into the linear combination of jsi and jai, the state localized in the left well [21,22]. Only after a time of the order of @ divided by the tunnel splitting does the electron acquire appreciable probability of appearing at the right well. Further, because of the exponentially sm ...
... well, it will enter into the linear combination of jsi and jai, the state localized in the left well [21,22]. Only after a time of the order of @ divided by the tunnel splitting does the electron acquire appreciable probability of appearing at the right well. Further, because of the exponentially sm ...
apchem - practice midterm_shs
... remove an electron from Hthan from Li+. d. The chemical properties of the two ions must be the same because they have the same electronic structure. e. None of these is a true statement. 24. The Heisenburg uncertainty principle states that a. electrons have no momentum b. the position of an electron ...
... remove an electron from Hthan from Li+. d. The chemical properties of the two ions must be the same because they have the same electronic structure. e. None of these is a true statement. 24. The Heisenburg uncertainty principle states that a. electrons have no momentum b. the position of an electron ...
Document
... adsorption of 10 cm3 of carbon monoxide corresponds to the adsorption saturation of the surface of 100g of copper (i.e. Vm = 10 cm3) The adsorption of 0.05 cm3 of CO already • suppresses the initial catalytic activity of the copper by 90%. Consequently, 10 cm 3 ...
... adsorption of 10 cm3 of carbon monoxide corresponds to the adsorption saturation of the surface of 100g of copper (i.e. Vm = 10 cm3) The adsorption of 0.05 cm3 of CO already • suppresses the initial catalytic activity of the copper by 90%. Consequently, 10 cm 3 ...
Lewis Acids and Bases Hard and Soft Acid/Base Theory
... 1) Monodentate (1-toothed) bases (ligands). These are ligands that donate one electron pair to one acid ion or molecule. Examples of monodentate ligands include anions such as OH-, O2-, NH2-, S2-, HS-, CH3-, H-, X-; neutral molecules such as H2O, NH3, CO, CH3CH2OH, (CH3)2C=O, (CH3CH2)2O (and many mo ...
... 1) Monodentate (1-toothed) bases (ligands). These are ligands that donate one electron pair to one acid ion or molecule. Examples of monodentate ligands include anions such as OH-, O2-, NH2-, S2-, HS-, CH3-, H-, X-; neutral molecules such as H2O, NH3, CO, CH3CH2OH, (CH3)2C=O, (CH3CH2)2O (and many mo ...
Chapter 8 CHEM 161
... Energy of photon of electromagnetic radiation is proportional to its frequency Energy of photon E = h h = Planck’s constant = 6.626 × 10–34 J s Jespersen/Brady/Hyslop ...
... Energy of photon of electromagnetic radiation is proportional to its frequency Energy of photon E = h h = Planck’s constant = 6.626 × 10–34 J s Jespersen/Brady/Hyslop ...
Physics Today
... atoms generate matched pulses. It is the interplay of these processes, especially with nonadiabatic pulses, that Propagation of matched pulses leads to interesting propagation dynamics. Extending Now consider the case in which the pulse envelopes of the these ideas to the quantum regime, Girish Agar ...
... atoms generate matched pulses. It is the interplay of these processes, especially with nonadiabatic pulses, that Propagation of matched pulses leads to interesting propagation dynamics. Extending Now consider the case in which the pulse envelopes of the these ideas to the quantum regime, Girish Agar ...
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
... As has been pointed out often throughout this thesis the use of Feshbach resonances are essential for the study of ultracold gases. Due to the resonant scattering in the open ...
... As has been pointed out often throughout this thesis the use of Feshbach resonances are essential for the study of ultracold gases. Due to the resonant scattering in the open ...
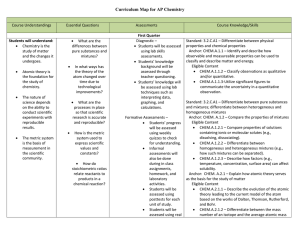
AP Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Anchor: CHEM.B.1.2 – Apply the mole concept to the composition of matter. Eligible Content CHEM.B.1.2.1 – Determine the empirical and molecular formulas of compounds. CHEM.B.1.2.3 – Relate the percent composition and mass of each element present in a compound. Standard: 3.2.C.A2 – Predict chemi ...
... Anchor: CHEM.B.1.2 – Apply the mole concept to the composition of matter. Eligible Content CHEM.B.1.2.1 – Determine the empirical and molecular formulas of compounds. CHEM.B.1.2.3 – Relate the percent composition and mass of each element present in a compound. Standard: 3.2.C.A2 – Predict chemi ...
114, 125301 (2015)
... exact. In the unstable region, the BEC is destroyed after a modulation time of just 10 ms to 50 ms, at which point the momentum space distribution is dominated by high momentum excitations, which would be interpreted as thermal excitations observed in the experiment. In general, the exact size of th ...
... exact. In the unstable region, the BEC is destroyed after a modulation time of just 10 ms to 50 ms, at which point the momentum space distribution is dominated by high momentum excitations, which would be interpreted as thermal excitations observed in the experiment. In general, the exact size of th ...
Chapter 13 Ideal Fermi gas
... absolute zero since the zero-momentum state can hold only one particle of a given spin state. Let us use our model of a Fermi gas of electrons contained in a box in order to describe electrons in a metal. For this case, since the density of electrons in a metal is n ≈ 1022 cm−3 , we find a zero-poin ...
... absolute zero since the zero-momentum state can hold only one particle of a given spin state. Let us use our model of a Fermi gas of electrons contained in a box in order to describe electrons in a metal. For this case, since the density of electrons in a metal is n ≈ 1022 cm−3 , we find a zero-poin ...
Concept Development Studies in Chemistry
... permit prediction of what quantity of lead sul de will be produced by a given amount of lead. For example, 6.5g of lead will produce exactly 7.5g of lead sul de, 50g of lead will produce 57.7g of lead sul de, etc. There is a problem, however. We can illustrate with three compounds formed from hydrog ...
... permit prediction of what quantity of lead sul de will be produced by a given amount of lead. For example, 6.5g of lead will produce exactly 7.5g of lead sul de, 50g of lead will produce 57.7g of lead sul de, etc. There is a problem, however. We can illustrate with three compounds formed from hydrog ...
Organic Compounds FT-IR Spectroscopy
... 4. Vibration of polyatomic molecules In the case the vibration diatomic molecules atoms can oscillate just in the direction of connection covalent) binding atoms. In the case of molecules consisting of several atoms (N atoms) the description of the assembly oscillations, even in harmonic approximati ...
... 4. Vibration of polyatomic molecules In the case the vibration diatomic molecules atoms can oscillate just in the direction of connection covalent) binding atoms. In the case of molecules consisting of several atoms (N atoms) the description of the assembly oscillations, even in harmonic approximati ...
Do You Need to Believe in Orbitals to Use Them - Philsci
... Knowledge of this electron density also allows us to develop the familiar contours wherein it is, for example, 95% likely that the electron would be found upon measurement of its position. For atoms with more than one electron the situation is not so simple. In order to determine the wave-function f ...
... Knowledge of this electron density also allows us to develop the familiar contours wherein it is, for example, 95% likely that the electron would be found upon measurement of its position. For atoms with more than one electron the situation is not so simple. In order to determine the wave-function f ...
Quantum Physics 2005
... variables in wave analysis. (They appear with one another in the phase of a harmonic wave.) )+)t = 1 • Since energy and frequency are related Planck constant we have, for a Gaussian packet: )E )t = h Notes 1 ...
... variables in wave analysis. (They appear with one another in the phase of a harmonic wave.) )+)t = 1 • Since energy and frequency are related Planck constant we have, for a Gaussian packet: )E )t = h Notes 1 ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.