Document
... found in a particular region using statistical functions. Electron energy and position are complementary because ...
... found in a particular region using statistical functions. Electron energy and position are complementary because ...
Organic Compounds FT-IR Spectroscopy
... 4. Vibration of polyatomic molecules In the case the vibration diatomic molecules atoms can oscillate just in the direction of connection covalent) binding atoms. In the case of molecules consisting of several atoms (N atoms) the description of the assembly oscillations, even in harmonic approximati ...
... 4. Vibration of polyatomic molecules In the case the vibration diatomic molecules atoms can oscillate just in the direction of connection covalent) binding atoms. In the case of molecules consisting of several atoms (N atoms) the description of the assembly oscillations, even in harmonic approximati ...
Do You Need to Believe in Orbitals to Use Them - Philsci
... Knowledge of this electron density also allows us to develop the familiar contours wherein it is, for example, 95% likely that the electron would be found upon measurement of its position. For atoms with more than one electron the situation is not so simple. In order to determine the wave-function f ...
... Knowledge of this electron density also allows us to develop the familiar contours wherein it is, for example, 95% likely that the electron would be found upon measurement of its position. For atoms with more than one electron the situation is not so simple. In order to determine the wave-function f ...
Physics and Philosophy
... A winner of the Nobel Prize, Werner Heisenberg was born in 1901 in Wurzberg, Germany. He studied physics at the University of Munich and for his Ph.D. wrote a dissertation on turbulence in fluid streams. Interested in Niels Bohr's account of the planetary atom, Heisenberg studied under Max Born at t ...
... A winner of the Nobel Prize, Werner Heisenberg was born in 1901 in Wurzberg, Germany. He studied physics at the University of Munich and for his Ph.D. wrote a dissertation on turbulence in fluid streams. Interested in Niels Bohr's account of the planetary atom, Heisenberg studied under Max Born at t ...
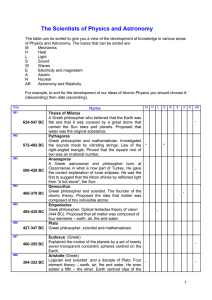
Scientists (date order)
... Danish physicist. Deflection of compass needle by the magnetic field of an electric current. Discovered that an electric current produces a magnetic field. Olbers, Heinrich German astronomer and physician. Olbers paradox . Discovered the second and third asteroids. Devised a method for calculating t ...
... Danish physicist. Deflection of compass needle by the magnetic field of an electric current. Discovered that an electric current produces a magnetic field. Olbers, Heinrich German astronomer and physician. Olbers paradox . Discovered the second and third asteroids. Devised a method for calculating t ...
Some remarks on the Quantum Hall Effect - IPhT
... change of shape can be modeled by a surface density proportional to the normal displacement. The electrostatic potential induced by this surface density must have the correct behavior tz 2 /4 + h.c. at infinity and vanish at the boundary |z| = 1, (the normalization is such that the potential between ...
... change of shape can be modeled by a surface density proportional to the normal displacement. The electrostatic potential induced by this surface density must have the correct behavior tz 2 /4 + h.c. at infinity and vanish at the boundary |z| = 1, (the normalization is such that the potential between ...
The Measurement of Mass
... The mass of an object is a measure of its resistance to a change in its velocity. The greater the mass the more difficult it is to change the velocity. On the other hand, the weight of the object is the force of gravity on the object. Force and mass are two distinct physical concepts. Mass is an int ...
... The mass of an object is a measure of its resistance to a change in its velocity. The greater the mass the more difficult it is to change the velocity. On the other hand, the weight of the object is the force of gravity on the object. Force and mass are two distinct physical concepts. Mass is an int ...
2009-College-IgorDotsenko
... 1. Trigger of the atom clock: resonant pulse 2. Dephasing of the clock: interaction with the cavity field 3. Measurement of the clock: ...
... 1. Trigger of the atom clock: resonant pulse 2. Dephasing of the clock: interaction with the cavity field 3. Measurement of the clock: ...
Document
... (a) Because copper lies below hydrogen in the activity series of the metals, Cu(s) cannot reduce H+(aq) to H2(g) and be oxidized to Cu2+(aq). Looking at it the other way, H+ is not a strong enough oxidizing agent to oxidize Cu(s) to Cu 2+(aq). Chloride ion in HCl(aq) can only be a reducing agent. As ...
... (a) Because copper lies below hydrogen in the activity series of the metals, Cu(s) cannot reduce H+(aq) to H2(g) and be oxidized to Cu2+(aq). Looking at it the other way, H+ is not a strong enough oxidizing agent to oxidize Cu(s) to Cu 2+(aq). Chloride ion in HCl(aq) can only be a reducing agent. As ...
Syllabus of the International Chemistry Olympiad
... time, how the color of Delft blue pottery can be understood, how a bio-compatible polymer can be made from lactic acid, how modern spectroscopy is applied, how the structure of the natural product carvone can be unravelled, how aspects of green chemistry can be treated more quantitatively, how deter ...
... time, how the color of Delft blue pottery can be understood, how a bio-compatible polymer can be made from lactic acid, how modern spectroscopy is applied, how the structure of the natural product carvone can be unravelled, how aspects of green chemistry can be treated more quantitatively, how deter ...
Degrees of freedom effect on fragmentation in tandem mass
... d Institute of Organic Chemistry, Research Centre for Natural Sciences, Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Pusztaszeri ut 59–67H-1025 Budapest, Hungary ...
... d Institute of Organic Chemistry, Research Centre for Natural Sciences, Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Pusztaszeri ut 59–67H-1025 Budapest, Hungary ...
Charge transport modelling in electron
... types of charged particles, and particularly to electrons. These materials can accumulate charges, building up the potential inside the dielectric, meaning a potential difference between different parts of the satellite. Electrostatic Surface Discharge (ESD) can occur, leading to possible damages of ...
... types of charged particles, and particularly to electrons. These materials can accumulate charges, building up the potential inside the dielectric, meaning a potential difference between different parts of the satellite. Electrostatic Surface Discharge (ESD) can occur, leading to possible damages of ...
150B2_2002
... Exam Bank II Fall 2002 A large mass collides elastically head on with a small mass which is initially at rest. The small mass (A) rebounds at a higher speed than the large mass, because energy an momentum are conserved. (B) sticks to the large mass, slowing it considerably because energy an momentum ...
... Exam Bank II Fall 2002 A large mass collides elastically head on with a small mass which is initially at rest. The small mass (A) rebounds at a higher speed than the large mass, because energy an momentum are conserved. (B) sticks to the large mass, slowing it considerably because energy an momentum ...
Pacing Guide, Revised Aug 17, 2010
... ICP.3.4 Understand how the microscopic kinetic molecular theory, explains observations of macroscopic gas behavior in terms of temperature, volume, pressure, and the number of particles (using the mole concept). 2.) Chemical Energy, Reactions, and Bonding- Describe how energy is produced and absorbe ...
... ICP.3.4 Understand how the microscopic kinetic molecular theory, explains observations of macroscopic gas behavior in terms of temperature, volume, pressure, and the number of particles (using the mole concept). 2.) Chemical Energy, Reactions, and Bonding- Describe how energy is produced and absorbe ...
Redox Flash Cards - No Brain Too Small
... If its oxidation compounds/ions) compounds/ions) number increases, is __ , except in is __ , except in the element has ...
... If its oxidation compounds/ions) compounds/ions) number increases, is __ , except in is __ , except in the element has ...
Car-Parrinello Molecular Dynamics
... R. Car and M. Parrinello (1985), “Unified Approach for Molecular Dynamics and Density Functional Theory”, Phys. Rev. Lett, 55(22), pages 2471-2474. R. Car and M. Parrinello (1989), “The Unified Approach for Molecular Dynamics and Density Functional Theory”, in Simple Molecular Systems at Very High D ...
... R. Car and M. Parrinello (1985), “Unified Approach for Molecular Dynamics and Density Functional Theory”, Phys. Rev. Lett, 55(22), pages 2471-2474. R. Car and M. Parrinello (1989), “The Unified Approach for Molecular Dynamics and Density Functional Theory”, in Simple Molecular Systems at Very High D ...
What is light? - beim Quantum Spin
... it originated from (where it says ‘air’ in the figure). Foucault then repeated his experiment, only now he filled the tube with water. If the speed of light is faster in water than it was in the air-filled tube, the light would return faster to the rotating mirror than before (which would have rotat ...
... it originated from (where it says ‘air’ in the figure). Foucault then repeated his experiment, only now he filled the tube with water. If the speed of light is faster in water than it was in the air-filled tube, the light would return faster to the rotating mirror than before (which would have rotat ...
Comparisons between classical and quantum mechanical
... The research on Bose-Einstein condensates has since taken many directions, one of the most exciting being to study their behavior when they are placed in optical lattices generated by laser beams. This has already produced a number of fascinating results, but it has also proven to be an ideal test-g ...
... The research on Bose-Einstein condensates has since taken many directions, one of the most exciting being to study their behavior when they are placed in optical lattices generated by laser beams. This has already produced a number of fascinating results, but it has also proven to be an ideal test-g ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.