Magic-wavelength optical traps for Rydberg atoms S. Zhang, F. Robicheaux, and M. Saffman
... between the ns and (n − 4)f Rydberg states are exactly zero when the atom is at the origin. For the low atom temperatures expected for Cs, the atom will be very near the center of the trap and thus this coupling will be strongly suppressed. The next closest states are in the (n − 4) degenerate manif ...
... between the ns and (n − 4)f Rydberg states are exactly zero when the atom is at the origin. For the low atom temperatures expected for Cs, the atom will be very near the center of the trap and thus this coupling will be strongly suppressed. The next closest states are in the (n − 4) degenerate manif ...
Equivalency of Momentum and Kinetic Energy and
... This paper is regular paper and to be continued with several papers along the same and too please waiting for a book named absolutely relativity that this paper is just several pages from this book. I announce here appearance of a new physics named absolute physics that, It is unification of differe ...
... This paper is regular paper and to be continued with several papers along the same and too please waiting for a book named absolutely relativity that this paper is just several pages from this book. I announce here appearance of a new physics named absolute physics that, It is unification of differe ...
66 - Narod.ru
... Realizations of a stationary stochastic process ξ(ti), such as that shown in Figure 3, may be interpreted as the change over time of the projection onto the X-axis of the position of the “point” in motion (Figures 2 and 3). That is, x(t) = ξ(ti). Even in the case of the statistical independence of t ...
... Realizations of a stationary stochastic process ξ(ti), such as that shown in Figure 3, may be interpreted as the change over time of the projection onto the X-axis of the position of the “point” in motion (Figures 2 and 3). That is, x(t) = ξ(ti). Even in the case of the statistical independence of t ...
Reaction Stoichiometry
... How many grams of NH4NO3 are required to produce 33.0g of N2O? How many grams of water are produced in this reaction? ...
... How many grams of NH4NO3 are required to produce 33.0g of N2O? How many grams of water are produced in this reaction? ...
Discussion 9, Mahaffy et al., Chapter 15
... Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to the total charge. e. In compounds, alkalis (group 1) have oxidation number +1; alkaline earths (group 2) have oxidation number +2. f. In compounds, flu ...
... Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to the total charge. e. In compounds, alkalis (group 1) have oxidation number +1; alkaline earths (group 2) have oxidation number +2. f. In compounds, flu ...
In the early 1930s, the relativistic electron
... usual interpretation of quantum theories, a submicroscopic observer – say Alice –, then the cat – our propagator – will reveal peculiar behaviours. The case is that the propagator does not vanish for a space-like separation. This means we would have an interaction between space-time points not conne ...
... usual interpretation of quantum theories, a submicroscopic observer – say Alice –, then the cat – our propagator – will reveal peculiar behaviours. The case is that the propagator does not vanish for a space-like separation. This means we would have an interaction between space-time points not conne ...
A Level Physics H2 Practice 2 P3 soln
... Determine the total number of bright spots of wavelength 644 nm that are visible. ...
... Determine the total number of bright spots of wavelength 644 nm that are visible. ...
P. LeClair
... The apparent density of the crown is far less than the expected value for gold, so the crown cannot be made of pure gold. The apparent density is also far less than that of most metals known to the ancient Greeks, like copper, iron, silver, lead, bronze, and brass. That means the crown can’t be a mi ...
... The apparent density of the crown is far less than the expected value for gold, so the crown cannot be made of pure gold. The apparent density is also far less than that of most metals known to the ancient Greeks, like copper, iron, silver, lead, bronze, and brass. That means the crown can’t be a mi ...
Quantum computers
... believe in the particle nature of light. Einstein, for example, explained the photoelectric effect in terms of the particle nature of light, and obtained a noble prize for it. So is light made up of particles or is it a wave? The answer is very beautifully contained in the words of Richard Feynman—o ...
... believe in the particle nature of light. Einstein, for example, explained the photoelectric effect in terms of the particle nature of light, and obtained a noble prize for it. So is light made up of particles or is it a wave? The answer is very beautifully contained in the words of Richard Feynman—o ...
Fusion Workbook - General Atomics Fusion Education
... This workbook is part of an educational outreach program sponsored by the General Atomics Fusion Group and the U.S. Department of Energy. The overall program consists of a pre-tour video to be shown in the classroom, a half-day educational tour of the DIII–D magnetic fusion research facility located ...
... This workbook is part of an educational outreach program sponsored by the General Atomics Fusion Group and the U.S. Department of Energy. The overall program consists of a pre-tour video to be shown in the classroom, a half-day educational tour of the DIII–D magnetic fusion research facility located ...
Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations
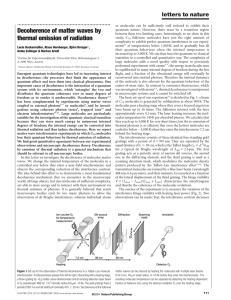
... 1. The substances undergoing reaction are called reactants, and their formulas are placed on the left side of the equation. 2. The substances generated by the reaction are called products, and their formulas are placed on the right sight of the equation. 3. Plus signs (+) separate individual reactan ...
... 1. The substances undergoing reaction are called reactants, and their formulas are placed on the left side of the equation. 2. The substances generated by the reaction are called products, and their formulas are placed on the right sight of the equation. 3. Plus signs (+) separate individual reactan ...
Chemical change is a process that involves recombining atoms and
... is carefully collected and placed on a scale, its mass is 39.0g. How can it weigh 16g more?? How does this make sense?? ...
... is carefully collected and placed on a scale, its mass is 39.0g. How can it weigh 16g more?? How does this make sense?? ...
- International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and
... then replaced by carbon dioxide and additional hydrogen in a water-gas shift reaction to produce 4 moles of hydrogen in total and one mole of carbon dioxide which is purified later in a pressure swing adsorption unit. After pure hydrogen is extracted from the PSA, it's supplied to a fuel cell that t ...
... then replaced by carbon dioxide and additional hydrogen in a water-gas shift reaction to produce 4 moles of hydrogen in total and one mole of carbon dioxide which is purified later in a pressure swing adsorption unit. After pure hydrogen is extracted from the PSA, it's supplied to a fuel cell that t ...
Residual dust charges in discharge afterglow
... path of buffer gas species. In our experiment, we work at an operating pressure around 1 mbar. In a previous paper [4], the size of grown dust particles was reported between 200 nm and 800 nm. It gives, using results from Varney [24] for an atom-atom cross section, Knudsen number 250 < Kn < 1000. Co ...
... path of buffer gas species. In our experiment, we work at an operating pressure around 1 mbar. In a previous paper [4], the size of grown dust particles was reported between 200 nm and 800 nm. It gives, using results from Varney [24] for an atom-atom cross section, Knudsen number 250 < Kn < 1000. Co ...
Decoherence of matter waves by thermal emission of radiation
... the signature of decoherence due to the enhanced probability for the emission of thermal photons that carry ‘which-path’ information. Second, we notice that the count rate also varies considerably. This is explained by the dependence of the ionization efficiency in the detector D2 on the internal en ...
... the signature of decoherence due to the enhanced probability for the emission of thermal photons that carry ‘which-path’ information. Second, we notice that the count rate also varies considerably. This is explained by the dependence of the ionization efficiency in the detector D2 on the internal en ...
e - Physlab
... is confined to a region of space the higher its kinetic energy will be. In an atom the electrons are confined by the Coulomb potential of the nucleus. The competition between the confining nature of the potential and the liberating tendency of the uncertainty principle gives rise to various quantum mec ...
... is confined to a region of space the higher its kinetic energy will be. In an atom the electrons are confined by the Coulomb potential of the nucleus. The competition between the confining nature of the potential and the liberating tendency of the uncertainty principle gives rise to various quantum mec ...
Atomic theory
In chemistry and physics, atomic theory is a scientific theory of the nature of matter, which states that matter is composed of discrete units called atoms. It began as a philosophical concept in ancient Greece and entered the scientific mainstream in the early 19th century when discoveries in the field of chemistry showed that matter did indeed behave as if it were made up of atoms.The word atom comes from the Ancient Greek adjective atomos, meaning ""uncuttable"". 19th century chemists began using the term in connection with the growing number of irreducible chemical elements. While seemingly apropos, around the turn of the 20th century, through various experiments with electromagnetism and radioactivity, physicists discovered that the so-called ""uncuttable atom"" was actually a conglomerate of various subatomic particles (chiefly, electrons, protons and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other. In fact, in certain extreme environments, such as neutron stars, extreme temperature and pressure prevents atoms from existing at all. Since atoms were found to be divisible, physicists later invented the term ""elementary particles"" to describe the ""uncuttable"", though not indestructible, parts of an atom. The field of science which studies subatomic particles is particle physics, and it is in this field that physicists hope to discover the true fundamental nature of matter.