G - Senger Science
... is increased from 715 mmHg to 3.55 atm at constant temperature. If the initial volume of the gas is 485 mL, what is the final volume of the gas? ...
... is increased from 715 mmHg to 3.55 atm at constant temperature. If the initial volume of the gas is 485 mL, what is the final volume of the gas? ...
Η - Knockhardy
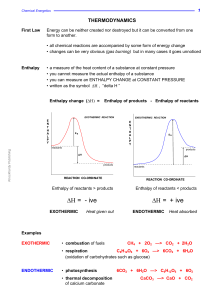
... The enthalpy change when ONE MOLE of a substance undergoes complete combustion under standard conditions. All reactants and products are in their standard states. ...
... The enthalpy change when ONE MOLE of a substance undergoes complete combustion under standard conditions. All reactants and products are in their standard states. ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Plan: The approach we take is outlined in Table 4.3. We can predict whether a substance is ionic or molecular, based on its composition. As we saw in Section 2.7, most ionic compounds we encounter in this text are composed of a metal and a nonmetal, whereas most molecular compounds are composed only ...
... Plan: The approach we take is outlined in Table 4.3. We can predict whether a substance is ionic or molecular, based on its composition. As we saw in Section 2.7, most ionic compounds we encounter in this text are composed of a metal and a nonmetal, whereas most molecular compounds are composed only ...
SOL Review Part 3 Nomenclature reactions
... ► If the anion is an element, change its ending to -ide; if the anion is a polyatomic ion, simply write the name of the polyatomic ion. ► If the cation can have more than one possible charge, write the charge as a Roman numeral in parentheses. ...
... ► If the anion is an element, change its ending to -ide; if the anion is a polyatomic ion, simply write the name of the polyatomic ion. ► If the cation can have more than one possible charge, write the charge as a Roman numeral in parentheses. ...
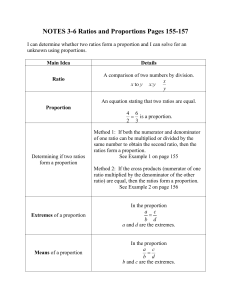
NOTES 3-6 Ratios and Proportions Pages 155-157
... NOTES 3-6 Ratios and Proportions Pages 155-157 I can determine whether two ratios form a proportion and I can solve for an unknown using proportions. Main Idea Ratio ...
... NOTES 3-6 Ratios and Proportions Pages 155-157 I can determine whether two ratios form a proportion and I can solve for an unknown using proportions. Main Idea Ratio ...
+ H 2 (g)
... gram to gram conversions Aluminum is an active metal that when placed in hydrochloric acid produces hydrogen gas and aluminum chloride. How many grams of aluminum chloride can be produced when 3.45 grams of aluminum are reacted with an excess of hydrochloric acid? 2 Al(s) + 6HCl(aq) 2AlCl3(aq) + ...
... gram to gram conversions Aluminum is an active metal that when placed in hydrochloric acid produces hydrogen gas and aluminum chloride. How many grams of aluminum chloride can be produced when 3.45 grams of aluminum are reacted with an excess of hydrochloric acid? 2 Al(s) + 6HCl(aq) 2AlCl3(aq) + ...
Homework Solutions Week 6
... According to Box 9-1, the source of calcium in the rivers is the mineral calcite, which dissolves by reacting with carbon dioxide in the river waver according to the equation: CaCO3(s) + CO2(aq) + H2O < == > Ca2+ + 2 HCO3If the predominate product is bicarbonate and not carbonate or carbonic acid,th ...
... According to Box 9-1, the source of calcium in the rivers is the mineral calcite, which dissolves by reacting with carbon dioxide in the river waver according to the equation: CaCO3(s) + CO2(aq) + H2O < == > Ca2+ + 2 HCO3If the predominate product is bicarbonate and not carbonate or carbonic acid,th ...
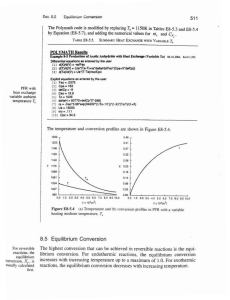
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
... These particles are unbound and can have any energy in the range; i.e., there are no quantized energy levels. Figure 4.6b shows a slightly constrained system, such as a rotating or translating molecule. The low constraints on the motion result in only slight constraints on the rotational energies, s ...
... These particles are unbound and can have any energy in the range; i.e., there are no quantized energy levels. Figure 4.6b shows a slightly constrained system, such as a rotating or translating molecule. The low constraints on the motion result in only slight constraints on the rotational energies, s ...
Organic Chemistry
... developed by E.J. Corey, starts with the target molecule and splices it to pieces according to known reactions. The pieces, or the proposed precursors, receive the same treatment, until available and ideally inexpensive starting materials are reached. Then, the retrosynthesis is written in the oppo ...
... developed by E.J. Corey, starts with the target molecule and splices it to pieces according to known reactions. The pieces, or the proposed precursors, receive the same treatment, until available and ideally inexpensive starting materials are reached. Then, the retrosynthesis is written in the oppo ...
Chemical Element
... The naming of elements precedes the atomic theory of matter, although at the time it was not known which chemicals were elements and which compounds. When it was learned, existing names (e.g., gold, mercury, iron) were kept in most countries, and national differences emerged over the names of eleme ...
... The naming of elements precedes the atomic theory of matter, although at the time it was not known which chemicals were elements and which compounds. When it was learned, existing names (e.g., gold, mercury, iron) were kept in most countries, and national differences emerged over the names of eleme ...
Ch 10 Practice Problems 1. Consider the process A(l) A(s). Which
... D) More information is needed. q is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. H is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. E is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater than zero. D) More infor ...
... D) More information is needed. q is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. H is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater than zero. D) More information is needed. E is A) less than zero. B) equal to zero. C) greater than zero. D) More infor ...
(1125) Catalytic Dehydration Reactions for Green Synthesis of
... rhenium(VI) oxide (ReO3) and rhenium(IV) oxide (ReO2) were very low (entries 4–6). The other metal oxides such as molybdenum(VI) oxide (MoO3), tungsten(VI) oxide (WO3) and vanadium(V) oxide (V2O5) were almost inert (entries 7–9). Under the reaction conditions described above, rhenium(VII) oxo comoun ...
... rhenium(VI) oxide (ReO3) and rhenium(IV) oxide (ReO2) were very low (entries 4–6). The other metal oxides such as molybdenum(VI) oxide (MoO3), tungsten(VI) oxide (WO3) and vanadium(V) oxide (V2O5) were almost inert (entries 7–9). Under the reaction conditions described above, rhenium(VII) oxo comoun ...
Chemical Thermodynamics - Winona State University
... Entropy is the Arrow of Time A Brief History of Time ...
... Entropy is the Arrow of Time A Brief History of Time ...
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry - Byron Senior High School
... (unknown to be found). Solve: By adding the atomic weights of C and 4 H, we have 1 mol CH4 = 16.0 g CH4. Thus, we can use the appropriate conversion factors to convert grams of CH4 to moles of CH4 to kilojoules: ...
... (unknown to be found). Solve: By adding the atomic weights of C and 4 H, we have 1 mol CH4 = 16.0 g CH4. Thus, we can use the appropriate conversion factors to convert grams of CH4 to moles of CH4 to kilojoules: ...
... for its structure in which the chart showed chemical shift signals at δ 57, 52, 27, 25, and 23 due to sp3-carbons, due to two (NCH2) and three (CH2) methylenes, in addition to a characteristic signal at δ 90 corresponding to sp2-carbon of enamine. Mass spectrum revealed the molecular ion (M+) as the ...
AP Thermodynamics ppt.
... Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics • For a reversible process: Suniv = 0. • For a spontaneous process (i.e. irreversible): Suniv > 0. Suniv< 0 means spontaneous is opposite direction. • Second law states that the entropy of the universe must increase in a spontaneous process. Entropy o ...
... Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics • For a reversible process: Suniv = 0. • For a spontaneous process (i.e. irreversible): Suniv > 0. Suniv< 0 means spontaneous is opposite direction. • Second law states that the entropy of the universe must increase in a spontaneous process. Entropy o ...
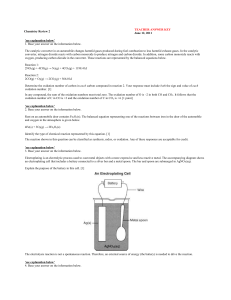
Chemistry Review 2 answer key
... Aluminum is one of the most abundant metals in Earth's crust. The aluminum compound found in bauxite ore is Al2O3. Over one hundred years ago, it was difficult and expensive to isolate aluminum from bauxite ore. In 1886, a brother and sister team, Charles and Julia Hall, found that molten (melted) c ...
... Aluminum is one of the most abundant metals in Earth's crust. The aluminum compound found in bauxite ore is Al2O3. Over one hundred years ago, it was difficult and expensive to isolate aluminum from bauxite ore. In 1886, a brother and sister team, Charles and Julia Hall, found that molten (melted) c ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.