
James W. Whittaker - Oxygen reactions of the copper oxidases
... electrons a complex can deliver, as well as the redox potential of the metal complex. The importance of nuclearity is illustrated by the binuclear Cu(I)–Cu(I) centre of the oxygen-reactive site in haemocyanin, which is capable of reducing O2 by two electrons; this enables haemocyanin to carry oxygen ...
... electrons a complex can deliver, as well as the redox potential of the metal complex. The importance of nuclearity is illustrated by the binuclear Cu(I)–Cu(I) centre of the oxygen-reactive site in haemocyanin, which is capable of reducing O2 by two electrons; this enables haemocyanin to carry oxygen ...
ExamView - 1999 AP Chemistry Exam.tst
... When the equation above is balanced and all coefficients are reduced to their lowest whole-number terms, the coefficient for O2(g) is? A) 6 B) 7 C) 12 D) 14 E) 28 27. Appropriate uses of a visible-light spectrophotometer include which of the following? I. Determining the concentration of a solution ...
... When the equation above is balanced and all coefficients are reduced to their lowest whole-number terms, the coefficient for O2(g) is? A) 6 B) 7 C) 12 D) 14 E) 28 27. Appropriate uses of a visible-light spectrophotometer include which of the following? I. Determining the concentration of a solution ...
Topic 15 Energetics - slider-dpchemistry-11
... The standard enthalpy change when 1 mole of an ionic compound is formed from its free gaseous ions. The negative (–) shows that energy is released as charges come together (i.e. to form a lattice). A positive sign (+) shows the energy to be added in order to break the lattice. An example: Na+(g) + C ...
... The standard enthalpy change when 1 mole of an ionic compound is formed from its free gaseous ions. The negative (–) shows that energy is released as charges come together (i.e. to form a lattice). A positive sign (+) shows the energy to be added in order to break the lattice. An example: Na+(g) + C ...
Chapter 6 PowerPoint
... PROBLEM: You place 50.0 mL of 0.500 M NaOH in a coffee-cup calorimeter at 25.000C and carefully add 25.0 mL of 0.500 M HCl, also at 25.000C. After stirring, the final temperature is 27.210C. Calculate qsoln (in J) and DHrxn (in kJ/mol). (Assume the total volume is the sum of the individual volumes a ...
... PROBLEM: You place 50.0 mL of 0.500 M NaOH in a coffee-cup calorimeter at 25.000C and carefully add 25.0 mL of 0.500 M HCl, also at 25.000C. After stirring, the final temperature is 27.210C. Calculate qsoln (in J) and DHrxn (in kJ/mol). (Assume the total volume is the sum of the individual volumes a ...
Synthesizing Nanoparticles Using Reactions Occurring in Aerosol
... A blank experiment was performed with distilled water. The QCM crystal was cleaned with acetone, dried with N2 gas, and the crystal frequency was recorded. The crystal was exposed to a distilled water aerosol at one minute’s intervals for a total of eight minutes and the frequency change was recorde ...
... A blank experiment was performed with distilled water. The QCM crystal was cleaned with acetone, dried with N2 gas, and the crystal frequency was recorded. The crystal was exposed to a distilled water aerosol at one minute’s intervals for a total of eight minutes and the frequency change was recorde ...
Downloaded on 2017-02
... with such atomic-scale control is a substantial challenge. One step towards this goal would be understanding the reactivity of surfaces towards particular reagents, and how to turn reactivity on and off at the level of single atomic layers. ALD shows great promise in achieving monolayer-by-monolayer ...
... with such atomic-scale control is a substantial challenge. One step towards this goal would be understanding the reactivity of surfaces towards particular reagents, and how to turn reactivity on and off at the level of single atomic layers. ALD shows great promise in achieving monolayer-by-monolayer ...
mass
... Calculating average r.a.m. from isotopes To calculate the average r.a.m. of a mixture of isotopes, multiply the percentage of each isotope( as a decimal) by its relative atomic mass and then add these together. Naturally-occurring bromine is composed of two isotopes: bromine-79 (50.5%) and bromine- ...
... Calculating average r.a.m. from isotopes To calculate the average r.a.m. of a mixture of isotopes, multiply the percentage of each isotope( as a decimal) by its relative atomic mass and then add these together. Naturally-occurring bromine is composed of two isotopes: bromine-79 (50.5%) and bromine- ...
5073 Chemistry (SPA)
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry
... o We will usually use scientific notation to avoid confusion about significant figures. What is an exact number? What are the rules for determining the number of significant figures in the following types of mathematical calculations? o Addition and subtraction o Multiplication and Division ...
... o We will usually use scientific notation to avoid confusion about significant figures. What is an exact number? What are the rules for determining the number of significant figures in the following types of mathematical calculations? o Addition and subtraction o Multiplication and Division ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry
... o We will usually use scientific notation to avoid confusion about significant figures. What is an exact number? What are the rules for determining the number of significant figures in the following types of mathematical calculations? o Addition and subtraction o Multiplication and Division ...
... o We will usually use scientific notation to avoid confusion about significant figures. What is an exact number? What are the rules for determining the number of significant figures in the following types of mathematical calculations? o Addition and subtraction o Multiplication and Division ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry 4.1
... Notice that classification of ionic compound solubility is primarily based on the anion in the compound. When classifying an ionic compound as soluble or insoluble, first determine whether the anion present is typically found in soluble or insoluble compounds. Next, see if the cation in the compound ...
... Notice that classification of ionic compound solubility is primarily based on the anion in the compound. When classifying an ionic compound as soluble or insoluble, first determine whether the anion present is typically found in soluble or insoluble compounds. Next, see if the cation in the compound ...
chem 102 class notes - Louisiana Tech University
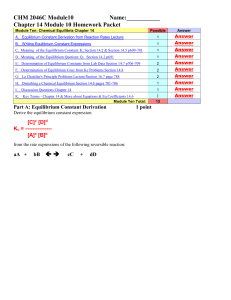
... K (Kc) in the equilibrium expression is usually the constant calculated based on moles/Liters concentration of reactants and products. This is also called Kc - equilibrium constant based on M, [A] or moles/L -Concentrations. However, many chemical reactions occur in gas phase and concentration of pr ...
... K (Kc) in the equilibrium expression is usually the constant calculated based on moles/Liters concentration of reactants and products. This is also called Kc - equilibrium constant based on M, [A] or moles/L -Concentrations. However, many chemical reactions occur in gas phase and concentration of pr ...
CHEM 1212 Module Ten-Chapter 16 Name
... Predict the effect on each of the following changes to the system on the direction of equilibrium: a. Moves to the Right b. Moves to the Left c. Has no effect/does not move left or right The combination of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas to give water vapor can be expressed by 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) 2 H2O ...
... Predict the effect on each of the following changes to the system on the direction of equilibrium: a. Moves to the Right b. Moves to the Left c. Has no effect/does not move left or right The combination of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas to give water vapor can be expressed by 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) 2 H2O ...
File
... Super-absorbent polymers have the ability to absorb 200-300 times their own mass of water. They are classified as hydrogels and they are widely used in personal disposable hygiene ...
... Super-absorbent polymers have the ability to absorb 200-300 times their own mass of water. They are classified as hydrogels and they are widely used in personal disposable hygiene ...
Science
... 11. Students shall relate the physical properties as they relate to different types of bonding. Stoichiometry 12. Students shall understand the relationship between balanced chemical equations and mole relationships. 13. Students shall understand the mole concept and Avogadro’s number. 14. Students ...
... 11. Students shall relate the physical properties as they relate to different types of bonding. Stoichiometry 12. Students shall understand the relationship between balanced chemical equations and mole relationships. 13. Students shall understand the mole concept and Avogadro’s number. 14. Students ...
Document
... 2. The third law of thermodynamics states that at 0 K, the entropy of a pure crystal is equal to 0. * Because this provides a starting point to compare all other entropies, an absolute entropy scale has meaning. 3. Standard molar entropy, So, is the entropy of one mole of a substance in its standard ...
... 2. The third law of thermodynamics states that at 0 K, the entropy of a pure crystal is equal to 0. * Because this provides a starting point to compare all other entropies, an absolute entropy scale has meaning. 3. Standard molar entropy, So, is the entropy of one mole of a substance in its standard ...
AP 3rd 9 weeks notes
... 2. The third law of thermodynamics states that at 0 K, the entropy of a pure crystal is equal to 0. * Because this provides a starting point to compare all other entropies, an absolute entropy scale has meaning. 3. Standard molar entropy, So, is the entropy of one mole of a substance in its standard ...
... 2. The third law of thermodynamics states that at 0 K, the entropy of a pure crystal is equal to 0. * Because this provides a starting point to compare all other entropies, an absolute entropy scale has meaning. 3. Standard molar entropy, So, is the entropy of one mole of a substance in its standard ...
5073 Chemistry IGCSE ordinary level for 2016
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
... particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique atoms and the atoms of an element are all the same. At that time, there were about 35 known elements. T ...
5/14/01 - Oklahoma State University
... Problem Solving Resources: This is an interactive feature that can be used to help students develop problem-solving skills. Each tutorial consists of three prototype questions that are randomly sequenced. In the tutorial the student views the first question and is given three choices of how to inter ...
... Problem Solving Resources: This is an interactive feature that can be used to help students develop problem-solving skills. Each tutorial consists of three prototype questions that are randomly sequenced. In the tutorial the student views the first question and is given three choices of how to inter ...
Slide 1
... • To make sure adequate amounts of product AB is being made during a rxn you might need 3.33 mols of A reacting with 2.68 mols of B. How many atoms of A are reacting with how many atoms of B? • If you burn sugar (C12H22O11) in pure oxygen you produce carbon dioxide and water as products. To burn 6.0 ...
... • To make sure adequate amounts of product AB is being made during a rxn you might need 3.33 mols of A reacting with 2.68 mols of B. How many atoms of A are reacting with how many atoms of B? • If you burn sugar (C12H22O11) in pure oxygen you produce carbon dioxide and water as products. To burn 6.0 ...
Modeling the Star-Branched Polymer Coupling Reaction in
... second order kinetic modes (see Eqs. 2 and 3) as the Damkohler number varies. In equations 14 and 15, the distribution parameters adopted (θ and σ for the Schulz-Zimm distribution, β and ν for the Beasley distribution) are the ones estimated for the parent polymer distribution as reported in Table 1 ...
... second order kinetic modes (see Eqs. 2 and 3) as the Damkohler number varies. In equations 14 and 15, the distribution parameters adopted (θ and σ for the Schulz-Zimm distribution, β and ν for the Beasley distribution) are the ones estimated for the parent polymer distribution as reported in Table 1 ...
Neutral ionic liquid [BMIm]BF4 promoted highly selective
... [BMIm][PhSO3 ]. It is important to note that the selectivities to tert-butyl acetate are all close to 100% in these ionic liquids (Entries 5–7). When using [BMIm]PF6 as medium, a lot of isobutene was detected beside desired tert-butyl acetate (Entry 8). It may contribute to the acidic hydrofluoric a ...
... [BMIm][PhSO3 ]. It is important to note that the selectivities to tert-butyl acetate are all close to 100% in these ionic liquids (Entries 5–7). When using [BMIm]PF6 as medium, a lot of isobutene was detected beside desired tert-butyl acetate (Entry 8). It may contribute to the acidic hydrofluoric a ...
Chemistry 6
... chemical combinations of elements. The law of definite composition (a.k.a. law of definite proportions) states that the elements forming a compound always combine in the same proportion by mass. Water, H2O, is always a chemical combination of hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:8 ratio by mass (1 g of hydrog ...
... chemical combinations of elements. The law of definite composition (a.k.a. law of definite proportions) states that the elements forming a compound always combine in the same proportion by mass. Water, H2O, is always a chemical combination of hydrogen and oxygen in a 1:8 ratio by mass (1 g of hydrog ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.



















![Neutral ionic liquid [BMIm]BF4 promoted highly selective](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017897985_1-047f9869d5604c115b21339541ccfffe-300x300.png)
