Gases - Chemistry 504
... Dalton found that since each gas particle behaves independently of other gases (KMT – no attraction or repulsion between particles) each gas in a mixture contributes to the total pressure based on its percentage of the mixture. A manometer cannot measure the partial pressure of a gas it can only me ...
... Dalton found that since each gas particle behaves independently of other gases (KMT – no attraction or repulsion between particles) each gas in a mixture contributes to the total pressure based on its percentage of the mixture. A manometer cannot measure the partial pressure of a gas it can only me ...
Chapter 3 2014
... (2). Iron (Fe), the main component of steel, is the most important metal in industrial society. How many Fe atoms are in 95.8g of Fe? (3). How many molecules of nitrogen dioxide are in 8.92 g of nitrogen dioxide? ...
... (2). Iron (Fe), the main component of steel, is the most important metal in industrial society. How many Fe atoms are in 95.8g of Fe? (3). How many molecules of nitrogen dioxide are in 8.92 g of nitrogen dioxide? ...
Name of Lecturer: Mr. J.Agius Course: FCES
... Suppose that Peter makes a model of his father’s boat. If the model is 1m long while the actual boat is 20m long, we say that the ratio of the length of the model to the length of the actual boat is 1m : 20m or, more simply, 1 : 20. We can also write the ratio as the fraction ...
... Suppose that Peter makes a model of his father’s boat. If the model is 1m long while the actual boat is 20m long, we say that the ratio of the length of the model to the length of the actual boat is 1m : 20m or, more simply, 1 : 20. We can also write the ratio as the fraction ...
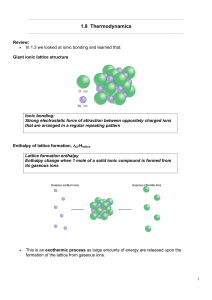
1.8 Thermodynamics
... Factors affecting hydration and lattice enthalpies 1) Lattice enthalpies • Lattice enthalpy is due to strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions. • The charge density affects how strong these forces of attractions are ...
... Factors affecting hydration and lattice enthalpies 1) Lattice enthalpies • Lattice enthalpy is due to strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions. • The charge density affects how strong these forces of attractions are ...
Chapter 6 Quantities in Chemical Reactions
... these examples, we cited moles of atoms and moles of molecules. The word mole represents a number of things—6.022 × 1023 of them—but does not by itself specify what “they” are. They can be atoms, formula units (of ionic compounds), or molecules. That information still needs to be specified. Because ...
... these examples, we cited moles of atoms and moles of molecules. The word mole represents a number of things—6.022 × 1023 of them—but does not by itself specify what “they” are. They can be atoms, formula units (of ionic compounds), or molecules. That information still needs to be specified. Because ...
The Mole
... 5. Calculate the percent composition of a compound by mass of each element. and 6. Calculate both the empirical (simplest) formula and molecular formula of a compound. NOTE: As we encounter Learning Checks write the answers down for a daily grade ...
... 5. Calculate the percent composition of a compound by mass of each element. and 6. Calculate both the empirical (simplest) formula and molecular formula of a compound. NOTE: As we encounter Learning Checks write the answers down for a daily grade ...
Topic 14 - Fertilisers
... Forrester High School. Chemistry Revision Notes Making fertilisers Nitrogen However, nitrogen is un-reactive but not inert. This means it is difficult getting it to react but it can be done (using electricity i.e. lightening or a spark plug). The nitrogen will form oxides which dissolve in water fo ...
... Forrester High School. Chemistry Revision Notes Making fertilisers Nitrogen However, nitrogen is un-reactive but not inert. This means it is difficult getting it to react but it can be done (using electricity i.e. lightening or a spark plug). The nitrogen will form oxides which dissolve in water fo ...
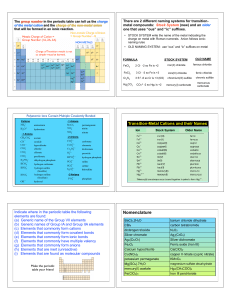
- Career Point Kota
... resonance hence the reactivity reduce" (b) CH3–NH2 is more basic then C6H5–NH2 Because In case of aniline the L.P of –NH2 (amino group) are in conjugation with benzene ring due to which e– density less available on N-atom hence higher the "electron density on N-atom more will be the basicity." ...
... resonance hence the reactivity reduce" (b) CH3–NH2 is more basic then C6H5–NH2 Because In case of aniline the L.P of –NH2 (amino group) are in conjugation with benzene ring due to which e– density less available on N-atom hence higher the "electron density on N-atom more will be the basicity." ...
Unit 4 Chemical Kinetics and Chemical Equilibrium
... the concentration of a reactant or product, consider how adding or removing weight from one side of a balanced teeter totter impacts the balance. ...
... the concentration of a reactant or product, consider how adding or removing weight from one side of a balanced teeter totter impacts the balance. ...
(a) From , 2013 General Chemistry I
... - For any ideal gas, ΔU = 0 for an isothermal process. No changes in the kinetic energy of an ideal gas if ΔT = 0 No intermolecular forces for ideal gas molecules No changes in potential energy during expansion ...
... - For any ideal gas, ΔU = 0 for an isothermal process. No changes in the kinetic energy of an ideal gas if ΔT = 0 No intermolecular forces for ideal gas molecules No changes in potential energy during expansion ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions - An Introduction to Chemistry
... Bonds between zinc atoms and oxygen atoms are lost in this reaction, so chemists say the zinc has been reduced. Like the term oxidation, the term reduction has been expanded to include similar reactions, even when oxygen is not a participant. The zinc ions in zinc oxide have a +2 charge, and the ato ...
... Bonds between zinc atoms and oxygen atoms are lost in this reaction, so chemists say the zinc has been reduced. Like the term oxidation, the term reduction has been expanded to include similar reactions, even when oxygen is not a participant. The zinc ions in zinc oxide have a +2 charge, and the ato ...
3.4 mol O 2
... 1. Begin by balancing the equation! 2. Convert the unit given to moles of that substance. 3. Use the balanced equation to set up a mole ratios. Every stoich problem has a mole-mole ratio! 4. Convert moles of given to moles of the wanted. If needed, convert moles to unit wanted. ...
... 1. Begin by balancing the equation! 2. Convert the unit given to moles of that substance. 3. Use the balanced equation to set up a mole ratios. Every stoich problem has a mole-mole ratio! 4. Convert moles of given to moles of the wanted. If needed, convert moles to unit wanted. ...
15equil1pp
... “If the concentrations of all the substances present at equilibrium are raised to the power of the number of moles they appear in the equation, the product of the concentrations of the products divided by the product of the concentrations of the reactants is a constant, provided the temperature rema ...
... “If the concentrations of all the substances present at equilibrium are raised to the power of the number of moles they appear in the equation, the product of the concentrations of the products divided by the product of the concentrations of the reactants is a constant, provided the temperature rema ...
Chapter 4
... 3) The oxidation state of oxygen in compounds is -2, except in peroxides, such as H2O2 where it is -1. 4) The oxidation state of hydrogen in compounds is +1, except in metal hydrides, like NaH, where it is -1. ...
... 3) The oxidation state of oxygen in compounds is -2, except in peroxides, such as H2O2 where it is -1. 4) The oxidation state of hydrogen in compounds is +1, except in metal hydrides, like NaH, where it is -1. ...
15.0 EquilibriumIHS2014
... increasing the container volume. Then the equilibrium shifts to the left (the side with more moles of gas) • At B, the temperature is increased. Then the equilibrium shifts to left. • At C, C2H6(g) is added to the system. Then the equilibrium shifts to the left. • At D, no shift in equilibrium posit ...
... increasing the container volume. Then the equilibrium shifts to the left (the side with more moles of gas) • At B, the temperature is increased. Then the equilibrium shifts to left. • At C, C2H6(g) is added to the system. Then the equilibrium shifts to the left. • At D, no shift in equilibrium posit ...
Topic 3: Chemical Kinetics - Manitoba Education and Training
... Demonstrate appropriate scientific skills when seeking answers to questions. Demonstrate curiosity, skepticism, creativity, open-mindedness, accuracy, precision, honesty, and persistence, and appreciate their importance as scientific and technological habits of mind. Understand the properties and st ...
... Demonstrate appropriate scientific skills when seeking answers to questions. Demonstrate curiosity, skepticism, creativity, open-mindedness, accuracy, precision, honesty, and persistence, and appreciate their importance as scientific and technological habits of mind. Understand the properties and st ...
08272012BC Science Chem 12 Chapter 1 Answer Key
... water will occur as water is formed in a reaction that occurs in aqueous solution. This is, of course, nonsense! As the entire reaction occurs in the solvent water, there will simply be a small amount of water formed, replacing the hydrogen and oxygen atoms (actually hydrogen and hydroxide ions) rea ...
... water will occur as water is formed in a reaction that occurs in aqueous solution. This is, of course, nonsense! As the entire reaction occurs in the solvent water, there will simply be a small amount of water formed, replacing the hydrogen and oxygen atoms (actually hydrogen and hydroxide ions) rea ...
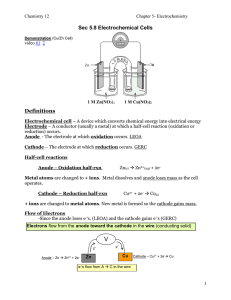
Sec 5.8 - 5.11 notes
... The rest of the overall rx involves Sn2+ changing to Sn4+. The ½ reaction for that must be reversed as well as its Eo. Since Sn2+ must stay on the left side, the half-rx on the table must be reversed as well as its Eo. Sn2+ Sn4+ + 2e- Eo = -0.15 V ...
... The rest of the overall rx involves Sn2+ changing to Sn4+. The ½ reaction for that must be reversed as well as its Eo. Since Sn2+ must stay on the left side, the half-rx on the table must be reversed as well as its Eo. Sn2+ Sn4+ + 2e- Eo = -0.15 V ...
Problem 5. Inorganic chains and rings
... formula of the corresponding GO hydrate? Use the Lerf-Klinowski model. Consider only contacts depicted in Fig.3 (one molecule of water between two epoxy and/or between two OH groups). ...
... formula of the corresponding GO hydrate? Use the Lerf-Klinowski model. Consider only contacts depicted in Fig.3 (one molecule of water between two epoxy and/or between two OH groups). ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.