SCH 4U REVIEW Notes
... toluene / phenyl methane methyl benzene acetate ethanoate acetamide ethanamide ...
... toluene / phenyl methane methyl benzene acetate ethanoate acetamide ethanamide ...
chemistry-subject test5 w. solutions
... dispersion forces (in the order of decreasing strength). For the ideal gas law to give an accurate prediction of the volume, then, we are looking for gases that do not have ahttp://doc.guandang.net/bbca35c11081d34250955e480.html strong dipole moment. Methane, CH4, does not have a dipole moment: What ...
... dispersion forces (in the order of decreasing strength). For the ideal gas law to give an accurate prediction of the volume, then, we are looking for gases that do not have ahttp://doc.guandang.net/bbca35c11081d34250955e480.html strong dipole moment. Methane, CH4, does not have a dipole moment: What ...
Student Study Guide Chemistry 534
... Gases play a very important role in our daily existence. Since we are surrounded by an ocean of gas called the atmosphere, many of the properties of gases are already familiar to us. We know that we can squeeze a balloon into a smaller shape and that perfume released into the corner of a room can, i ...
... Gases play a very important role in our daily existence. Since we are surrounded by an ocean of gas called the atmosphere, many of the properties of gases are already familiar to us. We know that we can squeeze a balloon into a smaller shape and that perfume released into the corner of a room can, i ...
A2 Module 2814: Chains, Rings and Spectroscopy
... A wide range of industrial catalysts consist of transition elements or their compounds. They work through many different mechanisms, of which two will be mentioned here. In the Haber process, Fe2O3 is reduced to finely divided iron metal, and this provides a surface for the nitrogen and hydrogen to ...
... A wide range of industrial catalysts consist of transition elements or their compounds. They work through many different mechanisms, of which two will be mentioned here. In the Haber process, Fe2O3 is reduced to finely divided iron metal, and this provides a surface for the nitrogen and hydrogen to ...
12 U Chem Review
... toluene / phenyl methane methyl benzene acetate ethanoate acetamide ethanamide ...
... toluene / phenyl methane methyl benzene acetate ethanoate acetamide ethanamide ...
C2H5OH + 3 O2 → 2 CO2 + 3 H2O + HEAT Q = mc ∆T
... **When a substance boils the liquid & gas are at equil'm so ∆G = 0 soooo T = ∆H / ∆S 329.2 K = 31.9 kJ / ∆S ∆S = 0.0969 kJ = 96.9 J *1:32. Microwaves are used to heat food. The microwave radiation is absorbed by moisture in the food. This heats the water and thus the food. How many photons having a ...
... **When a substance boils the liquid & gas are at equil'm so ∆G = 0 soooo T = ∆H / ∆S 329.2 K = 31.9 kJ / ∆S ∆S = 0.0969 kJ = 96.9 J *1:32. Microwaves are used to heat food. The microwave radiation is absorbed by moisture in the food. This heats the water and thus the food. How many photons having a ...
UNIT I: Introduction to Chemistry
... Objectives - The student will be able to: a. Contrast Dimitri Mendeleev and Henry Mosely’s contributions and method of organizing the Periodic Table. b. Collect and use information on the Periodic Table, including atomic number, atomic mass, family designation, period number, classification of eleme ...
... Objectives - The student will be able to: a. Contrast Dimitri Mendeleev and Henry Mosely’s contributions and method of organizing the Periodic Table. b. Collect and use information on the Periodic Table, including atomic number, atomic mass, family designation, period number, classification of eleme ...
Document
... Law of Heat Summation: the enthalpy change for a reaction is the same whether it occurs in one step or by a series of steps. Germain Henri Hess, in 1840, discovered a very useful principle which is named for him: The enthalpy of a given chemical reaction is constant, regardless of the reaction happe ...
... Law of Heat Summation: the enthalpy change for a reaction is the same whether it occurs in one step or by a series of steps. Germain Henri Hess, in 1840, discovered a very useful principle which is named for him: The enthalpy of a given chemical reaction is constant, regardless of the reaction happe ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... (1) An acid is an H⫹ acceptor, and a base is an H⫹ donor. (2) An acid is an H⫹ donor, and a base is an H⫹ acceptor. (3) An acid is an H⫺ acceptor, and a base is an H⫺ donor. (4) An acid is an H⫺ donor, and a base is an H⫺ acceptor. ...
... (1) An acid is an H⫹ acceptor, and a base is an H⫹ donor. (2) An acid is an H⫹ donor, and a base is an H⫹ acceptor. (3) An acid is an H⫺ acceptor, and a base is an H⫺ donor. (4) An acid is an H⫺ donor, and a base is an H⫺ acceptor. ...
Document
... You have a sample of zinc (Zn) and a sample of aluminum (Al). You have an equal number of atoms in each sample. Which of the following statements concerning the masses of the samples is true? a) The mass of the zinc sample is more than twice as great as the mass of the aluminum sample. b) The mass o ...
... You have a sample of zinc (Zn) and a sample of aluminum (Al). You have an equal number of atoms in each sample. Which of the following statements concerning the masses of the samples is true? a) The mass of the zinc sample is more than twice as great as the mass of the aluminum sample. b) The mass o ...
Unit C3 - Chemistry in Action
... Relative Formula Mass (Mr) of a gas will occupy a volume of 24 litres e.g. 2g of H2 has a volume of 24 litres 32g of O2 has a volume of 24 litres 44g of CO2 has a volume of 24 litres etc Q. When water is electrolysed it breaks down into hydrogen and oxygen: 2H2O ...
... Relative Formula Mass (Mr) of a gas will occupy a volume of 24 litres e.g. 2g of H2 has a volume of 24 litres 32g of O2 has a volume of 24 litres 44g of CO2 has a volume of 24 litres etc Q. When water is electrolysed it breaks down into hydrogen and oxygen: 2H2O ...
Unit C3 - Chemistry In Action
... Relative Formula Mass (Mr) of a gas will occupy a volume of 24 litres e.g. 2g of H2 has a volume of 24 litres 32g of O2 has a volume of 24 litres 44g of CO2 has a volume of 24 litres etc Q. When water is electrolysed it breaks down into hydrogen and oxygen: 2H2O ...
... Relative Formula Mass (Mr) of a gas will occupy a volume of 24 litres e.g. 2g of H2 has a volume of 24 litres 32g of O2 has a volume of 24 litres 44g of CO2 has a volume of 24 litres etc Q. When water is electrolysed it breaks down into hydrogen and oxygen: 2H2O ...
B - eko.olunet.org
... experiments, Thomas needed KBr with at least 95.0% purity. In order to determine the purity of an available inorganic compound, he weighed out 0.8230 g of KBr and dissolved it in water. Then to the resulting solution, 31.20 cm3 of 0.2180 M AgNO3 aqueous solution was added. For the back-titration of ...
... experiments, Thomas needed KBr with at least 95.0% purity. In order to determine the purity of an available inorganic compound, he weighed out 0.8230 g of KBr and dissolved it in water. Then to the resulting solution, 31.20 cm3 of 0.2180 M AgNO3 aqueous solution was added. For the back-titration of ...
Chapter 3 Sem 2 2013-14
... 2 atoms of Al and 3 molecules of (SO4)2- = 1 formula unit Al2(SO4)3 2 moles of Al and 3 moles of (SO4)2- = 1 formula unit Al2(SO4)3 1 formula unit Al2(SO4)3 = 342.17 amu Al2(SO4)3 1 mole Al2(SO4)3 = 342.17 g Al2(SO4)3 1 mole Al2(SO4)3 = 6.022 x 1023 formula units Al2(SO4)3 1 mole Al2(SO4)3 = 2 mol A ...
... 2 atoms of Al and 3 molecules of (SO4)2- = 1 formula unit Al2(SO4)3 2 moles of Al and 3 moles of (SO4)2- = 1 formula unit Al2(SO4)3 1 formula unit Al2(SO4)3 = 342.17 amu Al2(SO4)3 1 mole Al2(SO4)3 = 342.17 g Al2(SO4)3 1 mole Al2(SO4)3 = 6.022 x 1023 formula units Al2(SO4)3 1 mole Al2(SO4)3 = 2 mol A ...
9.1 REDOX Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction
... oxygen was discovered by Joseph Priestley (17331804) Quickly realized that oxygen forms oxides so the word oxidation was created to describe the addition of oxygen When oxygen is removed “reduction” is used Now oxidation and reduction refer to transfer of ...
... oxygen was discovered by Joseph Priestley (17331804) Quickly realized that oxygen forms oxides so the word oxidation was created to describe the addition of oxygen When oxygen is removed “reduction” is used Now oxidation and reduction refer to transfer of ...
chemical kinetics type 1.mdi
... a chemical reaction is known as mechanism of a reaction. Slow reaction. Those reactions which take place very slowly are called slow reactions, e.g., rusting of iron and reaction of oxalic acid with acidified KMnO4 at room temperature are slow reactions. Life time. The time in which 98% of the react ...
... a chemical reaction is known as mechanism of a reaction. Slow reaction. Those reactions which take place very slowly are called slow reactions, e.g., rusting of iron and reaction of oxalic acid with acidified KMnO4 at room temperature are slow reactions. Life time. The time in which 98% of the react ...
atomic mass
... • Proportion of a particular isotope, usually expressed as a percentage, relative to all the isotopes for that element in a natural sample • Assumes the same percentages over the surface of the Earth © 2014 W. W. Norton Co., Inc. ...
... • Proportion of a particular isotope, usually expressed as a percentage, relative to all the isotopes for that element in a natural sample • Assumes the same percentages over the surface of the Earth © 2014 W. W. Norton Co., Inc. ...
Writing Equilibrium Cons... and Liquids - Chemwiki
... No state symbols have been given, but they will be all (g), or all (l), or all (aq) if the reaction was between substances in solution in water. If you allow this reaction to reach equilibrium and then measure the equilibrium concentrations of everything, you can combine these concentrations into an ...
... No state symbols have been given, but they will be all (g), or all (l), or all (aq) if the reaction was between substances in solution in water. If you allow this reaction to reach equilibrium and then measure the equilibrium concentrations of everything, you can combine these concentrations into an ...
Electrochemistry Oxidation – Reduction and Oxidation Numbers
... Rules for assigning oxidation numbers: 1. Elements in their most abundant naturally occurring form are assigned an oxidation number of zero. e.g. Na, Fe, Cl2, O2 2. The sum of the oxidation numbers for a compound or formula unit is zero. 3. For a polyatomic ion, the oxidation numbers of the constit ...
... Rules for assigning oxidation numbers: 1. Elements in their most abundant naturally occurring form are assigned an oxidation number of zero. e.g. Na, Fe, Cl2, O2 2. The sum of the oxidation numbers for a compound or formula unit is zero. 3. For a polyatomic ion, the oxidation numbers of the constit ...
Major 01 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Solution of the 1st Major Exam, Term 061, Version 000, all correct choices are A 1. All of the following are properties of sodium. Which one is a physical change? A. It is a solid at 25oC and melts at 98oC. Since melting has no change of the chemical composition involved, this is a physical change. ...
... Solution of the 1st Major Exam, Term 061, Version 000, all correct choices are A 1. All of the following are properties of sodium. Which one is a physical change? A. It is a solid at 25oC and melts at 98oC. Since melting has no change of the chemical composition involved, this is a physical change. ...
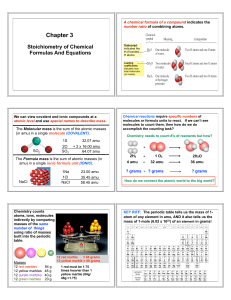
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.