DNA Recombinations
... form base pairs with the complementary bases on other DNA molecules. Thus, the sticky ends of DNA fragments can be used to join DNA pieces originating from different sources. http://www.accessexcellence.org/RC/AB/WYW/wkbooks/SFTS/activity6.html ...
... form base pairs with the complementary bases on other DNA molecules. Thus, the sticky ends of DNA fragments can be used to join DNA pieces originating from different sources. http://www.accessexcellence.org/RC/AB/WYW/wkbooks/SFTS/activity6.html ...
Genetic engineering
... Copying DNA It is relatively easy to extract DNA from cells and tissues. The extracted DNA can be cut into fragments of manageable size using restriction enzymes. These restriction fragments can then be separated according to size, using gel electrophoresis or another similar technique ...
... Copying DNA It is relatively easy to extract DNA from cells and tissues. The extracted DNA can be cut into fragments of manageable size using restriction enzymes. These restriction fragments can then be separated according to size, using gel electrophoresis or another similar technique ...
Chromosomes Notes
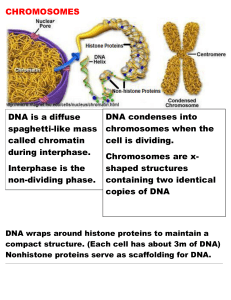
... DNA wraps around histone proteins to maintain a compact structure. (Each cell has about 3m of DNA) Nonhistone proteins serve as scaffolding for DNA. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... DNA wraps around histone proteins to maintain a compact structure. (Each cell has about 3m of DNA) Nonhistone proteins serve as scaffolding for DNA. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 7.1 - Fredericksburg City Schools
... 1. Why are there so many different kinds of proteins when there are only 20 different amino acids? _________ _________ 2. How are DNA and RNA different? _________ _________ 3. Describe the steps in protein synthesis. _________ _________ _________ _________ ...
... 1. Why are there so many different kinds of proteins when there are only 20 different amino acids? _________ _________ 2. How are DNA and RNA different? _________ _________ 3. Describe the steps in protein synthesis. _________ _________ _________ _________ ...
The Good, the bad and the ugly of Genetic Engineering
... Contains cells from fetus DNA or protein can be isolated and examined ...
... Contains cells from fetus DNA or protein can be isolated and examined ...
Presentation
... Amniocentesis - a small amount of amniotic fluid (containing fetal tissues and cells) is extracted from the amniotic sac surrounding the developing fetus - the DNA is examined for genetic abnormalities Chorionic Villi Sampling (CVS) - the removal of a small piece of the placenta (chorionic villi) d ...
... Amniocentesis - a small amount of amniotic fluid (containing fetal tissues and cells) is extracted from the amniotic sac surrounding the developing fetus - the DNA is examined for genetic abnormalities Chorionic Villi Sampling (CVS) - the removal of a small piece of the placenta (chorionic villi) d ...
EXAM B
... • The peculiarity found in the reproduction of flowering plants that does not occur in animal reproduction is • A. meiosis. • B. double fertilization. • C. crossing over. • D. union of ova and sperm. ...
... • The peculiarity found in the reproduction of flowering plants that does not occur in animal reproduction is • A. meiosis. • B. double fertilization. • C. crossing over. • D. union of ova and sperm. ...
Genomics Glossary - College of American Pathologists
... to bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in biological organisms. Recombinant DNA is possible because DNA molecules from all organisms share the same chemical structure; they differ only in the sequence of nucleotides within that ...
... to bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be found in biological organisms. Recombinant DNA is possible because DNA molecules from all organisms share the same chemical structure; they differ only in the sequence of nucleotides within that ...
handout 1
... beginning of the 20th Century, and are still widely used in clinical laboratories. We perform a number of these classic diagnostic test methods in a separate exercise. These traditional methods are being augmented, and in some cases supplanted, by molecular sequencing methods. You and your lab partn ...
... beginning of the 20th Century, and are still widely used in clinical laboratories. We perform a number of these classic diagnostic test methods in a separate exercise. These traditional methods are being augmented, and in some cases supplanted, by molecular sequencing methods. You and your lab partn ...
Primer on Comparative Genomics in PLoS
... impact on the fitness of an organism; such neutral mutations are not under selection. Sequence polymorphisms arise randomly in a population, most of which have no effect on function. Stochastic processes allow a small fraction of these to increase in frequency until they are fixed in a population; t ...
... impact on the fitness of an organism; such neutral mutations are not under selection. Sequence polymorphisms arise randomly in a population, most of which have no effect on function. Stochastic processes allow a small fraction of these to increase in frequency until they are fixed in a population; t ...
Student Name: Teacher
... Any organism in the same kingdom as the subject. Any plant, animal, or other living organism. Only organisms in the same species as the subject. Organisms in the same species as the subject only. ...
... Any organism in the same kingdom as the subject. Any plant, animal, or other living organism. Only organisms in the same species as the subject. Organisms in the same species as the subject only. ...
Biotechnology
... The HGP has allowed for the development of genetic tests. For example an individual can be tested for the presence of a gene that may contribute to breast cancer. Should the patient be notified of the presence of this gene, even though the presence of the gene does not guarantee breast cancer and ma ...
... The HGP has allowed for the development of genetic tests. For example an individual can be tested for the presence of a gene that may contribute to breast cancer. Should the patient be notified of the presence of this gene, even though the presence of the gene does not guarantee breast cancer and ma ...
Medical Genetics 2013
... syndromes? A. Two or more independent primary tumors in a single individual B. More often involve mutation in tumor suppressor genes than oncogenes C. One or more close relatives are affected by the same rare tumor D. Observed tumor types are rarely seen as sporadic cancers E. Earlier mean age of ca ...
... syndromes? A. Two or more independent primary tumors in a single individual B. More often involve mutation in tumor suppressor genes than oncogenes C. One or more close relatives are affected by the same rare tumor D. Observed tumor types are rarely seen as sporadic cancers E. Earlier mean age of ca ...
File
... deaths of males since they only have a single X chromosome. Not every cell in an organism’s body has to have an inactivated X chromosome which is how tricolor cats form. In the cells with inactivated X chromosomes, that patch of fur may be black while another with both of its chromosomes activated w ...
... deaths of males since they only have a single X chromosome. Not every cell in an organism’s body has to have an inactivated X chromosome which is how tricolor cats form. In the cells with inactivated X chromosomes, that patch of fur may be black while another with both of its chromosomes activated w ...
DNA Recombination
... partially, giving new phenotypes. • Some elements (e.g., Ds) correlated with chromosome breaks. • Elements often move during meiosis and mitosis. • Element movement accelerated by genome damage. ...
... partially, giving new phenotypes. • Some elements (e.g., Ds) correlated with chromosome breaks. • Elements often move during meiosis and mitosis. • Element movement accelerated by genome damage. ...
E. Coli - mrkeay
... circular chromosome, along with many small, circular pieces of DNA called plasmids • Plasmids carry genes which confer antibiotic resistance, as well as resistance to toxic heavy metals and industrial chemicals • We can use plasmids for biotechnology, since bacteria are able to express foreign genes ...
... circular chromosome, along with many small, circular pieces of DNA called plasmids • Plasmids carry genes which confer antibiotic resistance, as well as resistance to toxic heavy metals and industrial chemicals • We can use plasmids for biotechnology, since bacteria are able to express foreign genes ...
Biotechnology Powerpoint
... A new DNA sequence created when the DNA of one organism is inserted into the DNA of another organism. This “new combination” of DNA is known as recombinant DNA. ...
... A new DNA sequence created when the DNA of one organism is inserted into the DNA of another organism. This “new combination” of DNA is known as recombinant DNA. ...
problem set #2
... b) they regularly exchange parts by crossing over at meiosis. c) in a diploid cell in interphase they are found in pairs but they do not physically ...
... b) they regularly exchange parts by crossing over at meiosis. c) in a diploid cell in interphase they are found in pairs but they do not physically ...
Edvotek November Newsletter
... Modern technology has allowed scientists to determine the sequence the genome of many model organisms. DNA sequence comparison software like BLAST has allowed scientists to identify genes that are similar to those that are important for human health and development. Scientists can learn more about ...
... Modern technology has allowed scientists to determine the sequence the genome of many model organisms. DNA sequence comparison software like BLAST has allowed scientists to identify genes that are similar to those that are important for human health and development. Scientists can learn more about ...
DNA, Genes, and Chromosomes
... chromosome)? Stress that when DNA is being transferred (like during mitosis and DNA replication) it must be “wound up,” but when it is being used (during interphase) it is no longer wound up. 3. Uncoil about 2 feet of thread and color it red. What do students think this represents (a nucleotide sequ ...
... chromosome)? Stress that when DNA is being transferred (like during mitosis and DNA replication) it must be “wound up,” but when it is being used (during interphase) it is no longer wound up. 3. Uncoil about 2 feet of thread and color it red. What do students think this represents (a nucleotide sequ ...
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON THE UCL CANCER INSTITUTE
... J 2013). Recent work shows that the genome encodes chromosome structure at evolutionarily conserved CTCF motifs in the genome (Vietri Rudan M. et al. Cell Reports 2015). Candidate: The ideal candidate should have a PhD with a genomics or epigenetics background, be ambitious and self-motivated and po ...
... J 2013). Recent work shows that the genome encodes chromosome structure at evolutionarily conserved CTCF motifs in the genome (Vietri Rudan M. et al. Cell Reports 2015). Candidate: The ideal candidate should have a PhD with a genomics or epigenetics background, be ambitious and self-motivated and po ...
Genomic library

A genomic library is a collection of the total genomic DNA from a single organism. The DNA is stored in a population of identical vectors, each containing a different insert of DNA. In order to construct a genomic library, the organism's DNA is extracted from cells and then digested with a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments of a specific size. The fragments are then inserted into the vector using DNA ligase. Next, the vector DNA can be taken up by a host organism - commonly a population of Escherichia coli or yeast - with each cell containing only one vector molecule. Using a host cell to carry the vector allows for easy amplification and retrieval of specific clones from the library for analysis.There are several kinds of vectors available with various insert capacities. Generally, libraries made from organisms with larger genomes require vectors featuring larger inserts, thereby fewer vector molecules are needed to make the library. Researchers can choose a vector also considering the ideal insert size to find a desired number of clones necessary for full genome coverage.Genomic libraries are commonly used for sequencing applications. They have played an important role in the whole genome sequencing of several organisms, including the human genome and several model organisms.